每当误会消除冰释前嫌的时候,故事就距离结尾不远了。
栈
概念与结构
1. 栈⼀种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的⼀端进行插入和删除元素操作。2. 进行数据插入和删除操作的⼀端称为栈顶,另⼀端称为栈底。3. 栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出的原则。4. 栈的插入操作叫做进栈,栈的删除操作叫做出栈。5. 栈的实现⼀般可以使用数组或者链表实现。6. 相对而言,使用数组结构实现更优⼀些。因为数组结构更简单,而且能够胜任所有功能。7. 栈不能遍历,也不找到中间和下面的数据,只能找到最上面的数据,是阉割版的线性表。
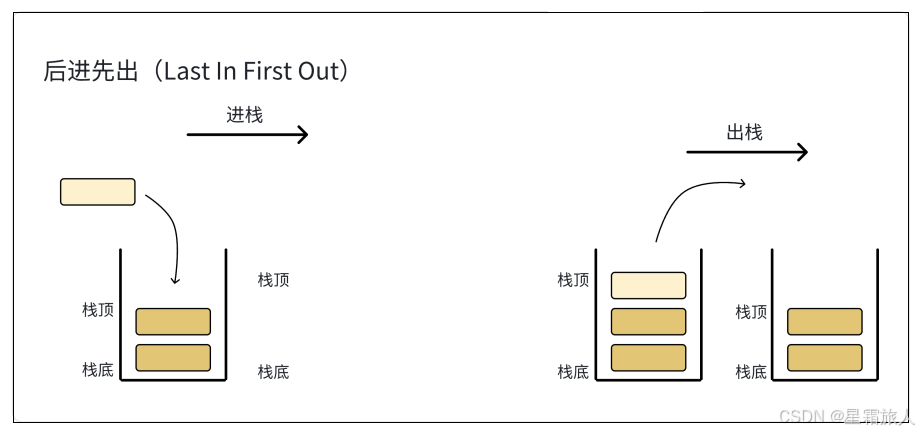
1. 想象一下玩具枪的弹夹,我们给弹夹上子弹的时候,先上的子弹被压在弹夹的最下面,后装的子弹在最上面,打枪的时候后装的子弹最先被打出。
2. 这个弹夹其实就是一种栈的数据结构。我们一般把先进后出,后进先出的这种数据结构称之为栈。
3. 从栈的操作特性上看栈这是一种"操作受限的线性表",它只支持在一端插入和删除数据。
分步实现栈的功能
创建栈的结构体
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* arr;//创建动态数组(指针)int capacity;//栈的空间大小int top;//栈顶,是栈中最后一个数据的下一位
}Stack;初始化栈
void InitStack(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);//Stack* ps=&stack;本质上是判断:调用函数时候有没有传参数,如果没有那么ps指向任意值,就有可能是NULL。ps->arr = NULL;ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}进栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, int x)
{//判断空间是否足够if (ps->capacity == ps->top ){int Newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4: 2 * ps->capacity;//在原有的空间基础上继续开辟空间,需要使用realloc()。STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, Newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));//判断空间开辟是否成功if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");exit(1);}else{ps->arr = tmp;ps->capacity = Newcapacity;}}ps->arr[ps->top++] = x;//指针当作动态数组使用
}出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top!=0);//当栈中没有元素时候,就不能出栈了。ps->top--;
}查找栈首元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top != 0);return ps->arr[ps->top - 1];//top指向最后一个元素的下一位
}销毁栈
void DestroyStack(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);if (ps->arr){free(ps->arr);//释放动态数组空间}ps->arr = NULL;ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}实现栈的代码
<stack.h> 文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* arr;//创建动态数组(指针)int capacity;//栈的空间大小int top;//栈顶
}Stack;
//初始化
void InitStack(Stack* ps);
void DestroyStack(Stack* ps);
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType x);
void StackPop(Stack* ps);
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps);<stack.c>文件
#include "stack.h"
void InitStack(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->arr = NULL;ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void DestroyStack(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);if (ps->arr)free(ps->arr);ps->arr = NULL;ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(Stack* ps, int x)
{//判断空间是否足够if (ps->capacity == ps->top ){int Newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4: 2 * ps->capacity;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, Newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");exit(1);}else{ps->arr = tmp;ps->capacity = Newcapacity;}}ps->arr[ps->top++] = x;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top!=0);ps->top--;
}
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top != 0);return ps->arr[ps->top - 1];//top指向最后一个元素的下一位
}<test.c>文件
#include "stack.h"
int main()//栈里面的数据不能被遍历,也不能被随机访问。
{Stack stack1;InitStack(&stack1);//DestroyStack(&stack1);StackPush(&stack1, 1);StackPush(&stack1, 2);StackPush(&stack1, 3);StackPush(&stack1, 4);StackPush(&stack1, 5);StackPush(&stack1, 6);while (stack1.top != 0){int data=StackTop(&stack1);printf("%d\n", data);StackPop(&stack1);}DestroyStack(&stack1);return 0;
}队列
概念与结构
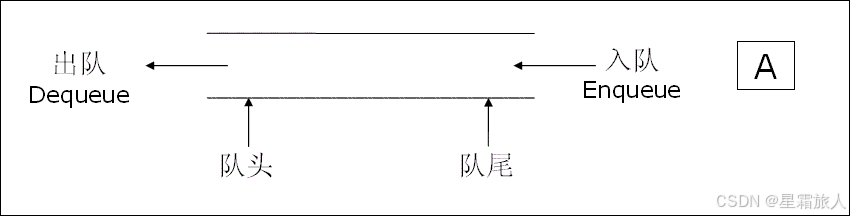
1. 只允许在⼀端进行插入数据操作,在另⼀端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表。
2. 队列具有先进先出的原则。
3. 队列也可以用数组和链表的结构实现。
4. 使用链表的结构实现更优⼀些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
5. 在数组实现的列队中,出队操作通常需要将队首元素移除。如果队首元素被移除后,队列中的其他元素需要向前移动一位以填补空缺。这个过程的时间复杂度是 O(n),其中 n 是队列中元素的数量。
分步实现列队的功能
创建列队结构体
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct QueueNode //列队节点结构体
{DataType data;struct QueueNode* next;
}QueueNode;
typedef struct Queue //列队结构体
{QueueNode* phead;QueueNode* ptail;int size;
}Queue;初始化列队
void InitQueue(Queue* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->phead = ps->ptail = NULL;ps->size = 0;
}入队
void AddQueue(Queue* ps, DataType x)
{assert(ps);QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(DataType));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(1);}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if ((ps->phead == NULL) && (ps->ptail == NULL)){ps->phead = ps->ptail = newnode;}else{ps->ptail->next = newnode;ps->ptail = newnode;}ps->size++;
}出队
void PopQueue(Queue* ps)
{assert(ps);if ((ps->phead == NULL) && (ps->ptail == NULL)){exit(1);//要求列队不能为空}if (ps->phead == ps->ptail){free(ps->phead);//列队只有一个节点时ps->phead = ps->ptail = NULL;}else{QueueNode* next = ps->phead->next;free(ps->phead);ps->phead = next;}ps->size--;
}查找队头
DataType TakeFrontQueue(Queue* ps)
{assert(ps);if ((ps->phead == NULL) && (ps->ptail == NULL)){exit(1);//要求列队不能为空}return ps->phead->data;
}
查找对尾
DataType TakeBackQueue(Queue* ps)
{assert(ps);if ((ps->phead == NULL) && (ps->ptail == NULL)){exit(1);//要求列队不能为空}return ps->ptail->data;
}查找队伍长度
int QueueSize(Queue* ps)
{return ps->size;
}销毁队列
void DestroyQueue(Queue* ps)
{assert(ps);if ((ps->phead == NULL) && (ps->ptail == NULL)){exit(1);//要求列队不能为空}QueueNode* pcur = ps->phead;while (pcur){QueueNode* next = pcur->next;free(pcur);pcur = next;}ps->phead = ps->ptail = NULL;ps->size = 0;
}实现列队的代码
<queue.h>文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>typedef int DataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{DataType data;struct QueueNode* next;
}QueueNode;
typedef struct Queue
{QueueNode* phead;QueueNode* ptail;int size;
}Queue;
void InitQueue(Queue* ps);
void AddQueue(Queue* ps, DataType x);
void PopQueue(Queue* ps);
DataType TakeFrontQueue(Queue* ps);
DataType TakeBackQueue(Queue* ps);
int QueueSize(Queue* ps);
void DestroyQueue(Queue* ps);<queue.c>文件
#include "queue.h"
void InitQueue(Queue* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->phead = ps->ptail = NULL;ps->size = 0;
}
void AddQueue(Queue* ps, DataType x)
{assert(ps);QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(DataType));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(1);}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if ((ps->phead == NULL) && (ps->ptail == NULL)){ps->phead = ps->ptail = newnode;}else{ps->ptail->next = newnode;ps->ptail = newnode;}ps->size++;
}
void PopQueue(Queue* ps)
{assert(ps);if ((ps->phead == NULL) && (ps->ptail == NULL)){exit(1);//要求列队不能为空}if (ps->phead == ps->ptail){free(ps->phead);//列队只有一个节点时ps->phead = ps->ptail = NULL;}else{QueueNode* next = ps->phead->next;free(ps->phead);ps->phead = next;}ps->size--;
}
DataType TakeFrontQueue(Queue* ps)
{assert(ps);if ((ps->phead == NULL) && (ps->ptail == NULL)){exit(1);//要求列队不能为空}return ps->phead->data;
}
DataType TakeBackQueue(Queue* ps)
{assert(ps);if ((ps->phead == NULL) && (ps->ptail == NULL)){exit(1);//要求列队不能为空}return ps->ptail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* ps)
{return ps->size;
}
void DestroyQueue(Queue* ps)
{assert(ps);if ((ps->phead == NULL) && (ps->ptail == NULL)){exit(1);//要求列队不能为空}QueueNode* pcur = ps->phead;while (pcur){QueueNode* next = pcur->next;free(pcur);pcur = next;}ps->phead = ps->ptail = NULL;ps->size = 0;
}<test.c> 文件
#include "queue.h"
int main()
{Queue q;InitQueue(&q); AddQueue(&q, 1);AddQueue(&q, 2);AddQueue(&q, 3);AddQueue(&q, 4);AddQueue(&q, 5);printf("%d\n", TakeFrontQueue(&q));PopQueue(&q);printf("%d\n", TakeFrontQueue(&q));printf("%d\n", TakeBackQueue(&q));printf("%d\n", QueueSize(&q));DestroyQueue(&q);//PopQueue(&q);//PopQueue(&q);//PopQueue(&q);return 0;
}致谢
感谢您花时间阅读这篇文章!如果您对本文有任何疑问、建议或是想要分享您的看法,请不要犹豫,在评论区留下您的宝贵意见。每一次互动都是我前进的动力,您的支持是我最大的鼓励。期待与您的交流,让我们共同成长,探索技术世界的无限可能!
