摘要:
昇思MindSpore的数据变换,包括通用变换Common Transforms、图像变换Vision Transforms、标准化Normalize、文本变换Text Transforms、匿名函数变换Lambda Transforms。
一、数据变换Transforms概念
原始数据需预处理后才能送入神经网络进行训练。
mindspore.dataset.transforms
支持图像、文本、音频等数据类型的数据变换。
支持使用Lambda函数。
二、环境准备
安装minspore模块
!pip uninstall mindspore -y
!pip install -i https://pypi.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/simple mindspore==2.3.0rc1导入minspore、dataset等相关模块
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from download import download
from mindspore.dataset import transforms, vision, text
from mindspore.dataset import GeneratorDataset, MnistDataset三、通用变换Common Transforms
mindspore.dataset.transforms模块支持一系列通用Transforms。
下面以Compose为例。
- 下载数据集:
# Download data from open datasetsurl = "https://mindspore-website.obs.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/" \"notebook/datasets/MNIST_Data.zip"
path = download(url, "./", kind="zip", replace=True)train_dataset = MnistDataset('MNIST_Data/train')输出:
Downloading data from https://mindspore-website.obs.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/notebook/datasets/MNIST_Data.zip (10.3 MB)file_sizes: 100%|███████████████████████████| 10.8M/10.8M [00:00<00:00, 173MB/s]
Extracting zip file...
Successfully downloaded / unzipped to ./2.加载训练数据集
image, label = next(train_dataset.create_tuple_iterator())
print(image.shape)输出:
(28, 28, 1)3.数据变换
# 定义compose变换
composed = transforms.Compose([vision.Rescale(1.0 / 255.0, 0),vision.Normalize(mean=(0.1307,), std=(0.3081,)),vision.HWC2CHW()]
)
# 注册compose变换
train_dataset = train_dataset.map(composed, 'image')
image, label = next(train_dataset.create_tuple_iterator())
print(image.shape)输出:
(1, 28, 28)四、图像变换Vision Transforms
mindspore.dataset.vision模块提供一系列图像数据变换
下面Mnist数据处理过程中,使用了缩放Rescale、标准化Normalize和格式转换HWC2CHW。
1. 缩放Rescale
用于调整图像像素值的大小,包括两个参数:
Rescale :缩放因子
Shift :平移因子
输出的像素值 :outputi=inputi*rescale+shift
下例使用numpy随机生成一个像素值在[0, 255]的图像。
random_np = np.random.randint(0, 255, (48, 48), np.uint8)
random_image = Image.fromarray(random_np)
print(random_np)输出:
[[104 213 39 ... 78 181 154][ 65 32 142 ... 3 78 137][166 225 9 ... 75 220 173]...[190 134 56 ... 171 213 135][109 57 118 ... 2 78 28][ 86 43 44 ... 186 233 193]]现在对其像素值进行缩放。
rescale = vision.Rescale(1.0 / 255.0, 0)
rescaled_image = rescale(random_image)
print(rescaled_image)输出:
[[0.40784317 0.8352942 0.15294118 ... 0.30588236 0.70980394 0.6039216 ][0.25490198 0.1254902 0.5568628 ... 0.01176471 0.30588236 0.5372549 ][0.6509804 0.882353 0.03529412 ... 0.29411766 0.86274517 0.6784314 ]...[0.74509805 0.5254902 0.21960786 ... 0.67058825 0.8352942 0.5294118 ][0.427451 0.22352943 0.46274513 ... 0.00784314 0.30588236 0.10980393][0.3372549 0.16862746 0.17254902 ... 0.7294118 0.91372555 0.7568628 ]]2. 标准化Normalize
用于对输入图像的归一化,包括三个参数:
Mean :图像每个通道的均值。
Std :图像每个通道的标准差。
is_hwc:bool值,输入图像的格式。
True为(height, width, channel)
False为(channel, height, width)
图像的每个通道下列公式进行调整,其中c代表通道索引:
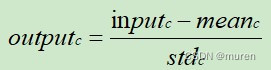
normalize = vision.Normalize(mean=(0.1307,), std=(0.3081,))
normalized_image = normalize(rescaled_image)
print(normalized_image)输出:
[[ 0.8995235 2.286901 0.07218818 ... 0.5685893 1.8795974 1.5359352 ][ 0.40312228 -0.01690946 1.3831964 ... -0.38602826 0.5685893 1.3195552 ][ 1.688674 2.4396398 -0.30965886 ... 0.5304046 2.3759987 1.7777716 ]...[ 1.9941516 1.2813705 0.28856817 ... 1.7523152 2.286901 1.2940987 ][ 0.9631647 0.3012964 1.0777187 ... -0.3987565 0.5685893 -0.06782239][ 0.67041516 0.12310111 0.13582934 ... 1.9432386 2.5414658 2.0323365 ]]3. 格式转换HWC2CHW
MindSpore设置HWC为默认图像格式。
不同设备会对(height, width, channel)或(channel, height, width)两种格式针对性优化。
将上例的normalized_image处理为HWC格式,再转换为CHW。
hwc_image = np.expand_dims(normalized_image, -1)
hwc2chw = vision.HWC2CHW()
chw_image = hwc2chw(hwc_image)
print(hwc_image.shape, chw_image.shape)输出:
(48, 48, 1) (1, 48, 48)五、文本变换Text Transforms
mindspore.dataset.text模块提供文本数据变换。
包括分词(Tokenize)、构建词表、Token转Index等操作。
示例:
1. 准备数据
定义三段文本,使用GeneratorDataset加载。
texts = ['Welcome to Beijing']
test_dataset = GeneratorDataset(texts, 'text')2. 分词
MindSpore提供多种分词器,此处选用PythonTokenizer,可以自由实现分词策略。
用map注册分词操作。
def my_tokenizer(content):return content.split()test_dataset = test_dataset.map(text.PythonTokenizer(my_tokenizer))
print(next(test_dataset.create_tuple_iterator()))输出:
[Tensor(shape=[3], dtype=String, value= ['Welcome', 'to', 'Beijing'])]3. 词表映射变换Lookup
为每个分词建立索引。
使用Vocab生成词表,用vocab方法查看词表。
vocab = text.Vocab.from_dataset(test_dataset)
print(vocab.vocab())输出:
{'to': 2, 'Welcome': 1, 'Beijing': 0}配合map方法进行词表映射变换,为分词建立索引。
test_dataset = test_dataset.map(text.Lookup(vocab))
print(next(test_dataset.create_tuple_iterator()))输出:
[Tensor(shape=[3], dtype=Int32, value= [1, 2, 0])]六、匿名函数变换Lambda Transforms
Lambda是匿名函数。
Lambda Transforms加载自定义Lambda函数。
下例的Lambda函数实现对输入数据乘2。
test_dataset = GeneratorDataset([1, 2, 3], 'data', shuffle=False)
test_dataset = test_dataset.map(lambda x: x * 2)
print(list(test_dataset.create_tuple_iterator()))输出:
[[Tensor(shape=[], dtype=Int64, value= 6)], [Tensor(shape=[], dtype=Int64, value= 18)], [Tensor(shape=[], dtype=Int64, value= 38)]]