
文章目录
- 前言
- 六、Udp Server 端代码
- 6.1 socket——创建套接字
- 6.2 bind——将套接字与一个 IP 和端口号进行绑定
- 6.3 recvfrom——从服务器的套接字里读取数据
- 6.4 sendto——向指定套接字中发送数据
- 6.5 绑定 ip 和端口号时的注意事项
- 6.5.1 云服务器禁止直接绑定公网 ip
- 6.5.2 绑定本地环回地址
- 6.5.2 端口号也不能胡乱绑定
- 6.6 服务端完整代码
- 七、Udp Client 端代码
- 八、基于 Udp 的指令处理
- 九、基于 Udp 的聊天室
- 9.1 server 端
- 9.1.1 地址转换函数
- 9.2 client 端
- 十、结语
前言
本篇文章接上一篇 【Linux取经路】网络套接字编程——初识篇,所以目录号从六开始。
六、Udp Server 端代码
6.1 socket——创建套接字
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol);
-
domain:协议域(协议族)。该参数决定了 socket 的地址类型。在通信中必须采用对应的地址,如
AF_INET决定了要用IPv4地址(32位的)与端口号(16位)的组合,AF_UNIX决定了要用一个绝对路径名作为地址,AF_INET6(IPv6)。 -
type:指定了 socket 的类型,如
SOCK_STREAM(流式套接字)、SOCK_DGRAM(数据报式套接字)等等。 -
protocol:指定协议,如 IPPROTO_TCP(TCP传输协议)、PPTOTO_UDP(UDP 传输协议)、IPPROTO_SCTP(STCP 传输协议)、IPPROTO_TIPC(TIPC 传输协议)。
-
返回值:一个文件描述符,创建套接字的本质其实就是打开一个文件。
void Init()
{// 1. 创建udp socketsockfd_ = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);if(sockfd_ < 0){lg(Fatal, "socket create error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));exit(SOCKET_ERR);}lg(Info, "socket is created successful, sockfd: %d", sockfd_);
}
6.2 bind——将套接字与一个 IP 和端口号进行绑定
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>int bind(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t addrlen);
void Init()
{// 1. 创建 udp socketsockfd_ = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);if(sockfd_ < 0){lg(Fatal, "socket create error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));exit(SOCKET_ERR);}lg(Info, "socket is created successful, sockfd: %d", sockfd_);// 2. bind socketstruct sockaddr_in local;bzero(&local, sizeof(local)); // 将内容清空成0local.sin_family = AF_INET; // 表明当前结构体的类型local.sin_port = htons(port_); // 当前服务器的端口号local.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip_.c_str()); // 将字符串风格的 ip 地址转化成 4 字节的网络序列// bind 的本质就是把上面这个参数设置进内核,设置到指定的套接字当中int n = bind(sockfd_, (struct sockaddr*)&local, sizeof(local));if(n < 0) {lg(Fatal, "bind error, error: %d, err string: %s", errno, strerror(errno));exit(BIND_ERR);}lg(Info, "bind success!");
}
因为是网络通信,所以首先定义一个 struct sockaddr_in 类型的对象,该对象中有四个字段,分别是:sin_family(表明当前结构体的类型)、sin_port(端口号)、sin_addr(ip地址)、sin_zero(填充字段)。我们需要自己设置前三个字段的信息。其中 sin_family 的值和 socket 函数中的 domain 参数保持一致;其次,端口号和 ip 地址,是需要再网络中传输的,因此要把主机序列转换成网络序列。其中使用 htons 将端口号从主机转成网络序列。ip 地址实际上是一个 4 字节的 uint32_t 类型,但是为了配合用户的使用习惯,我们让用户输入的 ip 地址是一个 string 类型,例如 “xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx” 的点分形式,因此 ip 地址的转换有两步,分别是将 string 类型转换成 uint32_t 类型,然后再从主机转化成网络序列。这两个转化使用 inet_addr 接口就可以实现,其次 sin_addr 的类型是 struct in_addr,该结构体中就只有一个字段 in_addr_t s_addr; 其中 in_addr_t 就是 uint32_t。

bind 本质就是将我们上一步中创建的套接字与一个 ip 和端口号建立关联。
6.3 recvfrom——从服务器的套接字里读取数据
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>ssize_t recvfrom(int sockfd, void *buf, size_t len, int flags, struct sockaddr *src_addr, socklen_t *addrlen);
-
buf:接收缓冲区。
-
len:接收缓冲区的大小。
-
flags:默认设置为 0,表示阻塞。
-
src_addr:输出型参数,获取客户端的套接字信息,也就是获取客户端的 ip 和端口号信息。因为是
udp网络通信,所以这里传入的还是struct sockaddr_in类型的对象地址。 -
addrlen:这里就是
struct sockaddr_in对象的大小。 -
返回值:成功会返回获取到数据的字节数;失败返回 -1。
void Run()
{isrunning_ = true;while (isrunning_){char buffer[size];struct sockaddr_in client;socklen_t len = sizeof(client);// 从当前服务器的套接字中读取数据int ret = recvfrom(sockfd_, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&client, &len);if (ret < 0){lg(Warning, "recvfrom error, error: %d, err string: %s", errno, strerror(errno));continue;}buffer[ret] = 0;std::string info = buffer;std::string echo_string = "server echo# <b>" + info;}
}
小Tips:我们发送和接收的数据内容是不需要我们自己进行主机专网络,再从网络转主机的,数据内容会由 recvfrom 函数和 sendto 函数自动帮我们进行转换。
6.4 sendto——向指定套接字中发送数据
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>ssize_t sendto(int sockfd, const void *buf, size_t len, int flags, const struct sockaddr *dest_addr, socklen_t addrlen);
-
sockfd:当前服务器的套接字,发送网络数据本质就是先向该主机的网卡(本质上就是文件)中进行写入。
-
buf:待发送的数据缓冲区。
-
len:数据缓冲区的大小。
-
flags:默认设置为 0。
-
dest_addr:接收方的套接字信息,这里也就是客户端的套接字信息。
-
addrlen:
struct sockaddr_in对象的大小。
void Run()
{isrunning_ = true;while (isrunning_){// 从套接字中读取数据char buffer[num];struct sockaddr_in client;socklen_t len = sizeof(client);int ret = recvfrom(sockfd_, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&client, &len);if (ret < 0){lg(Warning, "recvfrom error, error: %d, err string: %s", errno, strerror(errno));continue;}buffer[ret] = 0;std::string info = buffer;std::string echo_string = "server echo# <b>" + info;// 向 client端 发送数据int n = sendto(sockfd_, echo_string.c_str(), echo_string.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&client, len);if(n < 0){lg(Warning, "sendto error, error: %d, err string: %s", errno, strerror(errno));continue; }}
}
到这里,服务端的代码就编写的差不多了,接下来可以使用 netstat -naup 指令看看效果,其中 net 就表示网络,stat 就表示状态,n 选项是把所有能显示成数字的信息都以数字的形式进行显示;a表示所有;u 表示 udp;p 表示显示 PID 信息。
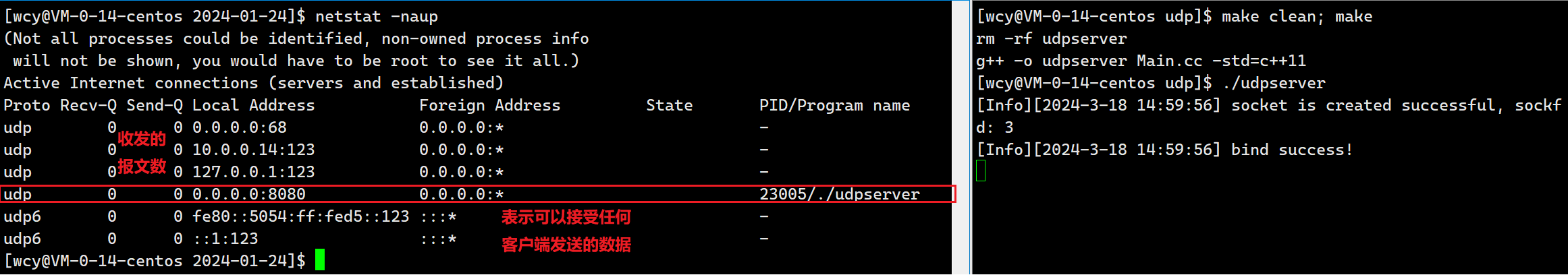
6.5 绑定 ip 和端口号时的注意事项
6.5.1 云服务器禁止直接绑定公网 ip
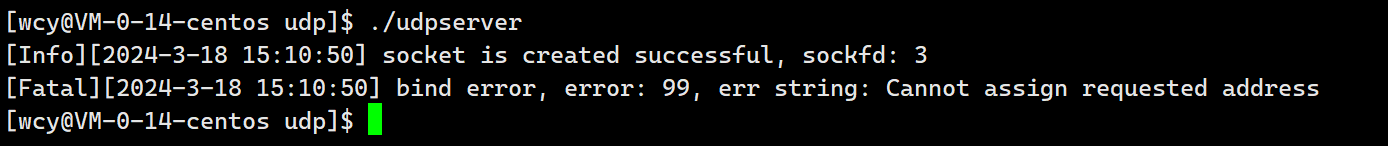
一般建议服务器端的代码 bind 时绑定 ip 0.0.0.0,表示任意地址绑定,这样只要是发送到这台主机的数据,该服务器进程都能收到,然后根据端口号向上交付。因为一个服务器可能有多个 ip,如果服务端的进程只 bind 某一个固定的 ip,那么通过其它 ip 发送到该服务器的数据,这个进程就无法收到。local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY。
6.5.2 绑定本地环回地址
任何服务器进程都可以绑定 127.0.0.1 这个 ip 地址,这个 ip 地址叫做本地环回地址,绑定了这个地址后,该进程不会向网络中发送数据,但是还是会走网络协议栈,通常用来进行 CS 的测试。
6.5.2 端口号也不能胡乱绑定
#include "UdpServer.hpp"
#include <memory>int main()
{std::unique_ptr<UdpServer> svr(new UdpServer(1023));svr->Init();svr->Run();return 0;
}

一般 [0, 1023] 是系统内定的端口号,都要有固定的应用层协议使用,例如:http(80)、https(443),端口号的范围是 0~65535,建议我们平时在自己的代码中就往大了去绑。
6.6 服务端完整代码
#pragma once
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <string>
#include "log.hpp"
#include <string.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <functional>#define num 1024extern Log lg;enum
{SOCKET_ERR = 1,BIND_ERR
};uint16_t defaultport = 8080;
std::string defaultip = "0.0.0.0";using func_t = std::function<std::string(const std::string &)>;class UdpServer
{
public:UdpServer(const uint16_t &port = defaultport, const std::string &ip = defaultip): ip_(ip), port_(port), isrunning_(false){}void Init(){// 1. 创建 udp socketsockfd_ = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);if (sockfd_ < 0){lg(Fatal, "socket create error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));exit(SOCKET_ERR);}lg(Info, "socket is created successful, sockfd: %d", sockfd_);// 2. bind socketstruct sockaddr_in local;bzero(&local, sizeof(local)); // 将内容清空成0local.sin_family = AF_INET; // 表明当前结构体的类型local.sin_port = htons(port_); // 当前服务器的端口号local.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip_.c_str()); // 将字符串风格的 ip 地址转化成 4 字节的网络序列// bind 的本质就是把上面这个参数设置进内核,设置到指定的套接字当中int n = bind(sockfd_, (struct sockaddr *)&local, sizeof(local));if (n < 0){lg(Fatal, "bind error, error: %d, err string: %s", errno, strerror(errno));exit(BIND_ERR);}lg(Info, "bind success!");}void Run(func_t func) // 参数是数据处理函数{isrunning_ = true;while (isrunning_){// 从套接字中读取数据char buffer[num];struct sockaddr_in client;socklen_t len = sizeof(client);int ret = recvfrom(sockfd_, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&client, &len);if (ret < 0){lg(Warning, "recvfrom error, error: %d, err string: %s", errno, strerror(errno));continue;}printf("client say@ %s\n", buffer);buffer[ret] = 0;std::string info = buffer;std::string echo_string = func(info); // 数据处理// 向 client端 发送数据int n = sendto(sockfd_, echo_string.c_str(), echo_string.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&client, len);if(n < 0){lg(Warning, "sendto error, error: %d, err string: %s", errno, strerror(errno));continue; }}}~UdpServer(){close(sockfd_);}private:int sockfd_; // 网络文件描述符std::string ip_; // 主机的 ip 地址uint16_t port_; // 服务器的端口号bool isrunning_; // 是否在运行
};
#include "UdpServer.hpp"
#include <memory>
#include <string>void Usage(const char *command)
{std::cout << "\n\tUsage: " << command << " port[1024+]" << std::endl;
}std::string Hander(const std::string &str)
{std::string res = "Server get a message: " + str;return res;
}int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{if(argc != 2){Usage(argv[0]);exit(0);}uint16_t port = std::stoi(argv[1]); std::unique_ptr<UdpServer> svr(new UdpServer(port));svr->Init();svr->Run(Hander);return 0;
}
七、Udp Client 端代码
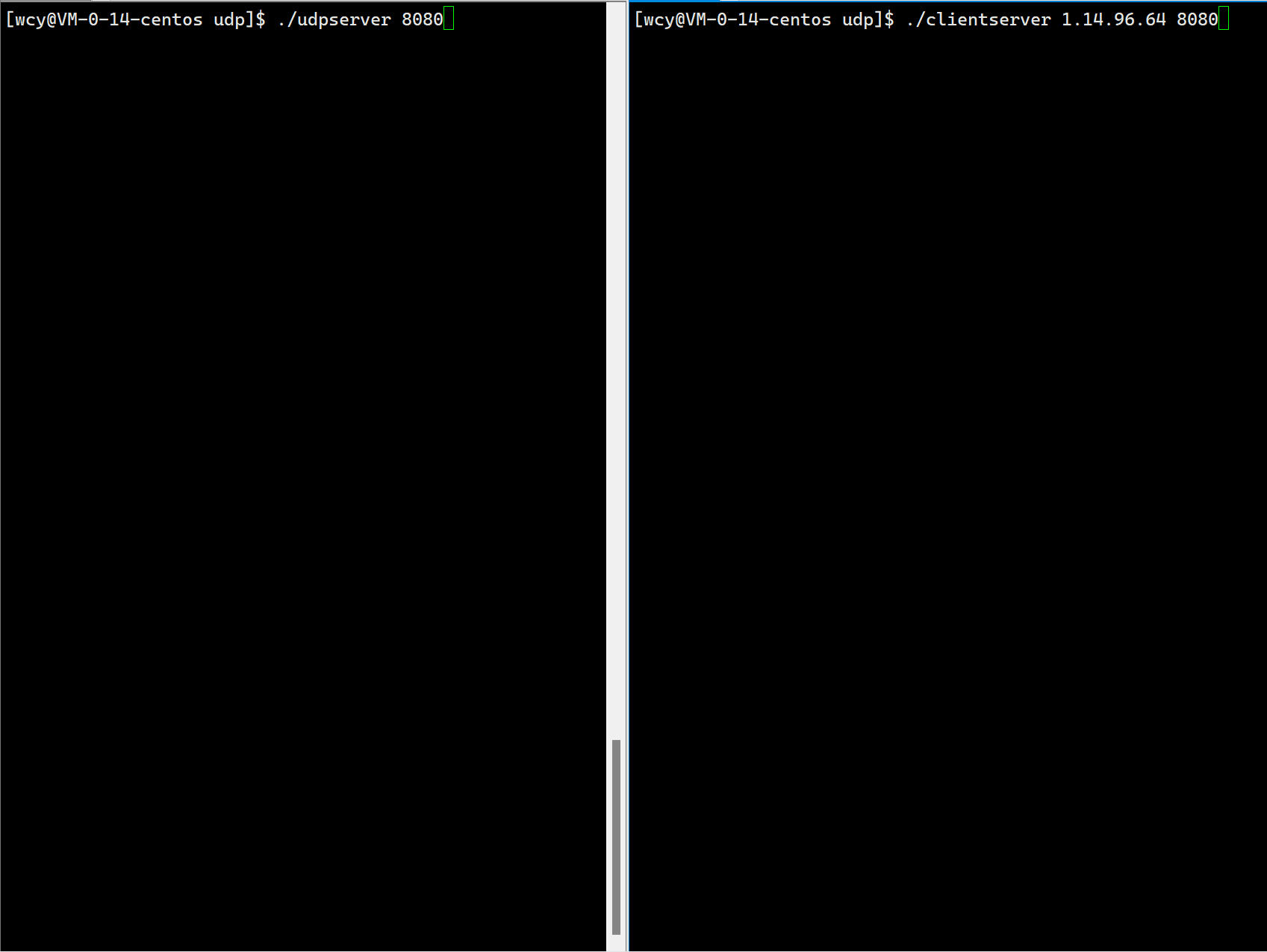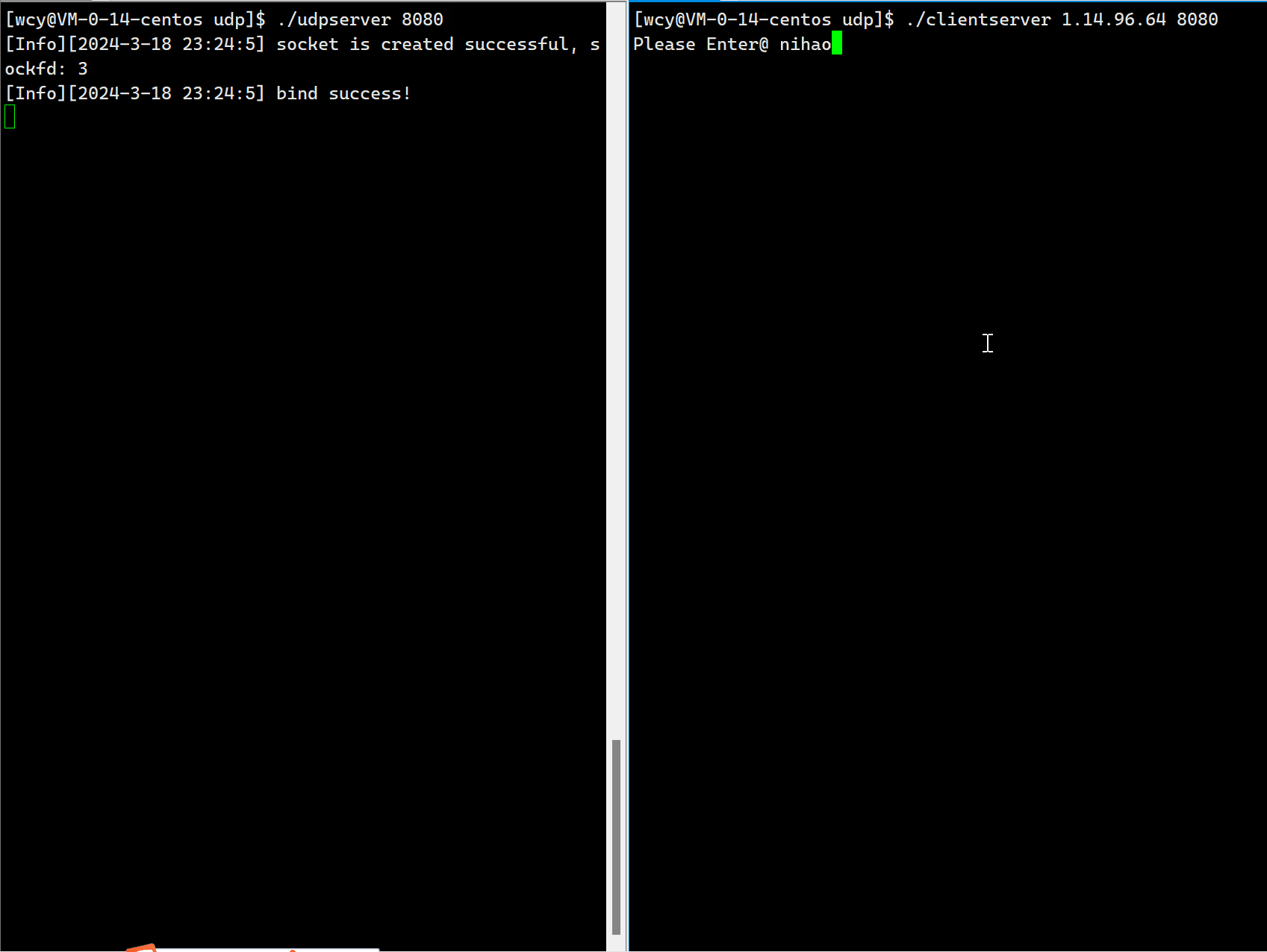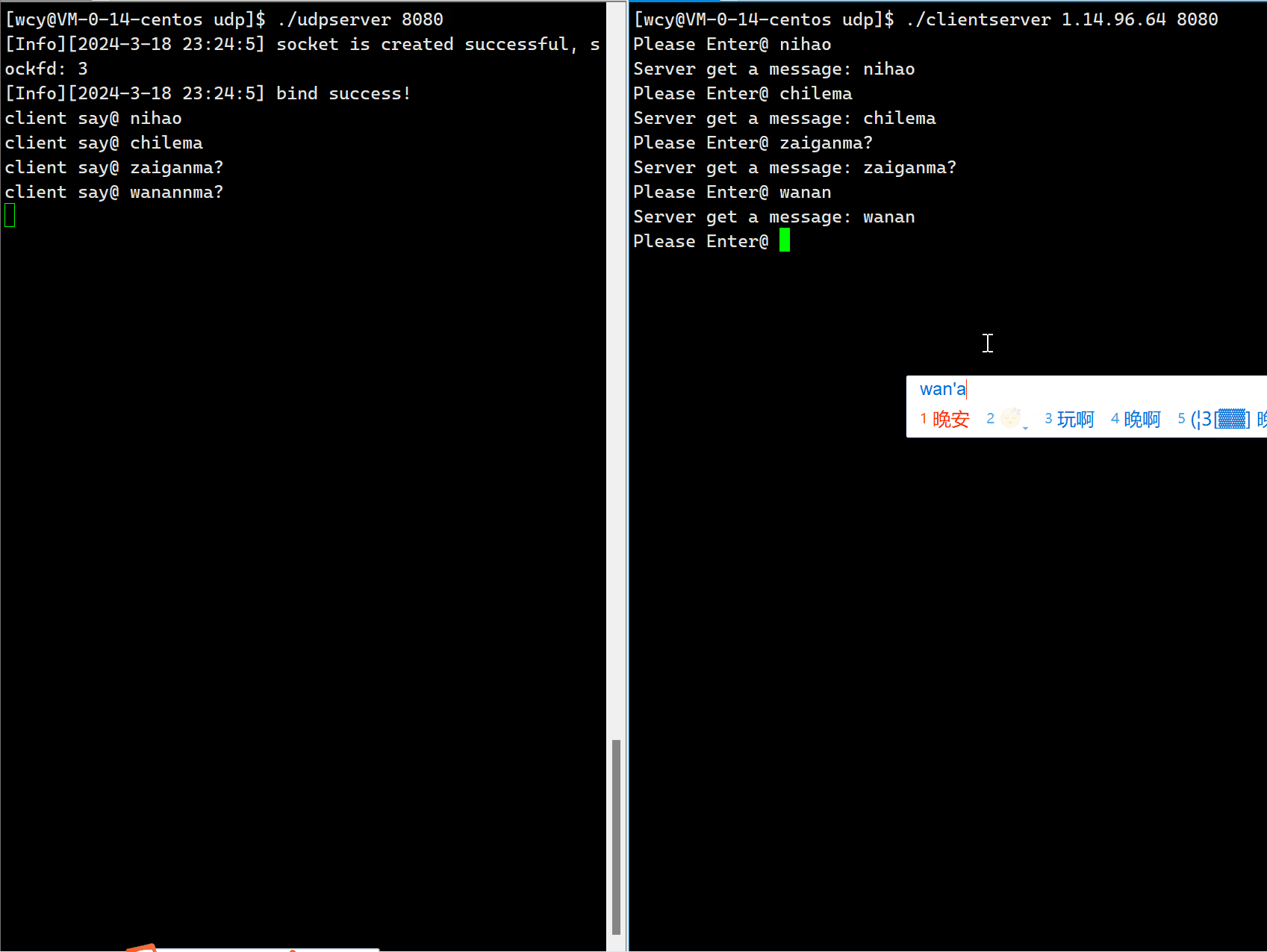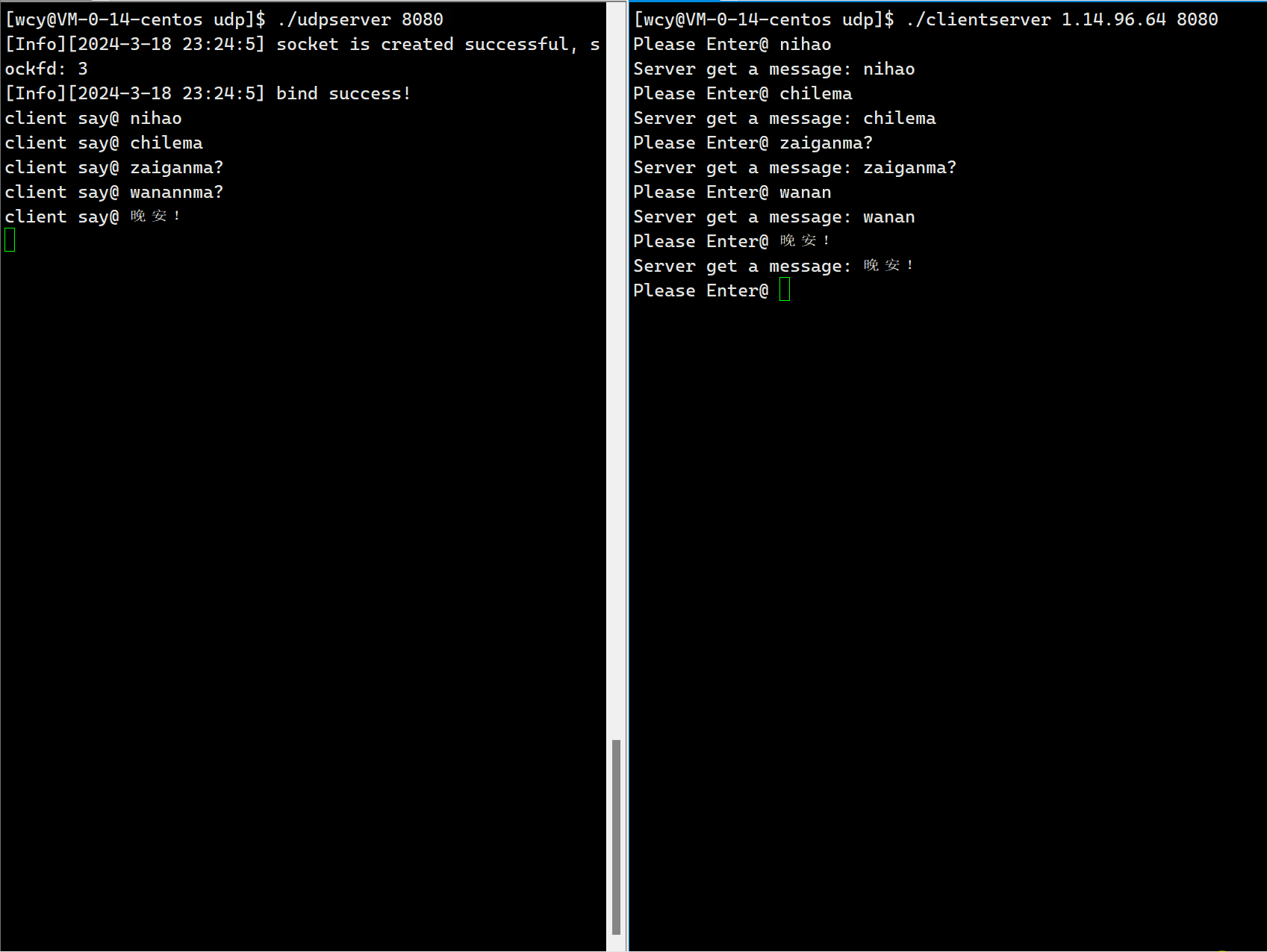
因为一个端口号只能被一个进程 bind,客户端的应用是非常多的,如果在客户端采用静态 bind,那可能会出现两个应用同时 bind 同一个端口号,此时就注定了这两个应用一定是不能同时运行的。为了解决这个问题,一般不建议客户端 bind 一个固定的端口,而是由操作系统来进行动态的 bind,这样就可以避免端口号发生冲突。这也间接说明,对一个 client 端的进程来说,它的端口号是几并不重要,只要能够标识该进程在主机上的唯一性就可以。因为,一般都是由 clinet 端主动的向 server 端发送消息,所以 client 一定是能够知道 client 端的端口号。相反,服务器的端口号必须是确定的。因此,在编写客户端的代码时,第一步就是创建套接字,创建完无需进行 bind,直接向服务器发送数据,发送的时候,操作系统会为我们进行动态 bind。
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <arpa/inet.h>using namespace std;void Usage(const char *command)
{std::cout << "\n\tUsage: " << command << " serverip serverport" << std::endl;
}int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{if (argc != 3){Usage(argv[0]);exit(0);}string serverip = argv[1];uint16_t serverport = stoi(argv[2]);sockaddr_in server;bzero(&server, sizeof(server));server.sin_family = AF_INET;server.sin_port = htons(serverport);server.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(serverip.c_str());socklen_t len = sizeof(server);// 1. 创建套接字int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);if (sockfd < 0){cout << "socker error" << endl;exit(1);}// 2. 接下来直接发送数据string message;char buffer[1024];while (true){cout << "Please Enter@ ";getline(cin, message);// 发送数据sendto(sockfd, message.c_str(), message.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&server, len);struct sockaddr_in temp;socklen_t temp_len = sizeof(temp);// 接收服务器数据ssize_t s = recvfrom(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer)-1, 0, (struct sockaddr*)&temp, &temp_len);if(s > 0){buffer[s] = 0;cout << buffer << endl;}}close(sockfd);return 0;
}
八、基于 Udp 的指令处理
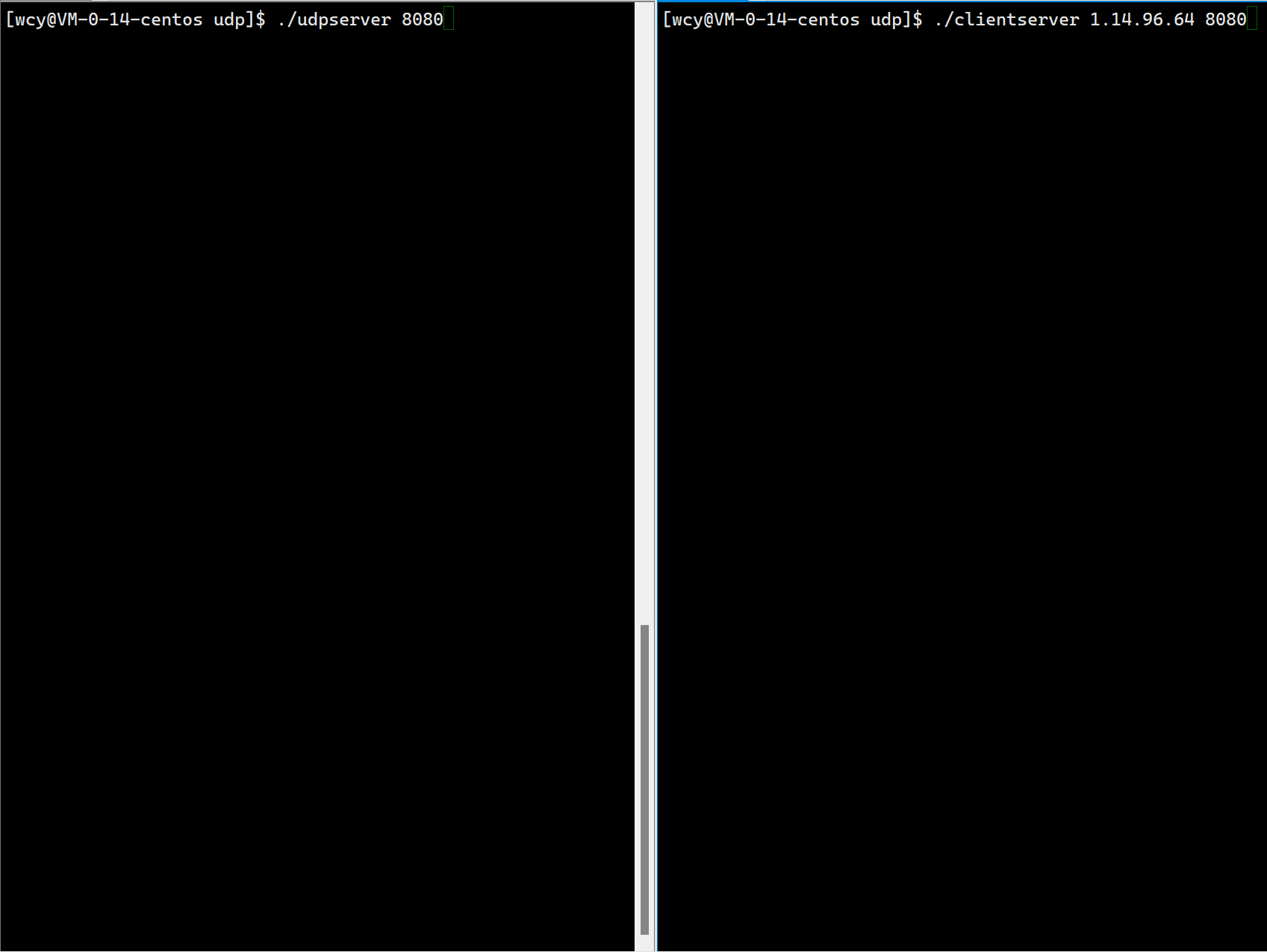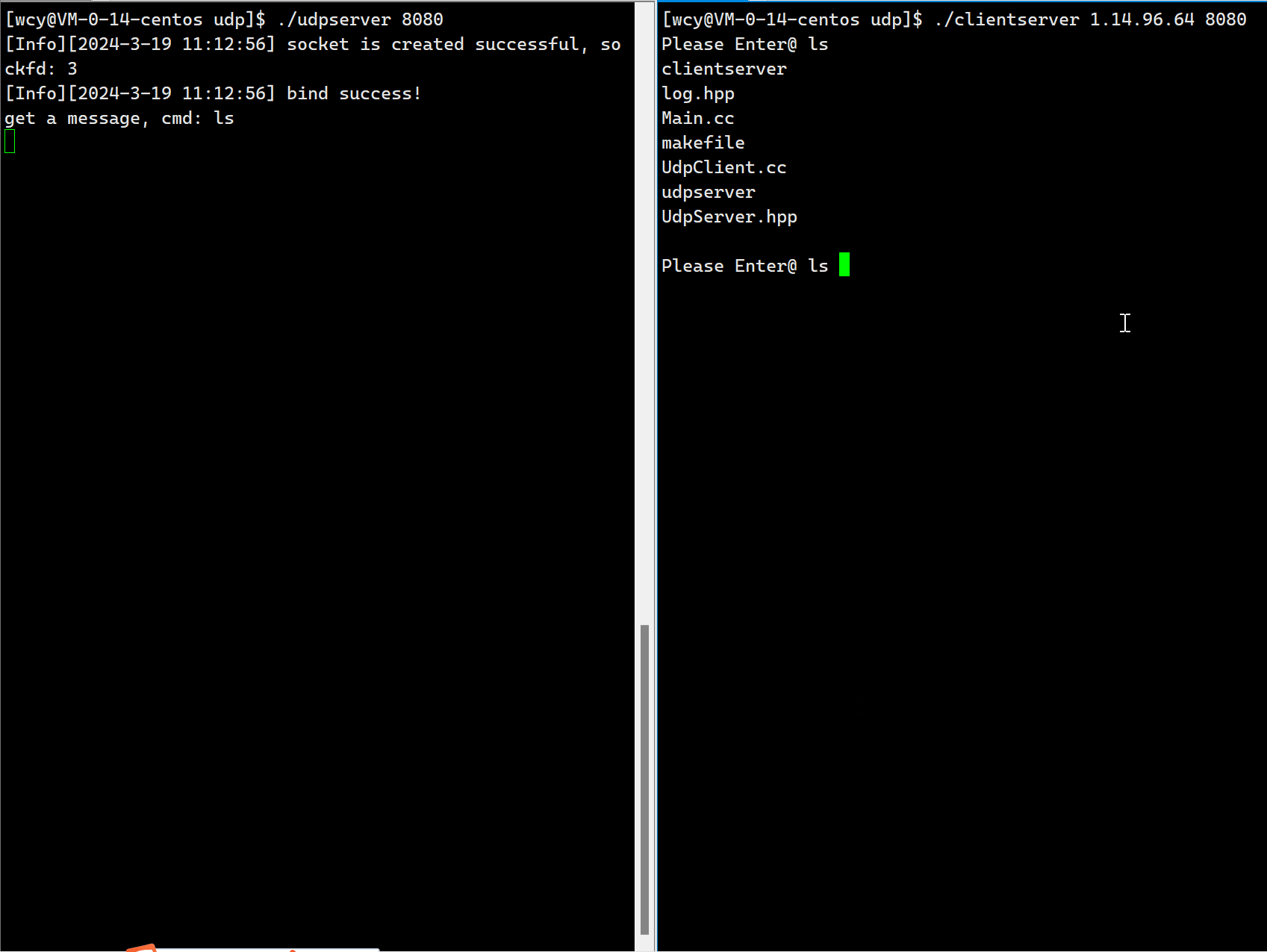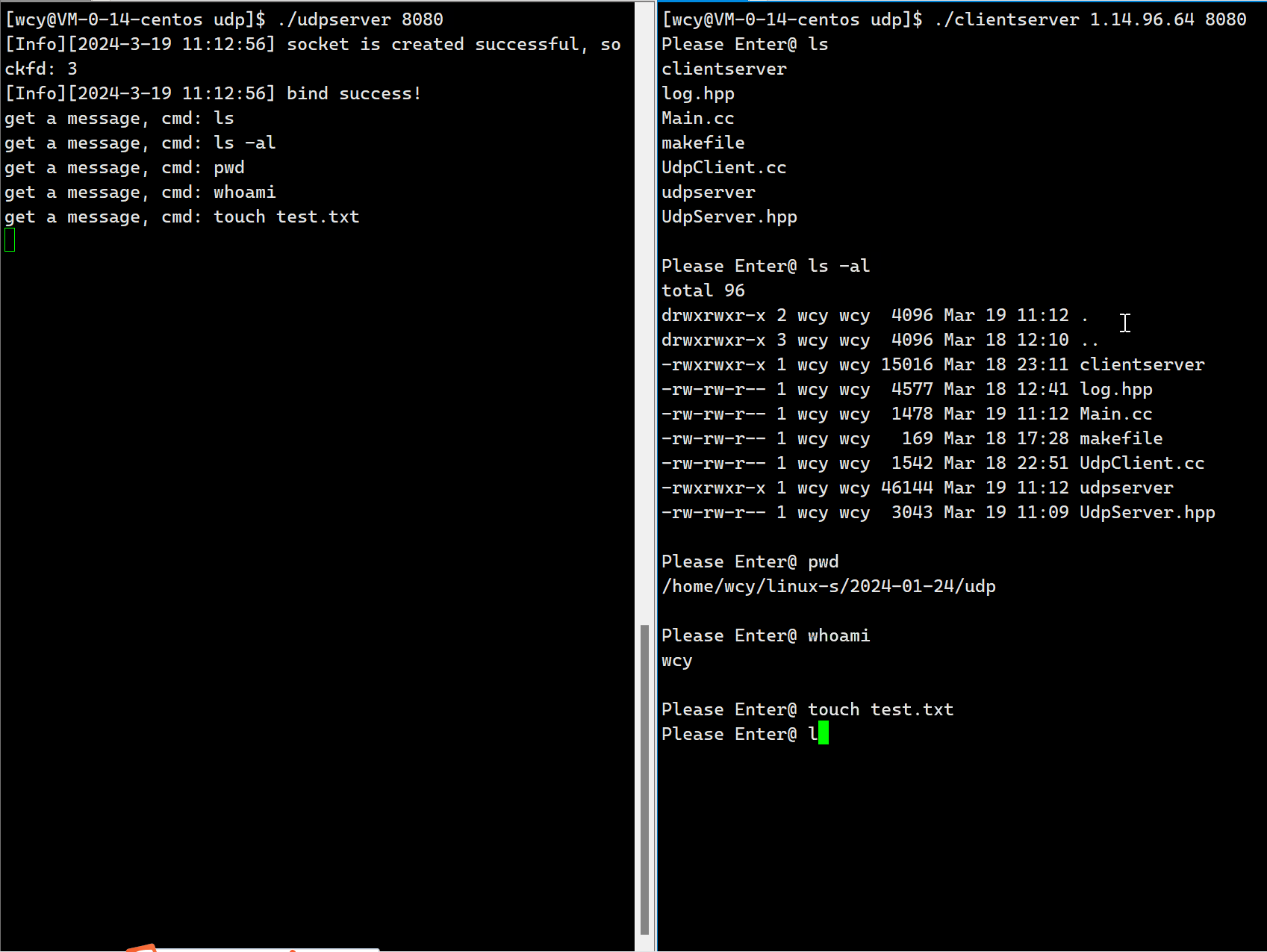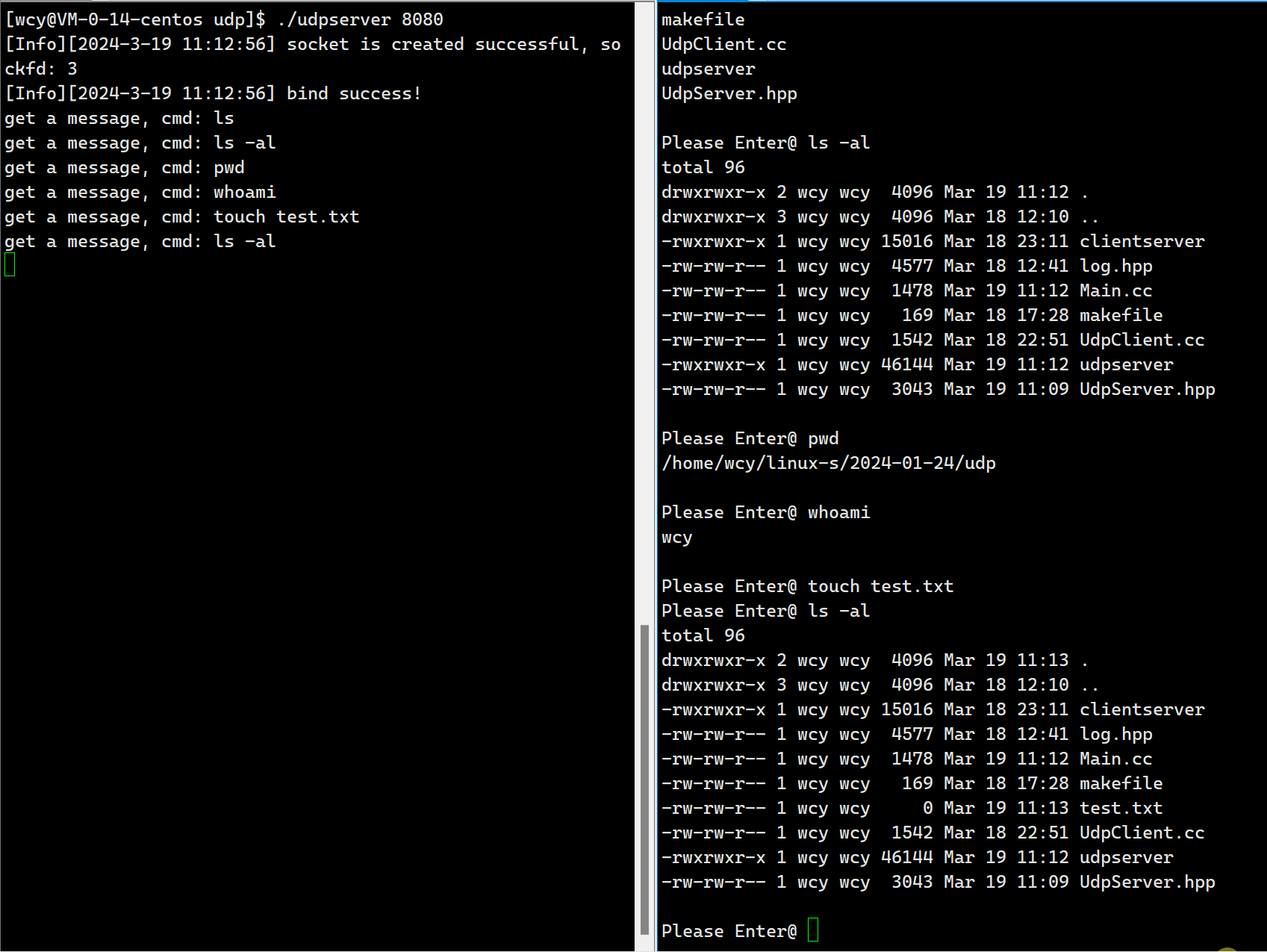
服务端在收到用户端的数据后,会对数据进行加工处理,然后再返回给客户端,可以将数据处理的过程独立出来,将数据处理的函数作为参数传递给服务端的 Run 方法,当前这个场景就是基于 Udp 的,客户端输入指令,客户端执行对应的指令,并将执行结果返回给用户。这里服务端指令的执行通过调用 popen 函数即可。
#include <stdio.h>FILE *popen(const char *command, const char *type);int pclose(FILE *stream);
popen 函数会调用 fork 创建子进程,然后子进程执行程序替换,去执行指令。其中 command 参数就是要执行的指令,type 使用 "r" 表示读取,使用 "w" 表示写入,根据这个参数,popen 会建立管道连接到子进程的标准输入输出设备或标准输入设备,然后返回一个文件指针,随后进程便可利用此文件指针来读取子进程的输出设备或者写入到子进程的标准输入设备中。此外,所有使用文件指针 (FILE*) 操作的函数也都可以使用,出了 fclose 以外。返回值:如果床工则返回文件指针,否则返回 NULL,错误原因存于 errno 中。
客户端的主题代码不动,只用将 ExcuteCommand 函数作为 svr->Run(); 的参数传递进去即可。
bool SafeCheak(const std::string &cmd)
{std::vector<std::string> key_word = {"rm", "mv", "cp", "kill", "sudo", "unlink", "uninstall", "yum", "top"};for(auto & key : key_word){if(cmd.find(key) != std::string::npos){return false;}}return true;
} std::string ExcuteCommand(const std::string &cmd)
{std::cout << "get a message, cmd: %s" << std::endl;// 指令检查if(!SafeCheak(cmd)) return "This action is prohibited";FILE *fp = popen(cmd.c_str(), "r");if(fp == NULL){perror("popen");return "error";}// 读取执行结果std::string result;char buffer[4096];while(true){char *ret = fgets(buffer, sizeof(buffer), fp);if(ret == NULL) break;result += buffer;}fclose(fp);return result;
}
九、基于 Udp 的聊天室
9.1 server 端
因为是聊天室,只要是进入该聊天室的用户,在该聊天室中发送的消息,应该是可以被所有在线用户看到的,所以我们需要在客户端维护一张在线用户列表,采用 unordered_map 结构,让用户的 ip 作为 key 值,用户端的套接字作为 value,当一个客户进入该聊天室的时候,客户端应该进行检查,看其是否在在线列表中,如果不在,应该先将其加入到在线列表。然后客户端需要将该用户发送的信息,再转发给其他所有在线用户,因此需要去遍历在线用户列表进行 sendto。服务端在转发用户消息前,先进行轻加工,在消息前加上用户端的 ip 和端口,用来标识该信息是谁发送的。因此服务端在接收到用户端信息后,需要对从网络中收到的用户套接字信息进行网路转主机操作。对于端口号,可以采用 ntohs 接口将网络序列转换成主句序列,对于 ip,可以采用 inet_ntoa 将 4 字节的网络 ip 序列转化成字符串类型的主机序列。
// UdpServer.hpp
#pragma once
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <string>
#include "log.hpp"
#include <string.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <functional>
#include <unordered_map>#define num 1024extern Log lg;enum
{SOCKET_ERR = 1,BIND_ERR
};uint16_t defaultport = 8080;
std::string defaultip = "0.0.0.0";using func_t = std::function<std::string(const std::string &, const std::string &, const uint16_t &)>;class UdpServer
{
private:void CheckUser(const sockaddr_in &client, const std::string &client_ip, uint16_t client_port){auto pos = userinfo_.find(client_ip);if (pos == userinfo_.end()){userinfo_.insert({client_ip, client});printf("[%s-%d] Enter the chat room\n", client_ip.c_str(), client_port);}}void Broadcast(const std::string &info, const std::string &client_ip, uint16_t client_port){for(auto &user : userinfo_){std::string message = "[";message += client_ip;message += "-";message += std::to_string(client_port);message += "]# ";message += info;socklen_t len = sizeof(user.second);sendto(sockfd_, message.c_str(), message.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&(user.second), sizeof(user.second));}}public:UdpServer(const uint16_t &port = defaultport, const std::string &ip = defaultip): ip_(ip), port_(port), isrunning_(false){}void Init(){// 1. 创建 udp socketsockfd_ = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);if (sockfd_ < 0){lg(Fatal, "socket create error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));exit(SOCKET_ERR);}lg(Info, "socket is created successful, sockfd: %d", sockfd_);// 2. bind socketstruct sockaddr_in local;bzero(&local, sizeof(local)); // 将内容清空成0local.sin_family = AF_INET; // 表明当前结构体的类型local.sin_port = htons(port_); // 当前服务器的端口号local.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip_.c_str()); // 将字符串风格的 ip 地址转化成 4 字节的网络序列// bind 的本质就是把上面这个参数设置进内核,设置到指定的套接字当中int n = bind(sockfd_, (struct sockaddr *)&local, sizeof(local));if (n < 0){lg(Fatal, "bind error, error: %d, err string: %s", errno, strerror(errno));exit(BIND_ERR);}lg(Info, "bind success!");}// 数据传输——(获取和发送)void Run(){isrunning_ = true;while (isrunning_){// 从套接字中读取数据char buffer[num];struct sockaddr_in client;socklen_t len = sizeof(client);int ret = recvfrom(sockfd_, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&client, &len);if (ret < 0){lg(Warning, "recvfrom error, error: %d, err string: %s", errno, strerror(errno));continue;}buffer[ret] = 0;uint16_t client_port = ntohs(client.sin_port); // 获取client 端的端口号std::string client_ip = inet_ntoa(client.sin_addr); // 获取 client 端的 ip 地址CheckUser(client, client_ip, client_port);std::string info = buffer;Broadcast(info, client_ip, client_port); // 将收到的消息广播给所有的在线用户// std::string info = buffer;// std::string echo_string; // = func(info, client_ip, client_port);// // 向 client端 发送数据// int n = sendto(sockfd_, echo_string.c_str(), echo_string.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&client, len);// if (n < 0)// {// lg(Warning, "sendto error, error: %d, err string: %s", errno, strerror(errno));// continue;// }}}~UdpServer(){close(sockfd_);}private:int sockfd_; // 网络文件描述符std::string ip_; // 主机的 ip 地址uint16_t port_; // 服务器的端口号bool isrunning_; // 是否在运行std::unordered_map<std::string, sockaddr_in> userinfo_; // 维护一张用户信息表。
};
// main.cc
#include "UdpServer.hpp"
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>void Usage(const char *command)
{std::cout << "\n\tUsage: " << command << " port[1024+]" << std::endl;
}int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{if(argc != 2){Usage(argv[0]);exit(0);}uint16_t port = std::stoi(argv[1]); std::unique_ptr<UdpServer> svr(new UdpServer(port));svr->Init();svr->Run();return 0;
}
补充:upd 的 socket 是全双工的,可以同时读数据和发数据。
9.1.1 地址转换函数
将字符串转化成 4 字节网络序列:
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>int inet_aton(const char *cp, struct in_addr *inp);
in_addr_t inet_addr(const char *cp);
int inet_pton(int af, const char *src, void *dst);
网络序列转化成字符串:
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>char *inet_ntoa(struct in_addr in);
const char *inet_ntop(int af, const void *src, char *dst, socklen_t size);
inet_ntoa 函数的返回值是一个地址,那转化出来的字符串在哪呢?答案是,在 inet_ntoa 函数的内部为我们申请了一块内存来保存 ip 字符串的结果,main 手册上说,inet_ntoa 函数,是把这个返回结果放到了静态存储区,这个时候不需要我们手动释放。但这也导致在一个进程中第二次调用 inet_ntoa 函数时,会对上一次的转换结果进行覆盖。在 APUE 中明确的提出 inet_ntoa 不是线程安全的函数,所以在多线程编程下建议使用 inet_ntop 函数,这个函数由调用者自己提供一个缓冲区保存结果,可以规避线程安全问题。
9.2 client 端
client 端主要有两个功能,一是该用户发送数据,二是该用户获取其他用户发送的消息,本质是获取服务端的消息,因为其他用户的消息是先交给服务端的。因此这里需要两个线程,一个线程用来获取用户输入,将用户的输入消息发送给服务器,另一个线程用来接收服务器的消息,采用两个线程的本质原因是,在获取用户输入的时候,如果用户一直没有进行输入,那么会阻塞住,就收不到服务器的消息,所以这里采用两个线程将获取用户输入和获取服务端的消息分开。这两个线程一个线程往套接字里面进行写入,一个从套接字里面进行读取,看似在访问同一份资源,但实际上,Udp 套接字是一个全双工的,发数据和收数据都有自己独立的缓冲区,因此不存在线程安全。
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <arpa/inet.h>using namespace std;struct ThreadData
{int socckfd;sockaddr_in server;
};void Usage(const char *command)
{std::cout << "\n\tUsage: " << command << " serverip serverport" << std::endl;
}void *send_rountine(void *args)
{ThreadData *td = static_cast<ThreadData *>(args);string message;while(true){cout << "Please Enter@ ";getline(cin, message);// 发送数据sendto(td->socckfd, message.c_str(), message.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&(td->server), sizeof(td->server));}
}void *recv_rountine(void *args)
{ThreadData *td = static_cast<ThreadData *>(args);char buffer[1024];while(true){struct sockaddr_in temp;socklen_t temp_len = sizeof(temp);// 接收服务器数据ssize_t s = recvfrom(td->socckfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer)-1, 0, (struct sockaddr*)&temp, &temp_len);if(s > 0){buffer[s] = 0;cerr << buffer << endl;}}
}int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{if (argc != 3){Usage(argv[0]);exit(0);}string serverip = argv[1];uint16_t serverport = stoi(argv[2]);// 1. 创建套接字int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);if (sockfd < 0){cout << "socker error" << endl;exit(1);}// 创建俩线程,一个获取用户输入向 server 发送,一个接收 server 端消息pthread_t send, recv;ThreadData *threaddata = new ThreadData();threaddata->socckfd = sockfd;threaddata->server.sin_family = AF_INET;threaddata->server.sin_port = htons(serverport);threaddata->server.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(serverip.c_str()); pthread_create(&send, nullptr, send_rountine, threaddata);pthread_create(&recv, nullptr, recv_rountine, threaddata);pthread_join(send, nullptr);pthread_join(recv, nullptr);close(sockfd);return 0;
}
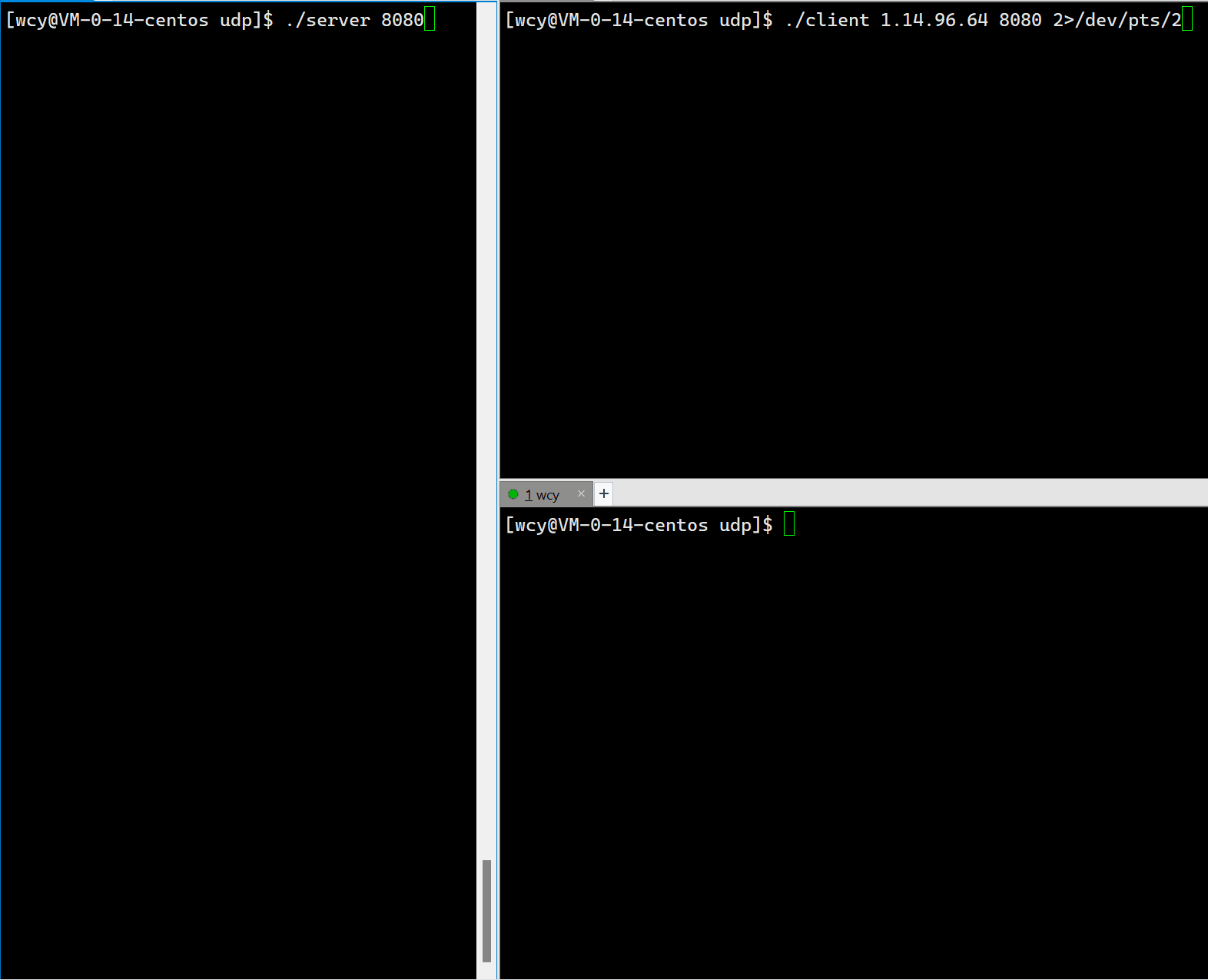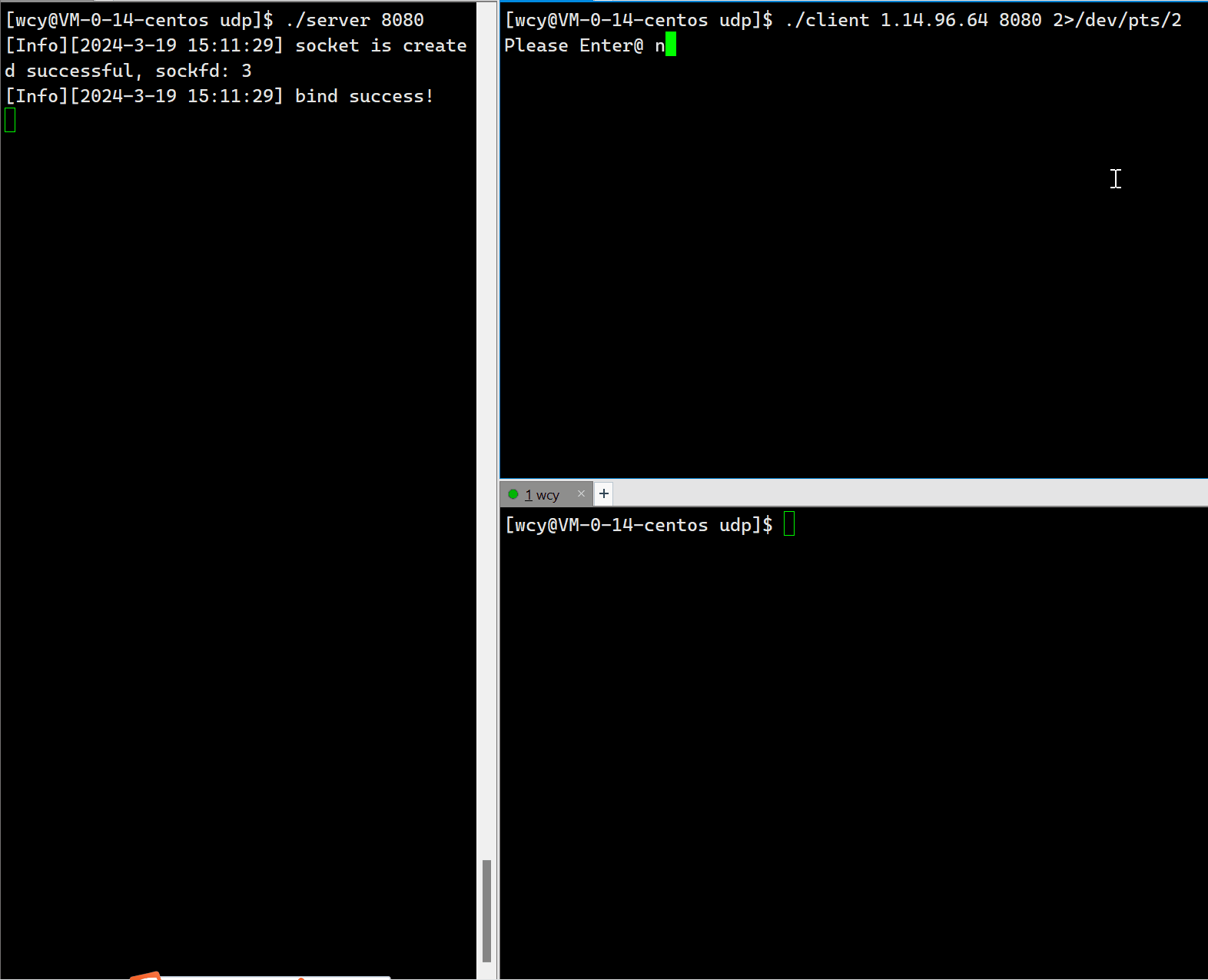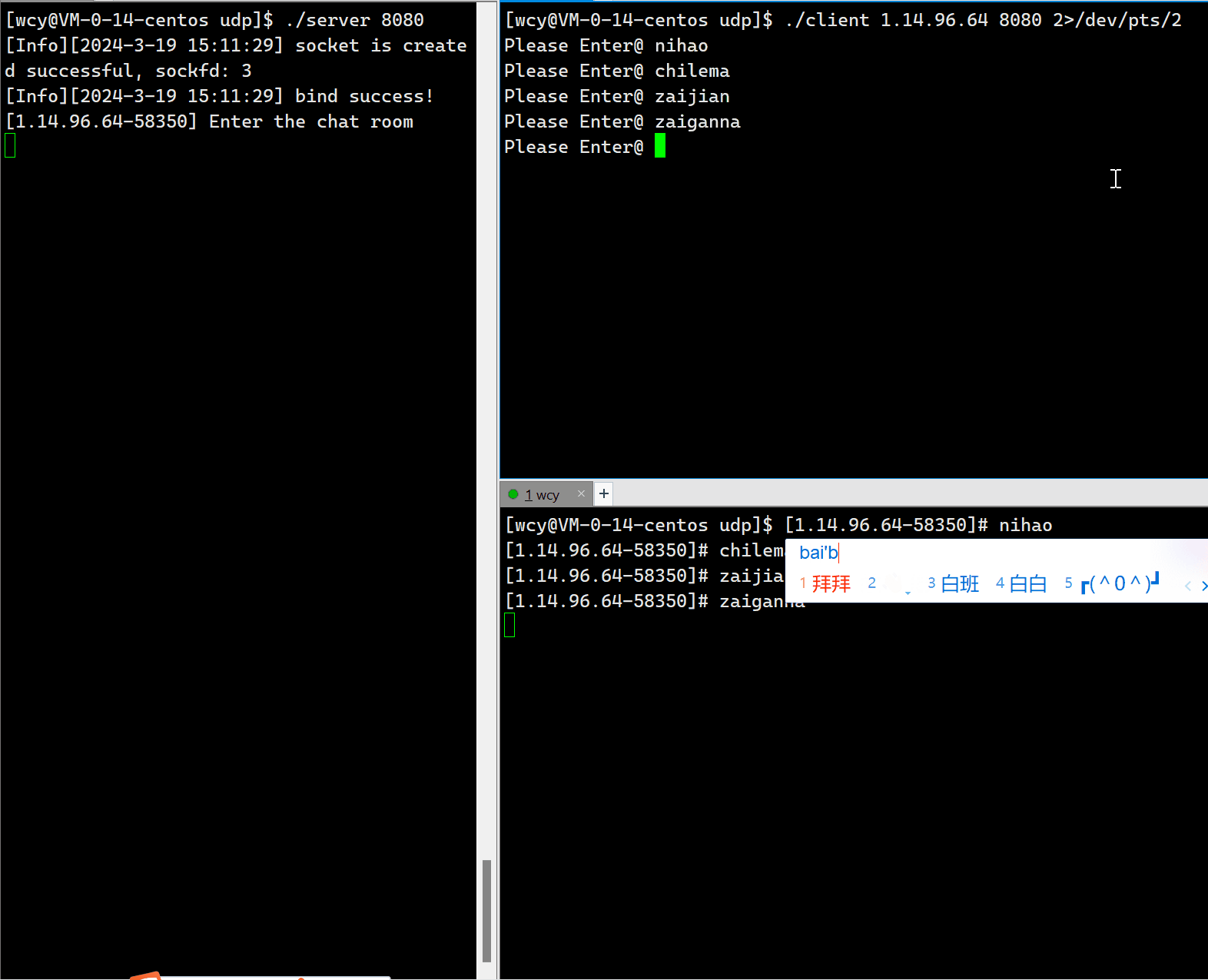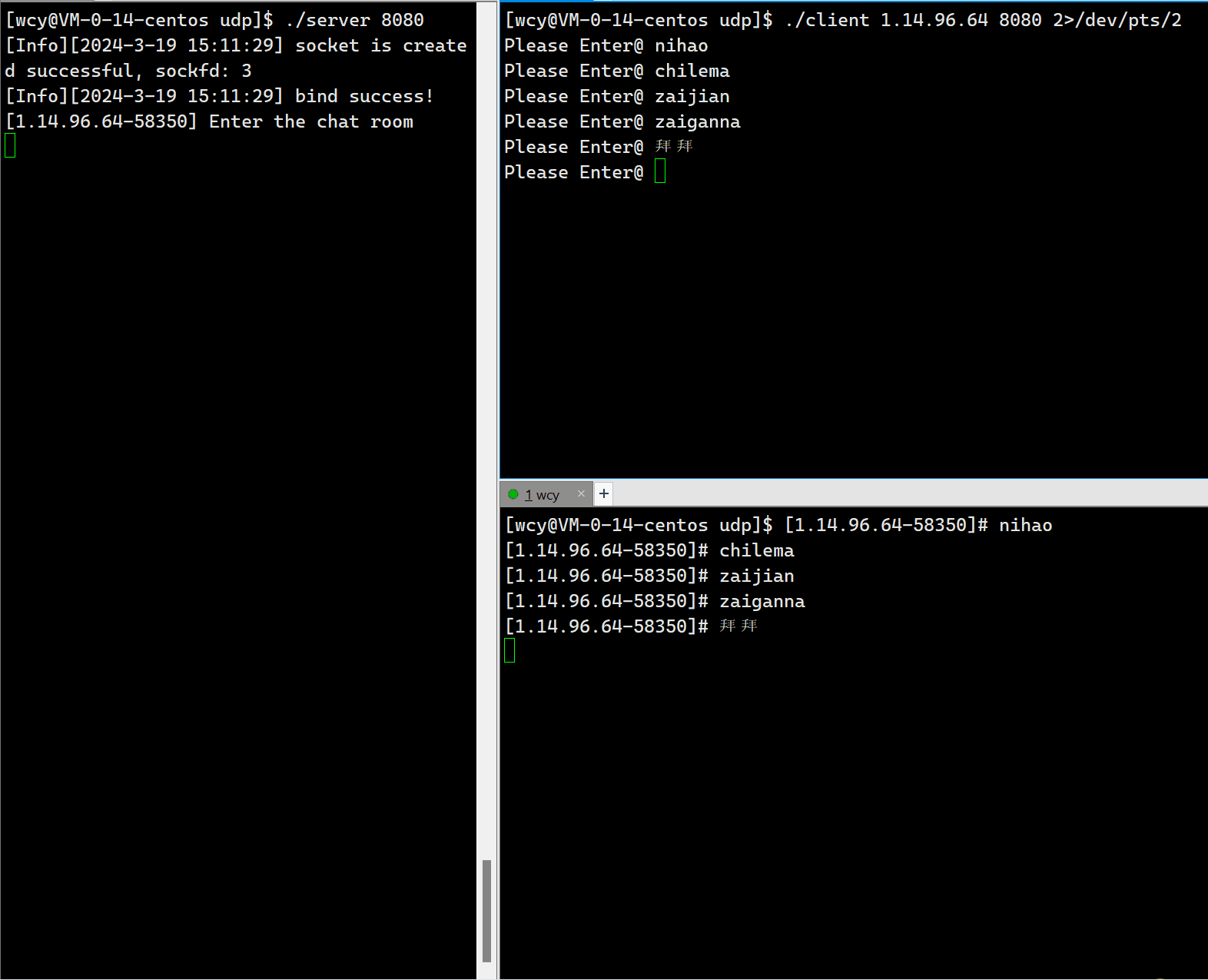
这里有个小细节,就是将用户输入消息的终端和显示消息的终端分离,在打印消息时,采用 cerr,然后在启动 client 的时候,将标准错误重定向到另一个终端。
十、结语
今天的分享到这里就结束啦!如果觉得文章还不错的话,可以三连支持一下,春人的主页还有很多有趣的文章,欢迎小伙伴们前去点评,您的支持就是春人前进的动力!

