第四章:static关键字
第十二课:声明static属性
1.在Java中什么是static
static是一个关键字,可以用来修饰方法和类的属性,当用static修饰类的属性时,被修饰的属性将和普通属性有以下区别:
(1.内存中的存放位置不同,普通属性存放在堆内存中,被static修饰的属性存放在全局数据区,
(2.普通属性在堆内存中只要新建了一个实例化对象,就会产生一份新的属性值,而被static修饰的属性在全局数据区有且仅有一份,不会随着实例化对象的产生而增多,
(3.普通属性不能通过类名直接调用,必须通过类的实例化后再调用,而被static修饰的属性可以直接被类调用修改,也可以被类的实例化对象调用修改(不推荐),被static修饰的属性一般是用于在一个类的公共属性上面,这种情况一般很少出现。
2.传统属性代码与使用static修饰的属性代码对比分析
传统代码:
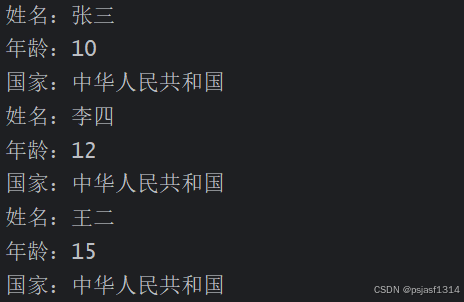
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {//给类实例化三个对象Person person1=new Person("张三",10);Person person2=new Person("李四",12);Person person3=new Person("王二",15);//修改国家名称person1.country="中华人民共和国";person2.country="中华人民共和国";person3.country="中华人民共和国";//输出三个实例化对象的信息System.out.println(person1.getInfo());System.out.println(person2.getInfo());System.out.println(person3.getInfo());}
}
class Person{//姓名private String name;//年龄private int age;//这是一个所有实例化对象的公共属性,即这是一个来自一个国家的类String country="中华民国";//构造函数public Person(String name, int age){this.name = name;this.age = age;}//setter、getter方法public void setName(String name){this.name=name;}public void setAge(int age){this.age=age;}public String getName(){return name;}public int getAge(){return age;}//类的信息输出public String getInfo(){return "姓名:"+this.name+"\n"+"年龄:"+this.age+"\n"+"国家:"+this.country;}
}
输出:

有static关键字修饰属性的代码:
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {//给类实例化三个对象Person person1=new Person("张三",10);Person person2=new Person("李四",12);Person person3=new Person("王二",15);//修改国家名称
// person1.country="中华人民共和国";
// person2.country="中华人民共和国";
// person3.country="中华人民共和国";//修改国家名称Person.country="中华人民共和国";//输出三个实例化对象的信息System.out.println(person1.getInfo());System.out.println(person2.getInfo());System.out.println(person3.getInfo());}
}
class Person{//姓名private String name;//年龄private int age;//这是一个所有实例化对象的公共属性,即这是一个来自一个国家的类static String country="中华民国";//构造函数public Person(String name, int age){this.name = name;this.age = age;}//setter、getter方法public void setName(String name){this.name=name;}public void setAge(int age){this.age=age;}public String getName(){return name;}public int getAge(){return age;}//类的信息输出public String getInfo(){return "姓名:"+this.name+"\n"+"年龄:"+this.age+"\n"+"国家:"+this.country;}
}
输出:
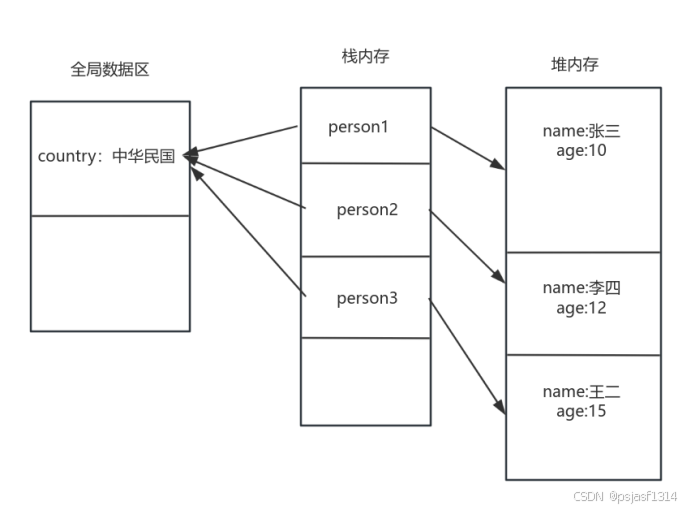
对比分析:两段代码主要的区别就是对属性country的处理,传统代码中country没有用static修饰,那么它和其它基本属性一样都是存在堆内存中,只有对象实例化后才能对其进行操作,且多次实例化会产生多次的country值,要修改它的值必须所有的实例化对象依次修改;但在用static修饰的代码中,country属性就不再存放在堆内存里面,而是放在了全局数据区,且只存了一份,可以用类名直接调用修改,各个实例化对象也能直接调用使用或者修改。对static修饰的属性的代码进行内存分析如下:
第十三课:声明static方法
1.static方法和非static方法的比较
static方法只能调用static属性或static方法;
非static方法允许调用static属性或static方法。
无论是static属性还是static方法都可以用类名直接调用,而一般属性和方法都必须在类实例化后用实例化对象进行调用。
注意:static定义的属性和方法都不是程序设计之初需要考虑的内容,只有在回避实例化调用并且描述公共属性下才会考虑使用static定义的方法和属性。
代码示例:
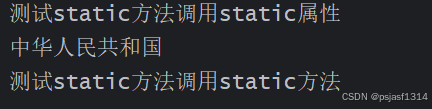
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {//static的方法里面可以使用static方法Person.setCountry("中华人民共和国");//把属性country定义为private这句就不能用了// Person.Country;//输出countrySystem.out.println(Person.getCountry());//测试static方法调用static方法Prictise();}public static void Prictise(){System.out.println("测试static方法调用static方法");}
}
class Person{//姓名private String name;//年龄private int age;//这是一个所有实例化对象的公共属性,即这是一个来自一个国家的类private static String country="中华民国";//构造函数public Person(String name, int age){this.name = name;this.age = age;}//setter、getter方法public void setName(String name){//一般方法使用static方法Person.setCountry(country);this.name=name;}public void setAge(int age){this.age=age;}public static void setCountry(String c){System.out.println("测试static方法调用static属性");country=c;}public String getName(){return this.name;}public int getAge(){return this.age;}public static String getCountry(){return country;}//类的信息输出public String getInfo(){return "姓名:"+this.name+"\n"+"年龄:"+this.age+"\n"+"国家:"+this.country;}
}
输出:
小总结:一般来说static方法就是为其他的static方法和static属性服务的,也可以在非static方法中使用,而static方法却不能出现一般属性和一般方法。
第十四课:static应用案例
程序要求:在实例化一个对象的时候要记录实例化对象的个数,当实例化对象使用无参构造时,给它一个初始值+个数。
代码:
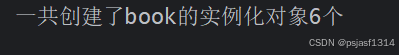
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {new Book("java");new Book("python");new Book("javascript");new Book();new Book();new Book();System.out.println("一共创建了book的实例化对象"+Book.getCount()+"个"); }}
class Book{//书名private String title;//记录实例化对象的个数private static int count=0;//无参构造public Book(){this("NO-Title"+count);}//构造方法public Book(String title){this.title=title;count++;}//setter,getter方法public String getTitle(){return this.title;}public void setTitle(String title){this.title=title;}//此处必须定义为static方法,才能通过类名直接调用public static int getCount(){return count;}
}
输出结果:
代码分析:要记录实例化对象的个数可以使用一个公共属性count来记录,并且在实例化对象时在构造方法中对count进行加一,另外注意在书写count属性的get方法时,要用static方法,不然在外部用类名称访问不到static的值。
