写在前面:Java相对于C/C++来说是更高级的语言,隐藏了指针,可读性更高,更容易学习,但是无法直接操作硬件、运行速度较慢也是不可回避的硬伤。JNI就是Java官方定义的一套标准“接口”,用于Java和C/C++之间互相调用,注意这里是互相调用,而不是只能用Java去调用C/C++。搞Android开发的,JNI是必须掌握的技术,以前我一直逃避,因为觉得比较难,但是真正学习下来并没有那么难。Java运行速度较慢,有一些对时间要求超高的场景,就必须用到JNI。
每一节文末会附上Demo APP的GitHub链接。
在正式使用JNI之前,我们必须搞清楚两个相关的概念:
Android NDK:这是Google官方提供的工具包,用于将C/C++代码链接它所需要的库,编译成.so或者.a文件。大白话说就是:没有它就不能在Android Studio 这个应用里面编译C/C++代码。
JNI:JNI不是包含于Android NDK里面的,两者相互独立,JNI只要是Java代码都能使用,不局限于Android应用开发,很多人容易把两者混为一潭。
下面开始介绍Android应用中如何使用JNI,以Java调用C/C++这种形式为例子,分两种情况:1、一开始就创建为C/C++项目;2、创建的是一般项目,开发中途想调用C/C++代码。
一、C/C++项目
1.1 创建一个Native C++项目
在new一个项目的时候,选择Native C++,创建一个名为JNI的项目。

创建完之后的项目结构如下:可以看到在java的同级目录,Android Studio已经自动为我们生成了cpp目录,cpp目录下自动生成了cpp文件和CMakeLists文件。

1.2 CMakeLists.txt 讲解
CMakeLists的作用就是告诉Android NDK,这个CPP项目的源文件是哪些,需要链接哪些库,需要生成静态库还是动态库。自动生成的 CMakeLists.txt 如下:
# For more information about using CMake with Android Studio, read the
# documentation: https://d.android.com/studio/projects/add-native-code.html.
# For more examples on how to use CMake, see https://github.com/android/ndk-samples.# Sets the minimum CMake version required for this project.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.22.1)# Declares the project name. The project name can be accessed via ${ PROJECT_NAME},
# Since this is the top level CMakeLists.txt, the project name is also accessible
# with ${CMAKE_PROJECT_NAME} (both CMake variables are in-sync within the top level
# build script scope).
project("jni")# Creates and names a library, sets it as either STATIC
# or SHARED, and provides the relative paths to its source code.
# You can define multiple libraries, and CMake builds them for you.
# Gradle automatically packages shared libraries with your APK.
#
# In this top level CMakeLists.txt, ${CMAKE_PROJECT_NAME} is used to define
# the target library name; in the sub-module's CMakeLists.txt, ${PROJECT_NAME}
# is preferred for the same purpose.
#
# In order to load a library into your app from Java/Kotlin, you must call
# System.loadLibrary() and pass the name of the library defined here;
# for GameActivity/NativeActivity derived applications, the same library name must be
# used in the AndroidManifest.xml file.
add_library(${CMAKE_PROJECT_NAME} SHARED# List C/C++ source files with relative paths to this CMakeLists.txt.native-lib.cpp)# Specifies libraries CMake should link to your target library. You
# can link libraries from various origins, such as libraries defined in this
# build script, prebuilt third-party libraries, or Android system libraries.
target_link_libraries(${CMAKE_PROJECT_NAME}# List libraries link to the target libraryandroidlog)
cmake_minimum_required:用来说明现在使用的CMake的最低版本。
project(“jni”):告诉NDK这个CMake的项目名称叫jni,与后续编译关系不大,有点吉祥物的意思。
add_library:这里其实是分三段来看——》${CMAKE_PROJECT_NAME}是规定最后编译产物的名字,这里直接用了上一步的project name jni,也就是说最后编译出来的库名字为 libjni,当然你也可以取其它任意名字,比如Xusu这样。——》SHARED 告诉NDK最后编译的是动态库,生成的是libjni.so,如果需要生成静态库把SHARED更换为STATIC即可,最后生成 libjni.a文件。——》native-lib.cpp 是告诉NDK 需要编译的源文件,这里可以列出来很多个.cpp文件或者.h头文件,每个文件占一行。
target_link_libraries:意思就是将NDK中现成的android库、log库链接到生成的libjni库中,链接到 android 库可以让你的 C/C++ 代码调用一些底层的 Android API,链接到 log 库就是为了打印日志嘛。写法也是固定的target_link_libraries(target_name library1 library2 …)。
1.3 native-lib.cpp 讲解
自动生成的native-lib.cpp如下:
#include <jni.h>
#include <string>extern "C" JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Java_com_htc_jni_MainActivity_stringFromJNI(JNIEnv* env,jobject thiz) {std::string hello = "Hello from C++"; /*声明一个字符串*/return env->NewStringUTF(hello.c_str()); /*将C语言中的字符通过.c_str()和NewStringUTF方法传化为Java中的String返回给Java代码使用*/
}
这里我们贴出MainActivity中声明的方法一起对照更容易理解:
package com.htc.jni;import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;import com.htc.jni.databinding.ActivityMainBinding;public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {// Used to load the 'jni' library on application startup.static { //固定写法,通过System.loadLibrary加载需要的C/C++动态库System.loadLibrary("jni");}private ActivityMainBinding binding;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater());setContentView(binding.getRoot());// Example of a call to a native methodTextView tv = binding.sampleText;tv.setText(stringFromJNI());}/*** A native method that is implemented by the 'jni' native library,* which is packaged with this application.*/public native String stringFromJNI();
}
可以看到我们在java代码中通过System.loadLibrary(“jni”) 去加载了libjni.so库,这是JNI的固定写法,然后我们用public native String stringFromJNI()声明了一个JNI方法,并通过tv.setText(stringFromJNI())去调用了它,Java声明JNI方法一定要用native修饰,这也是固定写法。
我们回到native-lib.cpp,开始就是常规的include头文件不用说,从extern "C"开始说:
extern “C”:是为了确保NDK按照 C 语言的方式来处理函数名称。C++ 和 C 语言在编译时对函数名称的处理方式有所不同,C++ 会进行名称修饰(name mangling),而 C 不会。下面举个例子——》如果没有 extern “C”,C++ 编译器会对函数名进行名称修饰,编译器会把函数名 Java_com_example_myapp_MainActivity_stringFromJNI 转换为一个复杂的符号,比如:_ZN12MainActivity13stringFromJNIEv 。 这就是 C++ 的名称修饰。Java 层的 JNI 机制无法识别这个符号,会导致无法正确调用该方法。
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL:JNIEXPORT 、JNICALL都是固定写法,它们中间夹着的jstring 是函数的返回值,还记得我们之前声明的native函数吗?public native String stringFromJNI() 这里的jstring对应的就是java中的String。JNI为了实现java和C/C++的通信,规定了一套基本数据类型的对照表:

Java_com_htc_jni_MainActivity_stringFromJNI(JNIEnv* env, jobject thiz):这个是stringFromJNI对应的JNI函数的名称,Java_是固定前缀,com_htc_jni_MainActivity_stringFromJNI是Java中声明的native方法所在的包名+类名+native方法名的组合,组合的顺序也是固定的。方法参数有两个JNIEnv* env, jobject,这里有同学就会问了,我们Java里声明的native方法明明没有参数,怎么这里有参数??public native String stringFromJNI() 是没参数,所以这里的JNIEnv* env, jobject thiz其实固定写法,JNIEnv* env代表的是Java环境,后续可以通过env创建Java中的数据对象,访问Java中的函数,jobect thiz表示调用这个方法的 Java 对象实例,在这个例子中指的就是MainActivity,如果声明成静态方法 public static native String stringFromJNI() ,jobject就需要更换成 jclass。
1.4 总结
如果从一开始就创建一个Native C++ 项目,Android Studio会帮我们把JNI需要的环境和文件都准备好,我们只需要学习它的语法即可,其中有几个需要关注的点:1、cpp目录和java目录是同级。2、Java代码中通过System.loadLibrary加载so动态库、通过native关键字声明JNI方法。3、cpp文件JNI方法的命名规则和参数规范。
点击下载Native C++项目Demo:https://github.com/xuhao120833/JN
二、一般的项目,中途想使用C/C++代码
上面我们讲了用Android Studio创建一般的Native C++项目,Android Studio 已经帮我们做好了准备工作,那么我们APP开发到一半,突然加了个需求对时效性要求很高,必须用C/C++实现,这个时候项目肯定不能推倒重来了,那怎么办???按下面的操作即可:
2.1 自己创建cpp目录和相关文件
选中main目录按右键,在java的同级目录创建cpp目录:

自己创建CMakeLists.txt、编写用到的cpp文件和头文件:

CMakeLists.txt的文件内容如下:
# For more information about using CMake with Android Studio, read the
# documentation: https://d.android.com/studio/projects/add-native-code.html# Sets the minimum version of CMake required to build the native library.cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10.2) #说明CMake的最低要求版本# Declares and names the project.project("Xctouch") #CMake项目名称取为Xctouch,随意取的# Creates and names a library, sets it as either STATIC
# or SHARED, and provides the relative paths to its source code.
# You can define multiple libraries, and CMake builds them for you.
# Gradle automatically packages shared libraries with your APK.add_library( # Sets the name of the library.PxScale #最后生成的库的名字取为PxScale# Sets the library as a shared library.SHARED #设置最后生成库为动态库,即.so文件# Provides a relative path to your source file(s).scdefine.h #列出所有的cpp文件和头文件,每个文件占一行jz_scale.cpptp_savedata_check.cppscJNIfun.cpp)# Searches for a specified prebuilt library and stores the path as a
# variable. Because CMake includes system libraries in the search path by
# default, you only need to specify the name of the public NDK library
# you want to add. CMake verifies that the library exists before
# completing its build.find_library( # Sets the name of the path variable. log-lib #找到NDK里面现成的log库,并给它取一个别名log-lib# Specifies the name of the NDK library that# you want CMake to locate.log )# Specifies libraries CMake should link to your target library. You
# can link multiple libraries, such as libraries you define in this
# build script, prebuilt third-party libraries, or system libraries.target_link_libraries( # Specifies the target library. #将log库链接到最后生成的libPxScale.so库中PxScale# Links the target library to the log library# included in the NDK.${log-lib} )
scJNIfun.cpp的文件内容如下:定义了三个方法,前两个相对复杂一些,extern 导入了两个其它cpp文件的方法。
#include <jni.h>
#include <string>
#include <android/log.h>
#include <linux/agpgart.h>
#include "scdefine.h"JNIEXPORT///
extern void ratio_tra_point(int *pRet, int *px4, int *py4, int oldRatio, int newRatio, float scale, int w, int h);
extern int check_bd_data(char *pBuf);
xtouch/////该方法的功能是将 Java 层的两个 int[] 数组(px4 和 py4)传递到 C++ 层,经过 ratio_tra_point 函数处理后,返回一个计算结果数组。
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jintArray JNICALL
Java_com_htc_server_PxScale_getpxRatioxy(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, jintArray px4, jintArray py4, jint oldRatio, jint newRatio, jfloat scale, jint w, jint h) {jintArray intArray = env->NewIntArray(20);jint *intdata = env->GetIntArrayElements(intArray, NULL);jint *tpx4 = NULL;jint *tpy4 = NULL;if(px4!=NULL){tpx4 = (jint *) env->GetIntArrayElements(px4, 0);}else{tpx4 = NULL;}if(py4!=NULL){tpy4 = (jint *) env->GetIntArrayElements(py4, 0);}else{tpy4 = NULL;}LOGD("CPP: Java_com_htc_server_PxScale_getpxRatioxy");memset(intdata,0,sizeof(int)*20);ratio_tra_point(intdata, tpx4, tpy4, oldRatio,newRatio, scale, w, h);env->ReleaseIntArrayElements(intArray, intdata, 0);return intArray;
}//Java 层接收一个字符串,将其进行字符过滤(只保留字母和数字),然后调用 check_bd_data 函数对过滤后的数据进行进一步处理,最终返回一个整型结果。
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_com_htc_server_PxScale_checkbddata(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, jstring data) {jint ret = 0;int i;char c,checkbuf[2048];const char *str;//LOGD("CPP: Java_com_htc_server_PxScale_checkbddata");str = env->GetStringUTFChars(data, NULL);if(str == NULL){return 0;}else{memset(checkbuf, 0, 2048);for(i=0;i<2048;i++){c = str[i];if((c>='0' && c<='9') || (c>='a' && c<='z') || (c>='A' && c<='Z')){checkbuf[i] = c;}else{break;}}ret = check_bd_data(checkbuf);}return ret;
}extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Java_com_htc_server_PxScale_sayHello(JNIEnv* env,jobject thiz) {// 创建 C++ 字符串std::string message = "I'm JNI, Hello Java.";// 返回一个 Java 字符串(jstring)return env->NewStringUTF(message.c_str());
}
2.2 java目录下创建PxScale.java文件
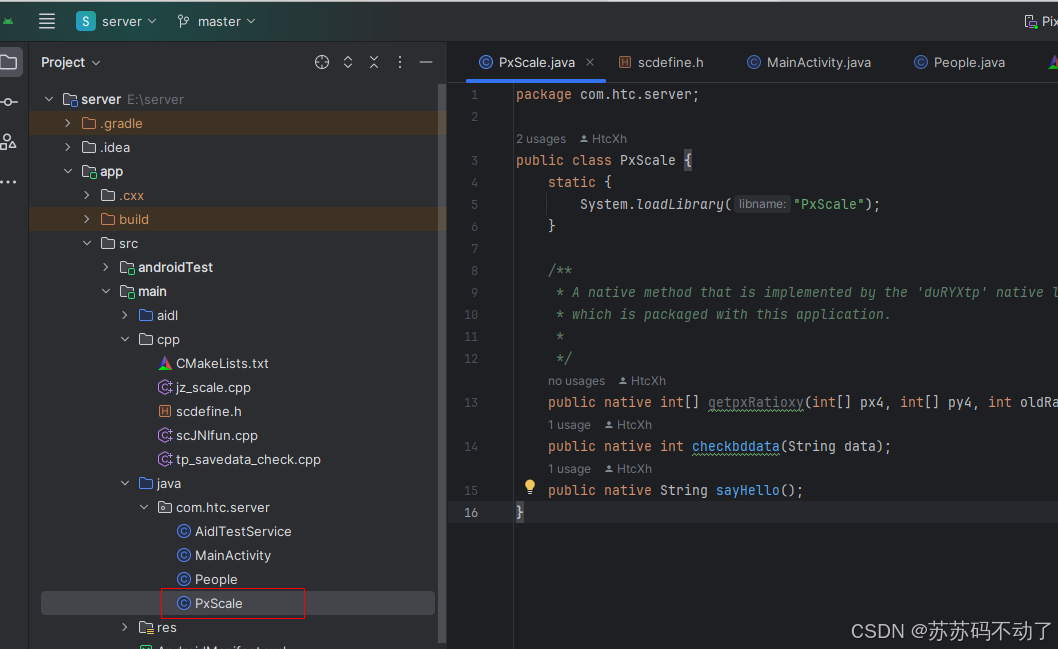
package com.htc.server;public class PxScale {static {System.loadLibrary("PxScale");}/*** A native method that is implemented by the 'duRYXtp' native library,* which is packaged with this application.**/public native int[] getpxRatioxy(int[] px4, int[] py4, int oldRatio, int newRatio, float scale, int w, int h);public native int checkbddata(String data);public native String sayHello();
}
2.3 build.gradle下添加NDK、JNI配置
我们需要手动指定CMakeLists.txt的位置和版本、ndk的版本、ndk最后编译产物的信息。
defaultConfig标签范围内添加如下标签信息:
externalNativeBuild {cmake {cppFlags ""}}ndk {ldLibs "log"moduleName "PxScale" //生成的so名字。abiFilters "arm64-v8a", "armeabi-v7a" //输出指定abi体系结构下的so库。}
android标签范围内添加如下标签信息:
externalNativeBuild {cmake {path "src/main/cpp/CMakeLists.txt" //指定CMakeLists的绝对路径。version "3.10.2" //指定CMake的版本。}}ndkVersion '21.0.6113669' //指定ndk的版本。
注意:build.gradle中不要打开代码混淆开关,打开会导致Java函数可以找到C/C++函数,但是C/C++函数执行完毕返回值给Java函数的时候找不到Java函数,导致执行报错。解决办法暂时未知。
buildTypes {release {minifyEnabled false //true混淆打开//zipAlignEnabled true //优化代码//shrinkResources true //优化资源proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android-optimize.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'}}
2.4 MainActivity调用JNI测试
MainActivity的代码如下:
package com.htc.server;import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.Toast;import androidx.activity.EdgeToEdge;
import androidx.annotation.Px;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.core.graphics.Insets;
import androidx.core.view.ViewCompat;
import androidx.core.view.WindowInsetsCompat;public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private PxScale pxScale;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);pxScale = new PxScale();pxScale.checkbddata("zojdoifjaoidj");String hello = pxScale.sayHello();Toast.makeText(this, hello, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();}
}
2.5 总结
一般项目和NativeC++项目相比,想要使用JNI需要自己去创建cpp目录、cpp文件、CMakeLists.txt等,这些文件的组成语法都是大同小异的,唯一值得注意的就是需要自己在build.gradle中去声明项目JNI的相关信息,不然无法运行。
点击下载 一般项目使用JNI 的 Demo APP:https://github.com/xuhao120833/Server
三、C/C++调用Java方法
前文举例子一直用的都是Java通过JNI去调用C/C++,那么反过来怎么弄呢???
从C/C++使用JNI调用Java方法分两种情况,一种是调用static静态方法,一种是调用普通方法,下面就分这两种情况分别说。以创建Native C++项目为例子。
3.1 调用静态方法
首先我们按照上文的方法创建一个Native C++项目,然后创建一个ArrayProcessor类供C/C++代码调用,最后的代码结构如下:

在ArrayProcessor中首先定义一个简单的静态方法:
package com.htc.jni2;public class ArrayProcessor {// 静态方法:打印日志public static void printLog(String message) {System.out.println("Log from Java: " + message);}
}MainActivity中定义一个native方法callSumArray,并调用它:
package com.htc.jni2;import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;import com.htc.jni2.databinding.ActivityMainBinding;public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {// Used to load the 'jni2' library on application startup.static {System.loadLibrary("jni2");}/*** A native method that is implemented by the 'jni2' native library,* which is packaged with this application.*/public native String stringFromJNI();public native int callSumArray(int[] array);private ActivityMainBinding binding;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater());setContentView(binding.getRoot());// Example of a call to a native methodTextView tv = binding.sampleText;tv.setText(stringFromJNI());// 创建一个整数数组int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};// 调用 JNI 方法int sum = callSumArray(array);// 打印结果System.out.println("Sum of array: " + sum);}
}
JNI中对应定义一个callSumArray方法:
#include <jni.h>
#include <string>
#include <android/log.h>#define LOG_TAG "JNI_LOG"
#define LOGI(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, __VA_ARGS__)extern "C" JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Java_com_htc_jni2_MainActivity_stringFromJNI(JNIEnv* env,jobject thiz) {std::string hello = "Hello from C++";return env->NewStringUTF(hello.c_str());
}extern "C" JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_com_htc_jni2_MainActivity_callSumArray(JNIEnv* env,jobject thiz,jintArray array) {// 获取数组长度jsize length = env->GetArrayLength(array);// 获取数组元素jint *elements = env->GetIntArrayElements(array, 0);// 调用静态方法 printLogjclass arrayProcessorClass = env->FindClass("com/htc/jni2/ArrayProcessor");if (arrayProcessorClass == nullptr) {LOGI("Class not found!");return -1; // 错误返回}jmethodID printLogMethod = env->GetStaticMethodID(arrayProcessorClass, "printLog", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V");if (printLogMethod == nullptr) {LOGI("Method not found!");return -1; // 错误返回}// 调用静态方法 printLogjstring logMessage = env->NewStringUTF("Hello from JNI!");env->CallStaticVoidMethod(arrayProcessorClass, printLogMethod, logMessage). . . . . .
}
要想在C/C++代码中调用Java的静态方法,总共分如下三步:
1、通过env->FindClass找到指定路径的Java类。
2、通过env->GetStaticMethodID指定Java类中的静态方法的jmethodID 。
解释一下函数中的参数意义:GetStaticMethodID(arrayProcessorClass, “printLog”, “(Ljava/lang/String;)V”),arrayProcessorClass是第一步找到的jclass——》 “printLog"是Java中对应函数的名字。——》”(Ljava/lang/String;)V") 对应方法的签名,说人话就是告诉JNI,要使用的Java函数的参数是什么?返回类型是什么?(Ljava/lang/String;)指printLog的参数是String,V指printLog的返回类型是void。对照表如下:


3、通过env->CallStaticVoidMethod调用Java中的printLog函数。有一个参数就是env->CallStaticVoidMethod(arrayProcessorClass, printLogMethod, logMessage),多个参数就是env->CallStaticVoidMethod(arrayProcessorClass, printLogMethod, 参数1,参数2,参数3. . . . . .)
到这里,C/C++如何调用静态Java方法就说完了。
3.2 调用普通实例方法
我们在ArrayProcessor中再定义两个普通方法:
// 非静态方法:计算数组的和public int sumArray(int[] array) {int sum = 0;for (int num : array) {sum += num;}return sum;}// 非静态方法:打印数组public void printArray(int[] array) {System.out.print("Array: ");for (int num : array) {System.out.print(num + " ");}System.out.println();}
JNI cpp文件中,如下调用:
// 获取数组长度jsize length = env->GetArrayLength(array);// 获取数组元素jint *elements = env->GetIntArrayElements(array, 0);// 获取构造函数 IDjmethodID constructor = env->GetMethodID(arrayProcessorClass, "<init>", "()V");if (constructor == nullptr) {LOGI("Constructor not found!");return -1; // 错误返回}// 创建 ArrayProcessor 类的实例对象jobject arrayProcessorObject = env->NewObject(arrayProcessorClass, constructor);// 获取实例方法 sumArray 的 IDjmethodID sumArrayMethod = env->GetMethodID(arrayProcessorClass, "sumArray", "([I)I");if (sumArrayMethod == nullptr) {LOGI("sumArray method not found!");return -1; // 错误返回}// 调用实例方法 sumArrayjint result = env->CallIntMethod(arrayProcessorObject, sumArrayMethod, array);// 调用实例方法 printArrayjmethodID printArrayMethod = env->GetMethodID(arrayProcessorClass, "printArray", "([I)V");if (printArrayMethod == nullptr) {LOGI("printArray method not found!");return -1; // 错误返回}env->CallVoidMethod(arrayProcessorObject, printArrayMethod, array);// 释放数组元素env->ReleaseIntArrayElements(array, elements, 0);return result;
1、我们都知道实例方法需要实例对象才能调用,所以第一步就是要构建ArrayProcessor的实例对象:通过env->GetMethodID(arrayProcessorClass, init , “()V”);找到ArrayProcessor的构造方法, init JNI中固定代表构造方法,"()V"就是说构造函数没有参数,返回类型为void,也就是Java中默认的构造函数。
2、通过 env->NewObject(arrayProcessorClass, constructor);获取到ArrayProcessor的实例对象。 JNI中用jobject 表示。
3、通过env->GetMethodID分别获取到sumArray和printArray的jmethodID。
4、通过CallIntMethod、CallVoidMethod调用Java中的静态方法。
最后把我们创建的指针释放掉env->ReleaseIntArrayElements。第四步中用的CallIntMethod、CallVoidMethod是根据Java函数的返回类型来的,有一个对照表如下:

3.3 总结
C/C++使用JNI调用Java方法,过程是相似的:1、静态方法——》先找到类然后调用。2、普通方法——》先创建Java实例对象,再通过Java对象调用。调用方法前都需要找到 jmethodID,流程都是固定的,重点在于正确使用JNI规定的语法。
点击下载C/C++通过JNI调用Java代码的Demo APP https://github.com/xuhao120833/JNI2
写在最后:
通篇看下来其实JNI没有想象中那么难,更多的是学习现有的规则和语法,然后再正确使用即可。生活中很多事也是这样,我们大多数时候在自己吓自己。不管你怕不怕,生活最重要的是勇敢出发。
