web基础之CSS
文章目录
- web基础之CSS
- 一、CSS简介
- 二、基本用法
- 2、CSS应用方式
- 2.1 行内样式
- 2.2内部样式
- 2.3外部样式
- 三、选择器
- 1、标签选择器
- 2、类选择器
- 3、ID选择器
- 4、选择器的优先级
- 四、常见的CSS属性
- 1、字体属性
- 2、文本属性
- 3、背景属性
- 4、表格属性
- 5、盒子模型的属性
- 6、定位
- 总结
一、CSS简介
CSS(Cascading Style Sheel)层叠样式表。是一组设置样式规则,并用于空值页面的外观布局的样式。
作用:用于页面的外观美化,以及页面组件的布局和定位。
二、基本用法
CSS语法:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title>css语法</title><style>选择器{ #表示要修饰的对象属性名:属性值; #修饰对象的具体属性(样式):样式的取值;}</style></head><body></body>
</html>
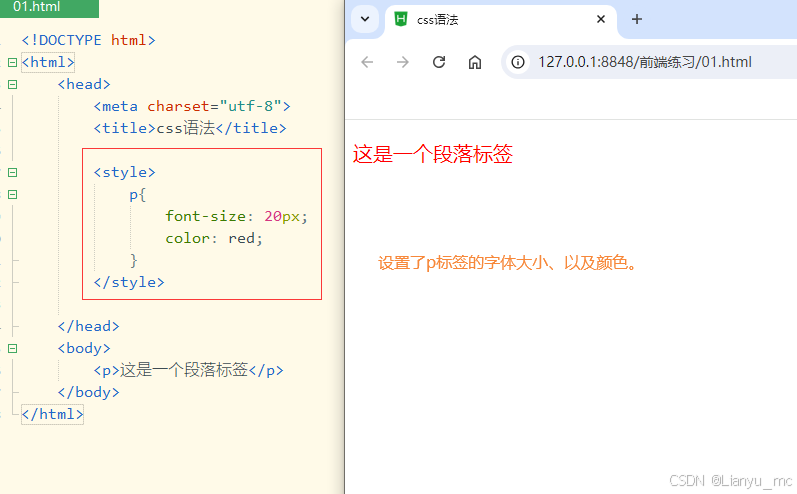
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title>css语法</title><style>p{font-size: 20px;color: red;}</style></head><body><p>这是一个段落标签</p></body>
</html>
2、CSS应用方式
引用方式一共有三种:行内样式、内部样式、外部样式。
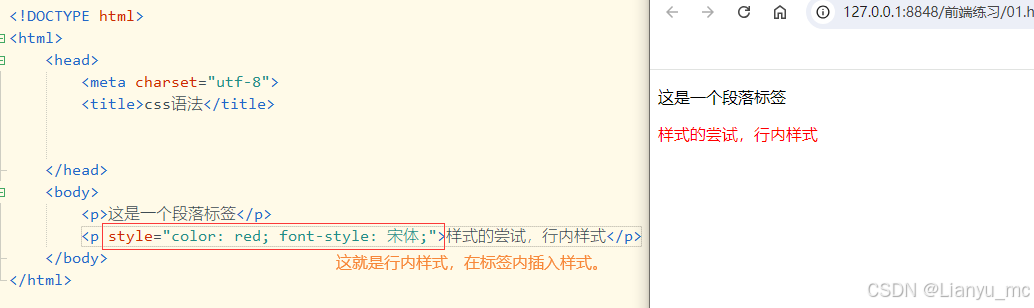
2.1 行内样式
被称为嵌入式,通过使用HTML 标签的style属性进行定义,样式只对设置了style属性的标签起作用。
<body><p>这是一个段落标签</p><p style="color: red; font-style: 宋体;">样式的尝试,行内样式</p>
</body>
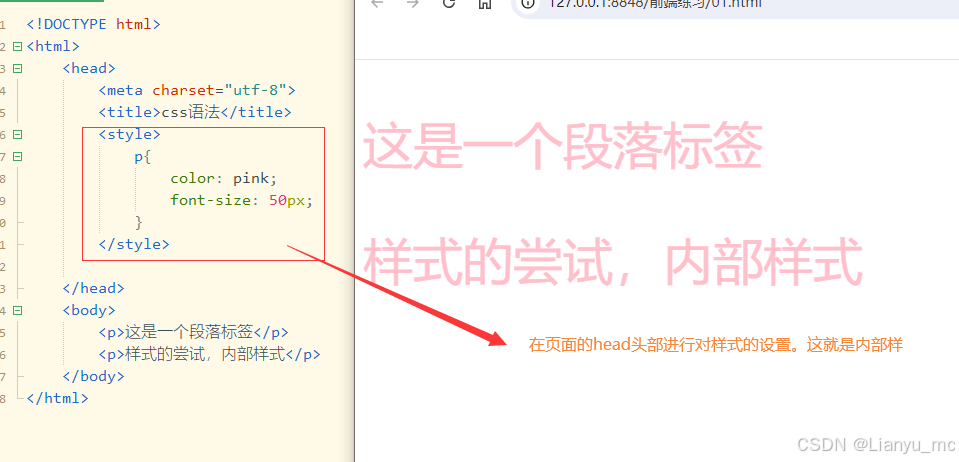
2.2内部样式
被称为内嵌样式,在页面头部通过style标签定义,对当前页面中所有符合样式的选择器标签都起作用。
<head><meta charset="utf-8"><title>css语法</title><style>p{color: pink;font-size: 50px;}</style></head><body><p>这是一个段落标签</p><p>样式的尝试,内部样式</p></body>
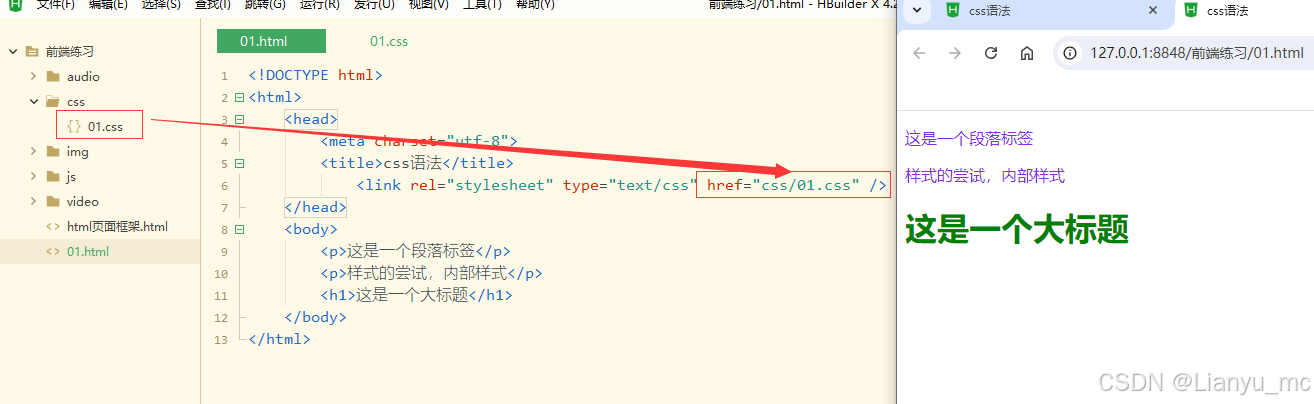
2.3外部样式
就是在页面文件外单独的创建一个.css 的文件。然后再页面文件中使用 link标签 进行引入。
引用:
<head><meta charset="utf-8"><title>css语法</title><link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/01.css" /></head>
css文件:
h1{color: green;
}
p{color: blueviolet;
}
三、选择器
1、标签选择器
也被称为元素选择器,使用HTML标签作为选择器的名称。


2、类选择器
使用自定义的名称,以 . (点)作为前缀,然后再通过HTML 标签的Class属性调用类选择器。
注意:
- 调用时不能添加
.号。 - 同时调用多个类选择器时,以
空格分隔。 - 类选择器名称不能以
数字开头。

3、ID选择器
使用自定义名称,以#作为前缀,然后通过HTML标签的id属性进行名称匹配,一对一的关系。


4、选择器的优先级
行内样式>ID选择器>类选择器>标签选择器
因为样式的加载顺序是,根据书写顺序进行加载的,在同优先级的前提下,后加载的会覆盖先加载的同名样式,就是就近原则,离得越近越优先。
四、常见的CSS属性
1、字体属性
设置字体的相关样式。
| 属性 | 含义 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| font-size | 大小、尺寸 | 可以使用多种单位 |
| font-weight | 粗细 | |
| font-family | 字体 | |
| font-style | 样式 | |
| font | 简写 |
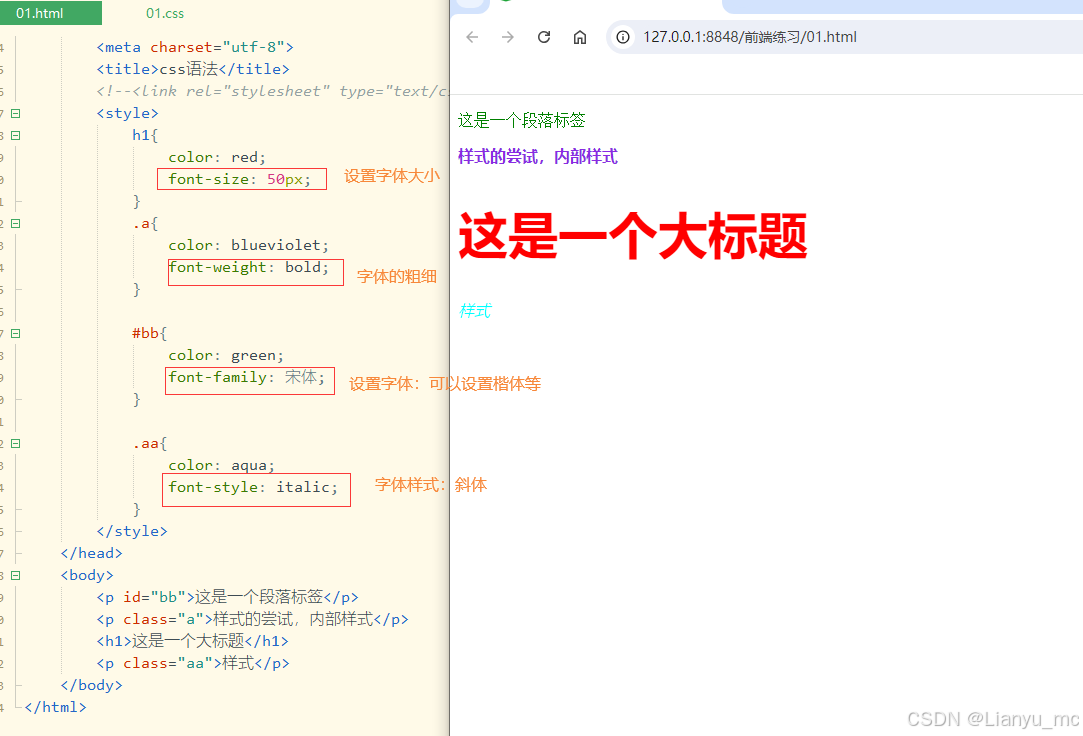
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title>css语法</title><!--<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/01.css" />--><style>h1{color: red;font-size: 50px;}.a{color: blueviolet;font-weight: bold;}#bb{color: green;font-family: 宋体;}.aa{color: aqua;font-style: italic;}</style></head><body><p id="bb">这是一个段落标签</p><p class="a">样式的尝试,内部样式</p><h1>这是一个大标题</h1><p class="aa">样式</p></body>
</html>
2、文本属性
| 属性 | 含义 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| color | 颜色 | |
| line-height | 行高 | 行之间的高度 |
| text-align | 水平对齐方式 | 取值:left、center、right |
| vertical-align | 竖直对齐方式 | 取值:top、middle、bottom可用于图片和文字的对齐方式 |
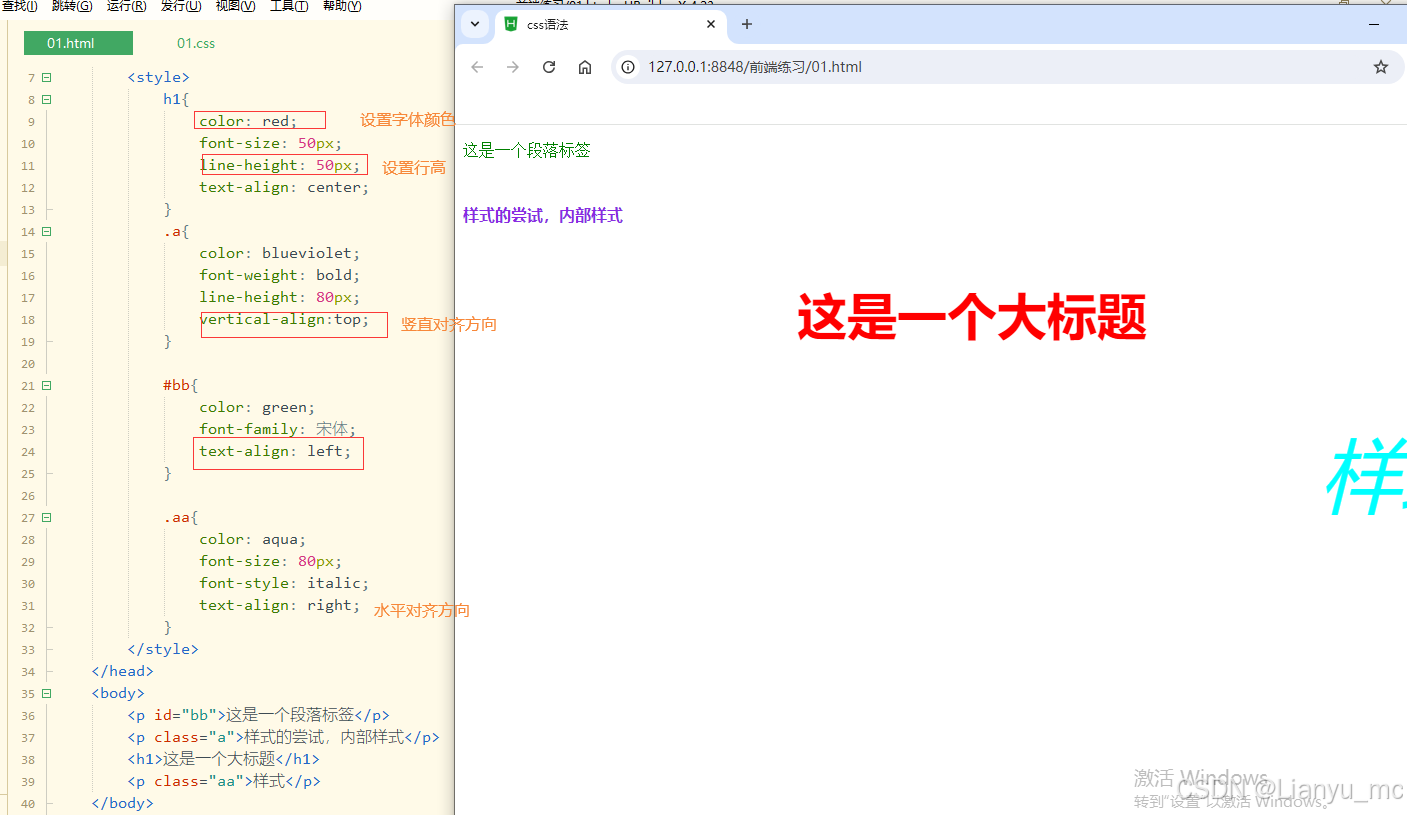
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title>css语法</title><!--<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/01.css" />--><style>h1{color: red;font-size: 50px;line-height: 50px;text-align: center;}.a{color: blueviolet;font-weight: bold;line-height: 80px;vertical-align:top;}#bb{color: green;font-family: 宋体;text-align: left;}.aa{color: aqua;font-size: 80px;font-style: italic;text-align: right;}</style></head><body><p id="bb">这是一个段落标签</p><p class="a">样式的尝试,内部样式</p><h1>这是一个大标题</h1><p class="aa">样式</p></body>
</html>
3、背景属性
| 属性 | 含义 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| background-color | 背景颜色 | |
| background-image | 背景图片 | 使用url()方式进行指定图片路径 |
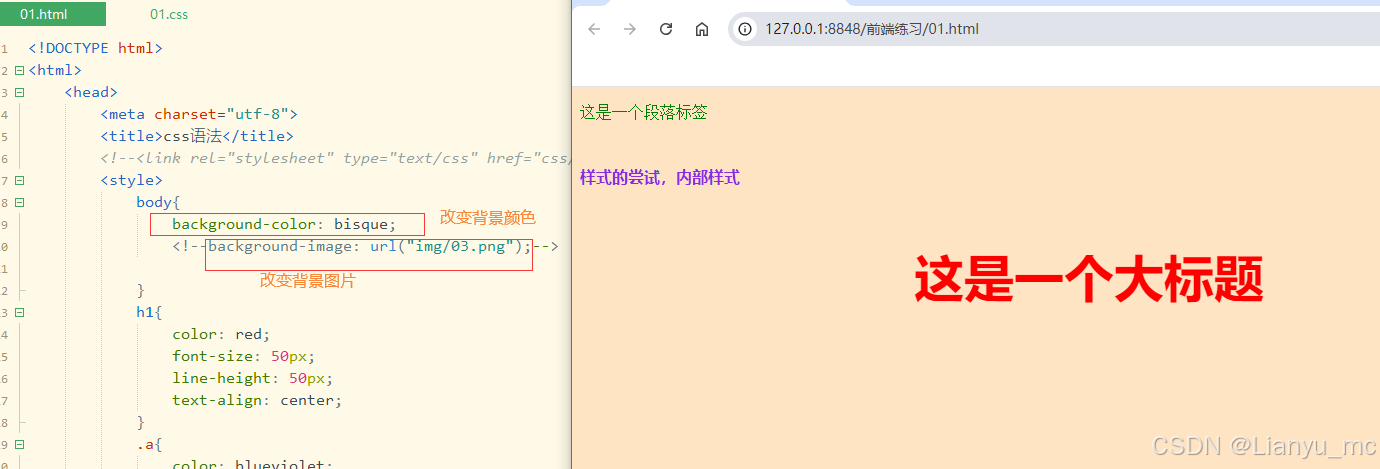
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title>css语法</title><!--<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/01.css" />--><style>body{background-color: bisque;<!--background-image: url("img/03.png");-->}h1{color: red;font-size: 50px;line-height: 50px;text-align: center;}.a{color: blueviolet;font-weight: bold;line-height: 80px;vertical-align:top;}#bb{color: green;font-family: 宋体;text-align: left;}.aa{color: aqua;font-size: 80px;font-style: italic;text-align: right;}</style></head><body><p id="bb">这是一个段落标签</p><p class="a">样式的尝试,内部样式</p><h1>这是一个大标题</h1><p class="aa">样式</p></body>
</html>
4、表格属性
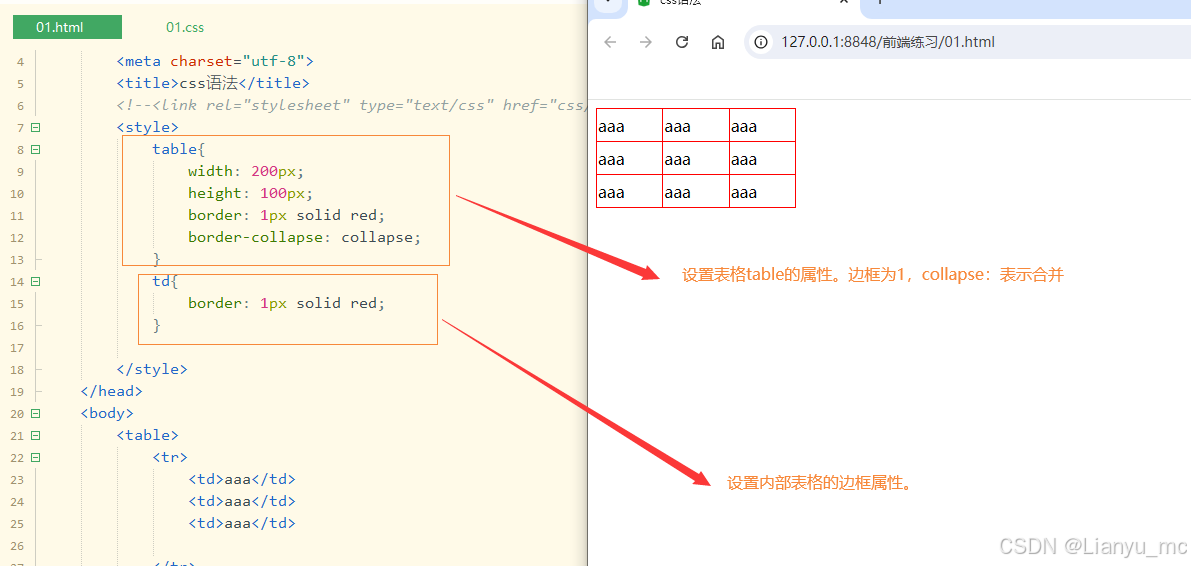
border-collapse:表格中相邻的边框是否合并为单一边框。
取值:separated(默认) collapse
<style>table{width: 200px;height: 100px;border: 1px solid red;border-collapse: collapse;}td{border: 1px solid red;}</style>
5、盒子模型的属性
盒子模型就是网页页面的布局。
- width:宽度
- height:高度
- border:边框
- padding:内边框
- margin:外边框
盒子的边框(border)
盒子的边框分为四个方向:
1、顶部:top:border -top 三个样式:分别是:1、color 、width、和style
2、右边:right border -right 三个样式:分别是:1、color 、width、和style
3、左边:left border-left 三个样式:分别是:1、color 、width、和style
4、下边:bottom border -bottom 三个样式:分别是:1、color 、width、和style - 边框样式的取值:
1、solid实线、
2、dashed:虚线
3、dotted:点线
4、double:双线
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title>盒子模型属性</title><!--<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/01.css" />--><style>p{width: 300px;background-color: aquamarine;}.a1{/* border-top-color:red;border-top-width: 2px;border-top-style: solid;border-right-color: blue;border-right-width: 3px;border-right-style: dotted;主要设置了顶部边框和右边框的属性*/border: 1px solid red;padding: 20px;margin: 10px;}.a2{padding: 30px;}.a3{margin: auto;text-align: center;height: 100px;line-height: 100px;}</style></head><body><p class="a1">这是一个元素</p><p class="a2">这是二个元素</p><p class="a3">这是三个元素</p></body>
</html>

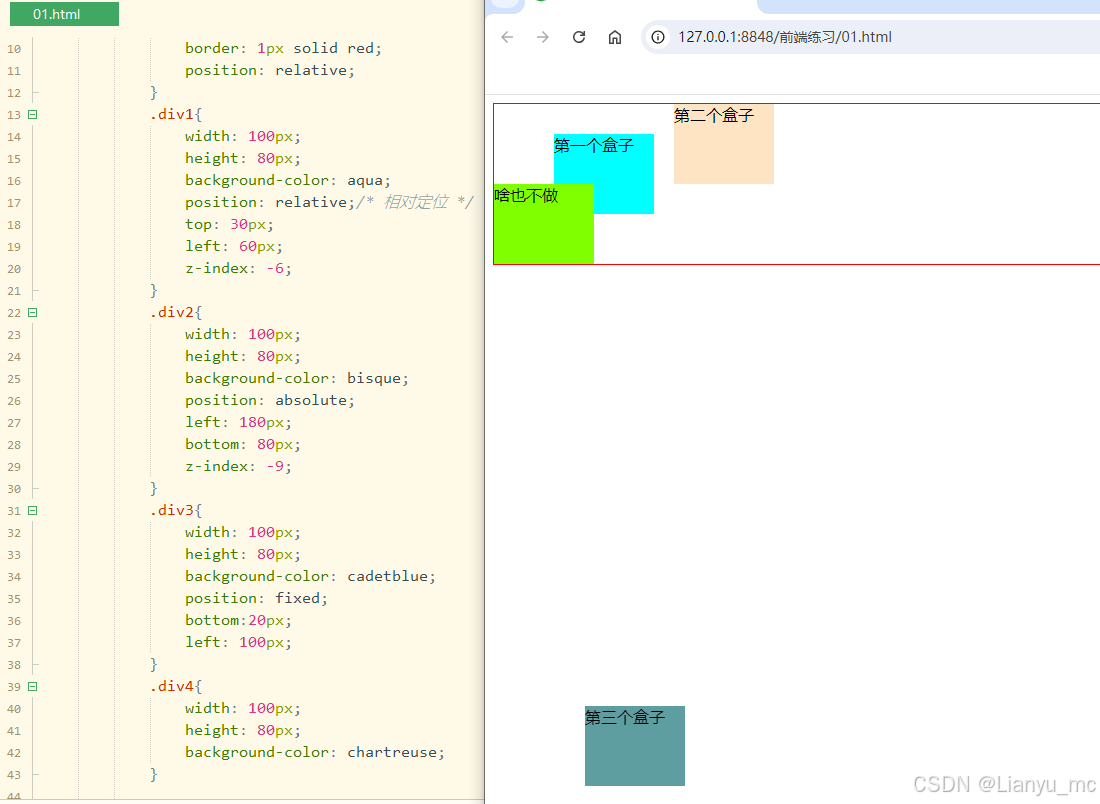
6、定位
通过position 属性实现对元素的定位,在设置定位方式后,还需要设置定位属性。
定位常见方式取值如下:
| 取值 | 含义 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| static | 默认值 | 按照常规文档流进行显示 |
| relative | 相对定位 | 相对于标签原来的位置进行定位 |
| absolute | 绝对定位 | 相对于第一个非static定位的父标签的定位 |
| fixed | 固定定位 | 相对于浏览器窗口进行定位 |
- 1、相对定位
先设置元素的position属性为relative,然后再设置定位属性(方向性)。
- 2、绝对定位
先设置父标签为非static定位,然后设置元素的position属性为absolute,最后再设置定位属性(也就是方向)。
- 3、固定定位
先将元素的position属性设置为fixed,然后再设置定位属性(方向)。 - 4、z-index元素
通过z-index元素进行设置优先级,通过z-index来控制元素的堆叠顺序,取值为数字,值越大优先级越高。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title>定位</title><!--<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/01.css" />--><style>#zhu{width: 900px;border: 1px solid red;position: relative;}.div1{width: 100px;height: 80px;background-color: aqua;position: relative;/* 相对定位 */top: 30px;left: 60px;z-index: -6;}.div2{width: 100px;height: 80px;background-color: bisque;position: absolute;left: 180px;bottom: 80px;z-index: -9;}.div3{width: 100px;height: 80px;background-color: cadetblue;position: fixed;bottom:20px;left: 100px;}.div4{width: 100px;height: 80px;background-color: chartreuse;}</style></head><body><div id="zhu"><div class="div1">第一个盒子</div><div class="div2">第二个盒子</div><div class="div3">第三个盒子</div><div class="div4">啥也不做</div></div></body>
</html>
总结
以上就是近期的学习,不足之处还望指点。未完待续…
