Golang学习笔记_40——模版方法模式
Golang学习笔记_41——观察者模式
Golang学习笔记_42——迭代器模式
文章目录
- 一、核心概念
- 1. 定义
- 2. 解决的问题
- 3. 核心角色
- 4. 类图
- 二、特点分析
- 三、适用场景
- 1. 多级审批流程
- 2. 用户身份验证
- 3. 日志处理系统
- 四、Go语言实现示例
- 完整实现代码
- 执行结果
- 五、高级应用
- 1. 动态链路配置
- 2. 熔断机制
- 六、与其他模式对比
- 七、实现建议
- 八、典型应用
一、核心概念
1. 定义
责任链模式是一种行为型设计模式,允许将请求沿着处理链传递,直到有对象处理它。其核心特点包括:
• 解耦请求与处理:发送者无需知道具体处理者
• 动态链式处理:可动态调整处理链顺序和组成
• 职责单一性:每个处理者专注特定类型请求
2. 解决的问题
• 复杂条件分支:避免大量if-else判断语句
• 请求处理流程扩展:新增处理节点不影响现有逻辑
• 分布式责任:多层级审批/验证场景
3. 核心角色
| 角色 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| Handler | 定义处理请求的接口,包含设置下家的方法 |
| ConcreteHandler | 具体处理逻辑实现,决定处理或传递请求 |
| Client | 组装责任链并触发首个处理者 |
4. 类图
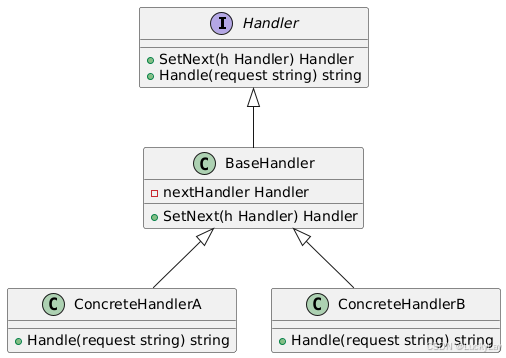
@startuml
interface Handler {+ SetNext(h Handler) Handler+ Handle(request string) string
}class BaseHandler {- nextHandler Handler+ SetNext(h Handler) Handler
}class ConcreteHandlerA {+ Handle(request string) string
}class ConcreteHandlerB {+ Handle(request string) string
}Handler <|-- BaseHandler
BaseHandler <|-- ConcreteHandlerA
BaseHandler <|-- ConcreteHandlerB
@enduml
二、特点分析
优点
- 解耦性强:请求发起方与处理方解耦
- 开闭原则:新增处理节点不影响现有代码
- 灵活组合:可动态调整处理链结构
缺点
- 性能损耗:长链路导致请求处理延迟
- 调试困难:请求可能未被处理且无反馈
- 循环风险:错误配置导致无限循环
三、适用场景
1. 多级审批流程
// 采购审批实现示例
type PurchaseRequest struct {Amount float64Purpose string
}type Approver interface {SetNext(Approver)ProcessRequest(PurchaseRequest) bool
}type Manager struct {next Approver
}func (m *Manager) SetNext(next Approver) {m.next = next
}func (m *Manager) ProcessRequest(req PurchaseRequest) bool {if req.Amount <= 5000 {fmt.Println("经理审批通过")return true}if m.next != nil {return m.next.ProcessRequest(req)}return false
}
2. 用户身份验证
// 多因素认证链
type AuthHandler interface {SetNext(AuthHandler)Handle(*User) bool
}type PasswordHandler struct {next AuthHandler
}func (p *PasswordHandler) SetNext(h AuthHandler) {p.next = h
}func (p *PasswordHandler) Handle(u *User) bool {if !verifyPassword(u) {return false}if p.next != nil {return p.next.Handle(u)}return true
}
3. 日志处理系统
// 多级日志处理器
type LogLevel intconst (DEBUG LogLevel = iotaINFOERROR
)type Logger interface {SetNext(Logger)Log(string, LogLevel)
}type EmailLogger struct {level LogLevelnext Logger
}func (e *EmailLogger) Log(msg string, l LogLevel) {if l >= e.level {fmt.Printf("发送邮件日志: %s\n", msg)}if e.next != nil {e.next.Log(msg, l)}
}
四、Go语言实现示例
完整实现代码
package chainofresponsibilityimport "fmt"type Handler interface {SetNext(Handler) HandlerHandle(string) string
}type BaseHandler struct {next Handler
}func (b *BaseHandler) SetNext(h Handler) Handler {b.next = hreturn h
}func (b *BaseHandler) Handle(s string) string {if b.next != nil {return b.next.Handle(s)}return ""
}type AuthHandler struct {BaseHandler
}func (a *AuthHandler) Handle(req string) string {if req == "auth" {fmt.Println("执行身份验证")return "AUTH_SUCCESS"}return a.BaseHandler.Handle(req)
}type LoggingHandler struct {BaseHandler
}func (l *LoggingHandler) Handle(req string) string {fmt.Printf("记录请求日志: %s\n", req)return l.BaseHandler.Handle(req)
}// 客户端使用示例
func ExampleChain() {handlers := &AuthHandler{}handlers.SetNext(&LoggingHandler{})fmt.Println(handlers.Handle("auth"))fmt.Println(handlers.Handle("data"))
}
执行结果
=== RUN TestExampleChain
执行身份验证
AUTH_SUCCESS
记录请求日志: data--- PASS: TestExampleChain (0.00s)
PASS
五、高级应用
1. 动态链路配置
type ChainBuilder struct {head Handlertail Handler
}func (c *ChainBuilder) AddHandler(h Handler) {if c.head == nil {c.head = hc.tail = hreturn}c.tail.SetNext(h)c.tail = h
}func (c *ChainBuilder) Execute(req string) {if c.head != nil {c.head.Handle(req)}
}
2. 熔断机制
type CircuitBreakerHandler struct {BaseHandlerfailureCount intthreshold int
}func (c *CircuitBreakerHandler) Handle(req string) string {if c.failureCount >= c.threshold {fmt.Println("熔断器已触发")return ""}result := c.BaseHandler.Handle(req)if result == "ERROR" {c.failureCount++}return result
}
六、与其他模式对比
| 模式 | 核心区别 | 典型场景 |
|---|---|---|
| 命令模式 | 请求封装 vs 请求传递 | 撤销操作管理 |
| 策略模式 | 算法选择 vs 处理流程控制 | 支付方式选择 |
| 装饰器模式 | 功能叠加 vs 责任传递 | 动态添加功能 |
七、实现建议
- 链路终止控制:增加处理成功标志位
- 优先级控制:实现带权重的处理节点
- 异步处理:结合goroutine实现并行处理链
- 监控埋点:记录各节点处理耗时和状态
八、典型应用
- 中间件管道:Gin框架的中间件链
- 风控系统:多规则顺序校验
- 订单处理:库存检查→支付→物流的链式处理
- API网关:认证→限流→日志记录的处理流程
通过责任链模式,可以有效处理需要多层级决策的业务场景。在Go语言中,利用接口和结构体组合的特性,可以构建灵活可扩展的处理链路。建议在以下场景优先考虑:
- 存在多个可能处理请求的对象
- 需要动态指定处理流程
- 处理流程需要灵活变更
- 需要解耦请求发送者和接收者
