

1.基本概念
1.Index索引
动词:相当于MySQL中的insert;
名词:相当于MySQL中的DataBase;
2.Type(类型)
在Index(索引)中,可以定义一个或多个类型
类似于MySQL中的Table;每一种类型的数据放在一起
3.Document(文档)
保存在某个索引(index)下,某种类型(Type) 的一个数据(Document),文档是JSON格式的,Document就像是MySQL 中的某个Table里面的内容 类似一行数据

4.倒排索引
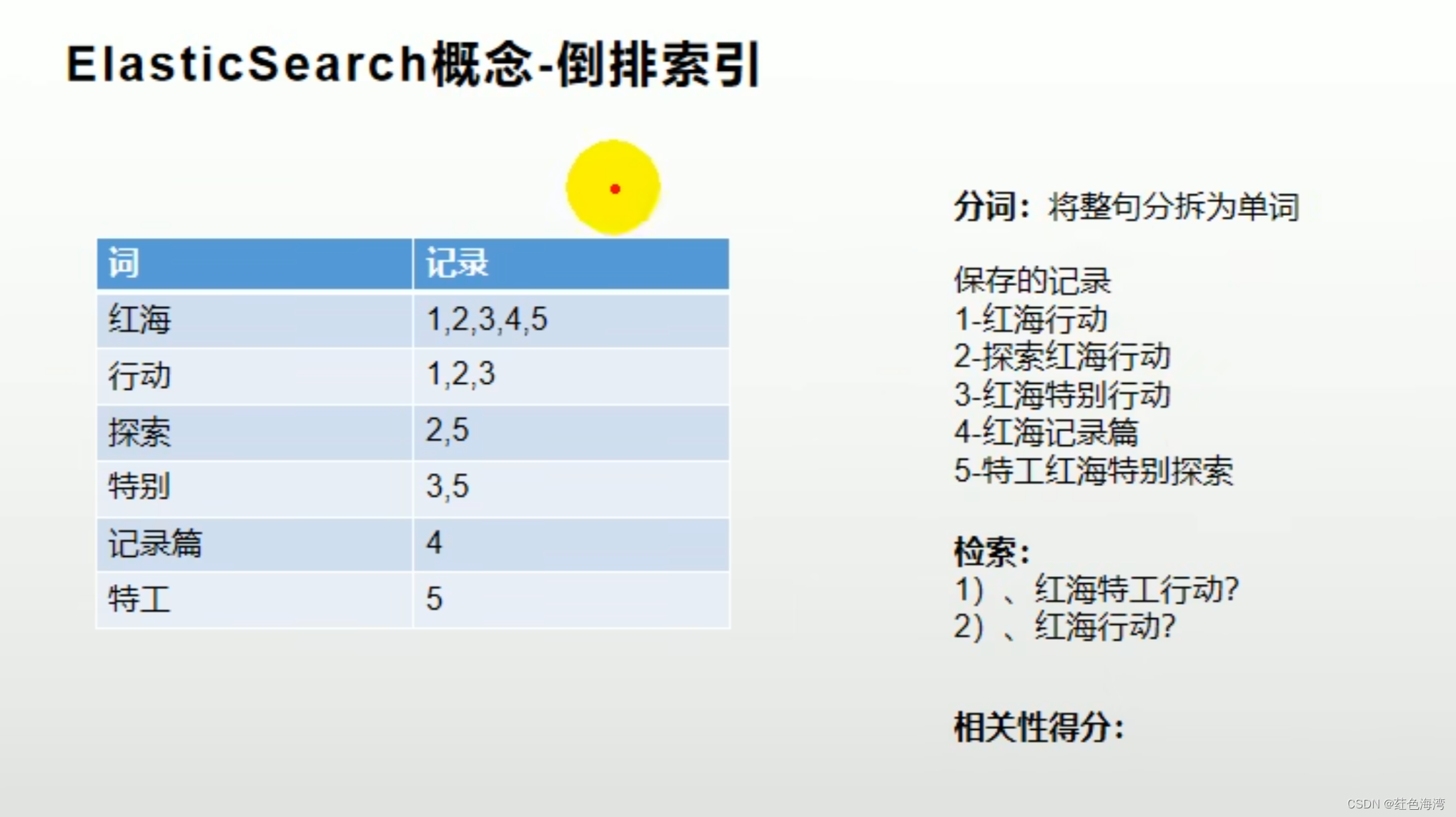
2.Docker 安装ElasticSearch
2.1 拉取镜像
docker pull elasticsearch:7.4.2docker pull kibana:7.4.22.2 创建实例
2.2.1 创建挂载目录
mkdir ./configmkdir ./data记得授予权限
chmod -R 777 ./elasticsearch2.2.2 使容器外任何地址都能够访问 elasticsearch
echo "http.host: 0.0.0.0">>./config/elasticsearch.ymlelasticsearch.yml
http.host: 0.0.0.0
2.2.3 docker 启动
docker run --name elasticsearch -p 9200:9200 -p9300:9300 \
-e "discovery.type=single-node" \
-e ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms512m -Xmx1024m" \
-v ./config/elasticsearch.yml:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml \
-v ./data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data \
-v ./plugins:/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins \
-d elasticsearch:7.4.2
2.3 安装Kibana
docker run --name kibana -e ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS=http://192.168.232.209:9200 -p 5601:5601 \
-d kibana:7.4.2
3.初步检索
3.1 _cat
查看节点信息
http://192.168.232.209:9200/_cat/nodes查看elasticsearch的健康状态
http://192.168.232.209:9200/_cat/health查看elasticsearch的主节点信息
http://192.168.232.209:9200/_cat/master查看所有索引
http://192.168.232.209:9200/_cat/indices3.2 索引一个文档(保存或修改一条记录)
保存一个数据,保存在那个索引的哪个类型下,指定用哪个唯一标识
http://192.168.232.209:9200/customer/external/1
3.3 查询文档
http://192.168.232.209:9200/customer/external/13.4 更新文档

3.4.1 _update
这个操作如果修改文档的值和原来一样,则不会更新版本。
3.4.2

3.5 删除文档

3.6 bulk 批量 API


批量操作
从这个网站复制
https://gitee.com/xlh_blog/common_content/blob/master/es%E6%B5%8B%E8%AF%95%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE.json#执行 /_bluk

4.进阶检索
1.searchAPI
ES支持两种基本方式检索:
- 一个是通过使用REST request URI 发送搜索参数(uri + 检索参数)
- 另一个是通过使用REST request body 来发送它们 (uri + 请求体)
GET /bank/_search?q=*&sort=account_number:ascq=* 查询所有
sort 跟据 account_number 升序
2.QueryDSL


GET /bank/_search
{"query": {"match_all": {}},"sort": [{"account_number": "asc"},{"balance": "desc"}]
}3.部分检索
GET /bank/_search
{"query": {"match_all": {}},"sort": [{"account_number": "desc"},{"balance": "desc"}],"from": 0,"size": 20,"_source": ["balance","account_number"]}4. match[匹配查询]
GET /bank/_search
{"query": {"match": {"account_number": 20}}}GET /bank/_search
{"query": {"match": {"address": "mill lane"}}}全文检索按照评分进行排序
5.match_phrase [短语匹配]
将需要匹配的值当成一个整体单词(不分词)进行检索
GET /bank/_search
{"query": {"match_phrase": {"address": "mill lane"}}}6.multi_match [多字段匹配]
这是或,只要一个字段满足,就返回
GET /bank/_search
{"query": {"multi_match": {"query": "mill","fields": ["state","address"]}}}能够正常分词
GET /bank/_search
{"query": {"multi_match": {"query": "mill Movico","fields": ["city","address"]}}}
7.bool复杂查询
bool用来做复杂查询:
复合语句可以合并 任何 其他查询语句,包括复合语句,了解这一点是很重要的。这就意味着,复合语句之间可以相互嵌套,可以表达非常复杂的逻辑。
must: 必须达到must列举所有条件 也就是相当于 AND
must_not: 且不满足里面的条件
should: 不是or 就是匹配上面有加分项
GET /bank/_search
{"query": {"bool": {"must": [{"match": {"gender": "m"}},{"match": {"address": "Mill"}}],"must_not": [{"match": {"age": 28 }}],"should": [{"match": {"lastname": "v"}}]}}}8.filter [结果过滤]
并不是所有的查询都需要产生分数,特别是那些仅用于 "filtering" (过滤) 的文档。为了不计算分数Elasticsearch 会自动检查场景并且优化查询的执行。
GET /bank/_search
{"query": {"bool": {"must": [{"match": {"gender": "m"}},{"match": {"address": "Mill"}}],"must_not": [{"match": {"age": 18 }}],"should": [{"match": {"lastname": "Wallace"}}],"filter": {"range": {"age": {"gte": 18,"lte": 20}}}}}
}9.term
和match一样。匹配某个属性的值。全文检索字段用match,其他非text 字段匹配用term
不用全文检索的时候用term 比如数字 年龄
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {"term": {"age": {"value": "28"}}
}
}GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {"match": {"email.keyword": "margueritewall@aquoavo.com"}
}
}address.keyword 和 match_phrase 区别:
前者 就是精确匹配 ,后者包含这个短语 就行
非文本字段 用 term
文本字段用 match
10. aggregations (执行聚合)
聚合提供了从数据中分组和提取数据的能力。最简单的聚合方法大致等于 SQL GROUP BY 和 SQL 的聚合函数 。在Elasticsearch 中, 您有执行搜索返回 hits (命中结果) ,并且同时返回聚合结果,把一个响应中的所有hits (命中结果) 分隔开的能力 。 这是非常强大且有效,您可以执行查询和多个聚合,并且在一次使用中得到各自 的(任何一个的) 返回结果,使用一次简化和简化的API 来避免网络往返。
搜索 address 中包含mill 的所有人的年龄分布以及平均年龄,但不显示这些人的详情。
GET /bank/_search
{"query": {"match": {"address": "mill"}},"aggs": {"ageAgg": {"terms": {"field": "age","size": 10}},"ageAvg":{"avg": {"field": "age"}},"blanceAvg":{"avg": {"field": "balance"}}},"size": 0
}复杂:
按照年龄聚合,并且请求这些年龄段的这些人的平均薪资
##按照年龄聚合,并且请求这些年龄段的这些人的平均薪资
GET /bank/_search
{"query": {"match_all": {}},"aggs": {"aggAgg": {"terms": {"field": "age","size": 100},"aggs": {"aggAvg": {"avg": {"field": "balance"}}}}}}
复杂2:
查出所有年龄分布,并且这些年龄段中M的平均薪资和F的平均薪资以及这个年龄段的总体平均薪资.
##查出所有年龄分布,并且这些年龄段中M的平均薪资和F的平均薪资以及这个年龄段的总体平均薪资GET /bank/_search
{"query": {"match_all": {}},"aggs": {"aggAggs": {"terms": {"field": "age","size": 100},"aggs": {"avgBalanceAll":{"avg": {"field": "balance"}},"genderAgg": {"terms": {"field": "gender.keyword","size": 2},"aggs": {"avgBlance": {"avg": {"field": "balance"}}}}}}}
}11.mapping(映射)
 所有数据类型
所有数据类型

创建一个有类型定义的索引
PUT /my_index
{"mappings": {"properties": {"age":{"type": "integer" },"email":{"type": "keyword"},"name":{"type": "text"}}}
}添加映射字段
PUT /my_index/_mapping
{"properties": {"employee-id":{"type":"keyword","index":false }}
}index =false 代表不参与索引,是搜索不到他的,相当于冗余存储字段,通过其他字段查出来
迁移数据
创建新索引
PUT /newbank
{"mappings": {"properties": {"account_number": {"type": "long"},"address": {"type": "text"},"age": {"type": "integer"},"balance": {"type": "long"},"city": {"type": "keyword"},"email": {"type": "keyword"},"employer": {"type": "text","fields": {"keyword": {"type": "keyword","ignore_above": 256}}},"firstname": {"type": "text"},"gender": {"type": "keyword"},"lastname": {"type": "text","fields": {"keyword": {"type": "keyword","ignore_above": 256}}},"state": {"type": "keyword"}}}
}

上面是6.0以后不用类型保存的迁移方法
下面是6.0之前

POST _reindex
{"source": {"index": "bank","type": "account"},"dest": {"index": "newbank"}
}5.分词

POST _analyze
{"analyzer": "standard","text": "The 2 QUICK Brown_Foxes jumped over the lazy dog's bone."
}1.安装ik分词器
注意:不能用默认elastics-plugin install xx.zip 进行自动安装
进入这个网址下
Index of: analysis-ik/stable/ (infinilabs.com)
进入es 容器·内部 plugins 目录
docker exec -it 容器id /bin/bash
POST _analyze
{"analyzer": "ik_smart","text": "我是中国人"
}POST _analyze
{"analyzer": "ik_max_word","text": "鸡你太美"
}
安装方法和我上一篇文章一样
ElasticSearch-CSDN博客
vagrant ssh密码登录 122集

2.自定义分词器


1.重新安装nginx
命令
在nginx文件夹下,执行
docker run -p 80:80 --name nginx \
-v ./html:/usr/share/nginx/html \
-v ./logs:/var/log/nginx \
-v ./conf:/etc/nginx \
-d nginx:1.102. 创建分词文件
/opt/nginx/html/es/fenci.txt
尚硅谷
乔碧螺3.在es插件,路径下找到xml文件对应的分词库路径,保存位置进行修改
"/opt/elasticearch/plugins/ik/config/IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE properties SYSTEM "http://java.sun.com/dtd/properties.dtd">
<properties><comment>IK Analyzer 扩展配置</comment><!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展字典 --><entry key="ext_dict"></entry><!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展停止词字典--><entry key="ext_stopwords"></entry><!--用户可以在这里配置远程扩展字典 --><entry key="remote_ext_dict">http://虚拟机地址:80/es/fenci.txt</entry><!--用户可以在这里配置远程扩展停止词字典--><!-- <entry key="remote_ext_stopwords">words_location</entry> -->
</properties>
4.修改以后重启restart es容器
docker restart elasticsearch
6.Elasticsearch整合Spirngboot使用
1.Elasticsearch-Rest-Client 官方 RestClient ,封装类ES操作,API层次分明,上手简单。
最终选择Elasticsearch-Rest-Client (elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client)
https://www.elastic.co/guid/en/elasticsearch/client/java-rest/current/java-rest-high.html<!-- 导入ES高阶API--><dependency><groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId><artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId><version>${elasticsearch.version}</version></dependency>package com.jmj.gulimall.search.config;import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** 导入依赖* 编写配置 给容器中注入一个 RestHighLevelClient* 参照官方API 操作就可以了 https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/client/java-rest/7.4/java-rest-high-getting-started-initialization.html*/
@Configuration
public class GulimallElasticSearchConfig {@Beanpublic RestHighLevelClient esRestClient() {RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("192.168.232.209", 9200, "http")));return client;}}
2.RequestOption
请求选项:比如安全验证,带token 请求头
package com.jmj.gulimall.search.config;import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** 导入依赖* 编写配置 给容器中注入一个 RestHighLevelClient* 参照官方API 操作就可以了 https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/client/java-rest/7.4/java-rest-high-getting-started-initialization.html*/
@Configuration
public class GulimallElasticSearchConfig {public static final RequestOptions COMMON_OPTIONS;static {RequestOptions.Builder builder = RequestOptions.DEFAULT.toBuilder();
// builder.addHeader("Authorization", "Bearer " + TOKEN);
// builder.setHttpAsyncResponseConsumerFactory(
// new HttpAsyncResponseConsumerFactory
// .HeapBufferedResponseConsumerFactory(30 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024));COMMON_OPTIONS = builder.build();}@Beanpublic RestHighLevelClient esRestClient() {RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("192.168.232.209", 9200, "http")));return client;}}
3.Index API
第一种

第二种

第三种

第四种

/*** 测试存储数据到ES* 更新也可以*/@Testvoid indexData() throws IOException {//index索引 usersIndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("users");//设置document id ,不设置就会默认生成/*** 若是同样的id重复执行,就是更新操作 乐观锁控制版本*/indexRequest.id("1");//1. key value pair
// indexRequest.source("userName","zhangsan","age",18,"gender","男");//2,JSONUser user = new User("zhangsan", "男", 18);String json = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(user);//一秒超时时间indexRequest.timeout(TimeValue.timeValueSeconds(1));indexRequest.source(json, XContentType.JSON);//要保存的内容//执行操作IndexResponse index = client.index(indexRequest, GulimallElasticSearchConfig.COMMON_OPTIONS);//提取有用的响应数据System.out.println(index);}4.查询API
@Datapublic static class Account{private int account_number;private String firstname;private String address;private int balance;private String gender;private String city;private String employer;private String state;private int age;private String email;private String lastname;}/*** search检索*/@Testvoid searchData() throws IOException {//1、创建检索请求SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest();//2、指定索引searchRequest.indices("bank");//3、检索条件DSLSearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();// sourceBuilder.query();
// sourceBuilder.from();
// sourceBuilder.size();
// sourceBuilder.aggregations();// sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("address","mill"));//按照年龄进行分组TermsAggregationBuilder ageAgg = AggregationBuilders.terms("ageAgg").field("age").size(10);sourceBuilder.aggregation(ageAgg);//计算平均薪资AvgAggregationBuilder balanceAge = AggregationBuilders.avg("balanceAvg").field("balance");sourceBuilder.aggregation(balanceAge);System.out.println("检索条件:"+sourceBuilder);searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);//4、执行检索SearchResponse response = client.search(searchRequest, GulimallElasticSearchConfig.COMMON_OPTIONS);//5、响应 分析结果
// System.out.println(response.toString());SearchHits hits = response.getHits();SearchHit[] hits1 = hits.getHits();for (SearchHit documentFields : hits1) {String sourceAsString = documentFields.getSourceAsString();Account account = new ObjectMapper().readValue(sourceAsString, Account.class);System.out.println(account);}//获取分析数据Aggregations aggregations = response.getAggregations();Terms ageAgg1 = aggregations.get("ageAgg");for (Terms.Bucket bucket : ageAgg1.getBuckets()) {String keyAsString = bucket.getKeyAsString();System.out.println("年龄:"+keyAsString+"=>"+bucket.getDocCount());}Avg balanceAvg = aggregations.get("balanceAvg");System.out.println("平均薪资:"+balanceAvg.getValue());}
7.SKU 在es种存储的模型
其中,库存信息的标题使用了ik分词器,图片信息,品牌名,品牌id等信息均不可检索。商品的规格参数等信息以nested类型,即嵌入属性存储。相关的细节这里不再赘述。
PUT product
{"mappings": {"properties": {"skuId": {"type": "long"},"spuId": {"type": "long"},"skuTitle": {"type": "text","analyzer": "ik_smart"},"skuPrice": {"type": "keyword"},"skuImg": {"type": "keyword","index": false,"doc_values": false},"saleCount": {"type": "long"},"hosStock": {"type": "boolean"},"hotScore": {"type": "long"},"brandId": {"type": "long"},"catalogId": {"type": "long"},"brandName": {"type": "keyword","index": false,"doc_values": false},"brandImg": {"type": "keyword","index": false,"doc_values": false},"catalogName": {"type": "keyword","index": false,"doc_values": false},"attrs": {"type": "nested","properties": {"attrId": {"type": "long"},"attrName": {"type": "keyword","index": false,"doc_values": false},"attrValue": {"type": "keyword"}}}}}
}
8.ES扁平化处理
PUT my_index/_doc/1
{"group":"fans","user":[{"first":"John","last":"Smith"},{"first":"Alice","last":"White"}]
}
GET my_index/_search
{"query": {"bool": {"must": [{"match": {"user.first": "Alice"}},{"match": {"user.first": "Alice"}}]}}
}
取消扁平化处理
PUT my_index
{"mappings": {"properties": {"user":{"type": "nested"}}}
}再次查询

9. 商城上架
@Override@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)public void up(Long spuId) {//组装需要的数据//1. 查出当前 spuid 对应的所有sku 信息,品牌 的名字。List<SkuInfoEntity> skuInfoEntityList = skuInfoService.getSkusBySpuId(spuId);//TODO 查询当前sku的所有可以用来检索的属性List<ProductAttrValueEntity> baseAttrs = productAttrValueService.baseAttrlistforspu(spuId);List<Long> attrIds = baseAttrs.stream().map(a -> a.getAttrId()).collect(Collectors.toList());List<Long> searchAttrIds = attrService.selectSearchAtts(attrIds);List<SkuEsModel.Attrs> attrsList = baseAttrs.stream().filter(item -> searchAttrIds.contains(item.getAttrId())).map(item -> {SkuEsModel.Attrs attrs1 = new SkuEsModel.Attrs();BeanUtils.copyProperties(item, attrs1);return attrs1;}).collect(Collectors.toList());//TODO 发送远程调用 库存系统查询是否有库存List<Long> skuIds = skuInfoEntityList.stream().map(s -> s.getSkuId()).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());List<SkuHasStockVo> skusHasStock = wareFeignService.getSkusHasStock(skuIds);Map<Long, Boolean> stockMap = skusHasStock.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(s -> s.getSkuId(), s -> s.getHasStock()));//2.封装每个SKU 的信息List<SkuEsModel> upProducts = skuInfoEntityList.stream().map(sku -> {SkuEsModel esModel = new SkuEsModel();BeanUtils.copyProperties(sku, esModel);esModel.setSkuPrice(sku.getPrice());esModel.setSkuImg(sku.getSkuDefaultImg());Long skuId = esModel.getSkuId();Boolean aBoolean = stockMap.get(skuId);if (aBoolean!=null){esModel.setHasStock(aBoolean);}else {esModel.setHasStock(false);}//TODO 热度评分esModel.setHotScore(0L);//TODO 查询品牌和分类的名字信息BrandEntity brand = brandService.getById(esModel.getBrandId());esModel.setBrandName(brand.getName());esModel.setBrandImg(brand.getLogo());CategoryEntity category = categoryService.getById(esModel.getCatalogId());esModel.setCatalogName(category.getName());//设置检索属性esModel.setAttrs(attrsList);return esModel;}).collect(Collectors.toList());//TODO 将数据发送给es进行保存searchFeignService.productStatusUp(upProducts);//TODO 修改状态this.update(new UpdateWrapper<SpuInfoEntity>().set("publish_status", ProductConstant.StatusEnum.SPU_UP.getCode()).set("update_taime",new Date()).eq("id",spuId));//Feign调用流程/*** 1、构造请求数据,将对象转为json* 2、发送请求进行执行(执行成功会解码响应数据)* 3、执行请求会有重试机制* //默认重试机制是关闭状态* while(true){* * }*/}