目录
1 描述
2 结构体
2.1 net_device
2.2 sk_buff
2.3 net_device_ops
2.4 ethtool_ops
3 相关函数
3.1 网络协议接口层
3.1.1 dev_queue_xmit
3.1.2 netif_rx
3.1.3 alloc_skb
3.1.4 kfree_skb
3.1.5 skb_put
3.1.6 skb_push
3.1.7 skb_reserve
3.2 网络设备驱动的注册与注销
3.2.1 register_netdev
3.2.2 unregister_netdev
3.2.3 alloc_netdev
3.2.3 free_netdev
3.3 网络设备的打开与释放
3.3.1 netif_start_queue
3.3.2 netif_stop_queue
3.3.3 模板
3.4 网络连接状态
3.4.1 netif_carrier_on
3.4.2 netif_carrier_off
3.4.3 netif_carrier_ok
3.4.4 模板
4 dm9000驱动解读
1 描述
与字符设备和块设备不同,网络设备并不对应于/dev目录下的文件,应用程序最终使用套接字完成与网络设备的接口。因而在网络设备身上并不能体现出“一切都是文件”的思想。
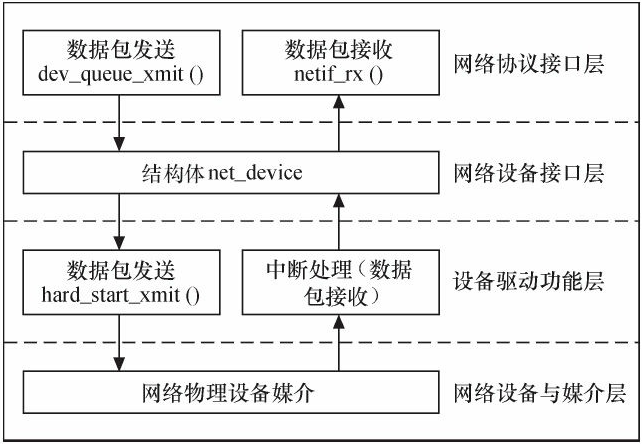
Linux网络设备驱动程序的体系结构如图所示,从上到下可以划分为4层,依次为网络协议接口层、网络设备接口层、提供实际功能的设备驱动功能层以及网络设备与媒介层,这4层的作用如下所示。
1)网络协议接口层向网络层协议提供统一的数据包收发接口,不论上层协议是ARP,还是IP,都通过dev_queue_xmit()函数发送数据,并通过netif_rx()函数接收数据。这一层的存在使得上层协议独立于具体的设备。
2)网络设备接口层向协议接口层提供统一的用于描述具体网络设备属性和操作的结构体net_device,该结构体是设备驱动功能层中各函数的容器。实际上,网络设备接口层从宏观上规划了具体操作硬件的设备驱动功能层的结构。
3)设备驱动功能层的各函数是网络设备接口层net_device数据结构的具体成员,是驱使网络设备硬件完成相应动作的程序,它通过hard_start_xmit()函数启动发送操作,并通过网络设备上的中断触发接收操作。
4)网络设备与媒介层是完成数据包发送和接收的物理实体,包括网络适配器和具体的传输媒介,网络适配器被设备驱动功能层中的函数在物理上驱动。对于Linux系统而言,网络设备和媒介都可以是虚拟的。
2 结构体
2.1 net_device
1784 struct net_device {
1785 char name[IFNAMSIZ];
1786 struct hlist_node name_hlist;
1787 struct dev_ifalias __rcu *ifalias;
1788 /*
1789 * I/O specific fields
1790 * FIXME: Merge these and struct ifmap into one
1791 */
1792 unsigned long mem_end;
1793 unsigned long mem_start;
1794 unsigned long base_addr;
1795 int irq;
1796
1797 /*
1798 * Some hardware also needs these fields (state,dev_list,
1799 * napi_list,unreg_list,close_list) but they are not
1800 * part of the usual set specified in Space.c.
1801 */
1802
1803 unsigned long state;
1804
1805 struct list_head dev_list;
1806 struct list_head napi_list;
1807 struct list_head unreg_list;
1808 struct list_head close_list;
1809 struct list_head ptype_all;
1810 struct list_head ptype_specific;
1811
1812 struct {
1813 struct list_head upper;
1814 struct list_head lower;
1815 } adj_list;
1816
1817 netdev_features_t features;
1818 netdev_features_t hw_features;
1819 netdev_features_t wanted_features;
1820 netdev_features_t vlan_features;
1821 netdev_features_t hw_enc_features;
1822 netdev_features_t mpls_features;
1823 netdev_features_t gso_partial_features;
1824
1825 int ifindex;
1826 int group;
1827
1828 struct net_device_stats stats;
1829
1830 atomic_long_t rx_dropped;
1831 atomic_long_t tx_dropped;
1832 atomic_long_t rx_nohandler;
1833
1834 /* Stats to monitor link on/off, flapping */
1835 atomic_t carrier_up_count;
1836 atomic_t carrier_down_count;
1837
1838 #ifdef CONFIG_WIRELESS_EXT
1839 const struct iw_handler_def *wireless_handlers;
1840 struct iw_public_data *wireless_data;
1841 #endif
1842 const struct net_device_ops *netdev_ops;
1843 const struct ethtool_ops *ethtool_ops;
1844 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_SWITCHDEV
1845 const struct switchdev_ops *switchdev_ops;
1846 #endif
1847 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_L3_MASTER_DEV
1848 const struct l3mdev_ops *l3mdev_ops;
1849 #endif
1850 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_IPV6)
1851 const struct ndisc_ops *ndisc_ops;
1852 #endif
1853
1854 #ifdef CONFIG_XFRM_OFFLOAD
1855 const struct xfrmdev_ops *xfrmdev_ops;
1856 #endif
1857
1858 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_TLS_DEVICE)
1859 const struct tlsdev_ops *tlsdev_ops;
1860 #endif
1861
1862 const struct header_ops *header_ops;
1863
1864 unsigned int flags;
1865 unsigned int priv_flags;
1866
1867 unsigned short gflags;
1868 unsigned short padded;
1869
1870 unsigned char operstate;
1871 unsigned char link_mode;
1872
1873 unsigned char if_port;
1874 unsigned char dma;
1875
1876 /* Note : dev->mtu is often read without holding a lock.
1877 * Writers usually hold RTNL.
1878 * It is recommended to use READ_ONCE() to annotate the reads,
1879 * and to use WRITE_ONCE() to annotate the writes.
1880 */
1881 unsigned int mtu;
1882 unsigned int min_mtu;
1883 unsigned int max_mtu;
1884 unsigned short type;
1885 unsigned short hard_header_len;
1886 unsigned char min_header_len;
1887
1888 unsigned short needed_headroom;
1889 unsigned short needed_tailroom;
1890
1891 /* Interface address info. */
1892 unsigned char perm_addr[MAX_ADDR_LEN];
1893 unsigned char addr_assign_type;
1894 unsigned char addr_len;
1895 unsigned char upper_level;
1896 unsigned char lower_level;
1897 unsigned short neigh_priv_len;
1898 unsigned short dev_id;
1899 unsigned short dev_port;
1900 spinlock_t addr_list_lock;
1901 unsigned char name_assign_type;
1902 bool uc_promisc;
1903 struct netdev_hw_addr_list uc;
1904 struct netdev_hw_addr_list mc;
1905 struct netdev_hw_addr_list dev_addrs;
1906
1907 #ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS
1908 struct kset *queues_kset;
1909 #endif
1910 unsigned int promiscuity;
1911 unsigned int allmulti;
1912
1913
1914 /* Protocol-specific pointers */
1915
1916 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_VLAN_8021Q)
1917 struct vlan_info __rcu *vlan_info;
1918 #endif
1919 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_NET_DSA)
1920 struct dsa_port *dsa_ptr;
1921 #endif
1922 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_TIPC)
1923 struct tipc_bearer __rcu *tipc_ptr;
1924 #endif
1925 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_IRDA) || IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_ATALK)
1926 void *atalk_ptr;
1927 #endif
1928 struct in_device __rcu *ip_ptr;
1929 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_DECNET)
1930 struct dn_dev __rcu *dn_ptr;
1931 #endif
1932 struct inet6_dev __rcu *ip6_ptr;
1933 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_AX25)
1934 void *ax25_ptr;
1935 #endif
1936 struct wireless_dev *ieee80211_ptr;
1937 struct wpan_dev *ieee802154_ptr;
1938 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MPLS_ROUTING)
1939 struct mpls_dev __rcu *mpls_ptr;
1940 #endif
1941
1942 /*
1943 * Cache lines mostly used on receive path (including eth_type_trans())
1944 */
1945 /* Interface address info used in eth_type_trans() */
1946 unsigned char *dev_addr;
1947
1948 struct netdev_rx_queue *_rx;
1949 unsigned int num_rx_queues;
1950 unsigned int real_num_rx_queues;
1951
1952 struct bpf_prog __rcu *xdp_prog;
1953 unsigned long gro_flush_timeout;
1954 rx_handler_func_t __rcu *rx_handler;
1955 void __rcu *rx_handler_data;
1956
1957 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT
1958 struct mini_Qdisc __rcu *miniq_ingress;
1959 #endif
1960 struct netdev_queue __rcu *ingress_queue;
1961 #ifdef CONFIG_NETFILTER_INGRESS
1962 struct nf_hook_entries __rcu *nf_hooks_ingress
1962 struct nf_hook_entries __rcu *nf_hooks_ingress;
1963 #endif
1964
1965 unsigned char broadcast[MAX_ADDR_LEN];
1966 #ifdef CONFIG_RFS_ACCEL
1967 struct cpu_rmap *rx_cpu_rmap;
1968 #endif
1969 struct hlist_node index_hlist;
1970
1971 /*
1972 * Cache lines mostly used on transmit path
1973 */
1974 struct netdev_queue *_tx ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
1975 unsigned int num_tx_queues;
1976 unsigned int real_num_tx_queues;
1977 struct Qdisc *qdisc;
1978 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED
1979 DECLARE_HASHTABLE (qdisc_hash, 4);
1980 #endif
1981 unsigned int tx_queue_len;
1982 spinlock_t tx_global_lock;
1983 int watchdog_timeo;
1984
1985 #ifdef CONFIG_XPS
1986 struct xps_dev_maps __rcu *xps_cpus_map;
1987 struct xps_dev_maps __rcu *xps_rxqs_map;
1988 #endif
1989 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT
1990 struct mini_Qdisc __rcu *miniq_egress;
1991 #endif
1992
1993 /* These may be needed for future network-power-down code. */
1994 struct timer_list watchdog_timer;
1995
1996 int __percpu *pcpu_refcnt;
1997 struct list_head todo_list;
1998
1999 struct list_head link_watch_list;
2000
2001 enum { NETREG_UNINITIALIZED=0,
2002 NETREG_REGISTERED, /* completed register_netdevice */
2003 NETREG_UNREGISTERING, /* called unregister_netdevice */
2004 NETREG_UNREGISTERED, /* completed unregister todo */
2005 NETREG_RELEASED, /* called free_netdev */
2006 NETREG_DUMMY, /* dummy device for NAPI poll */
2007 } reg_state:8;
2008
2009 bool dismantle;
2010
2011 enum {
2012 RTNL_LINK_INITIALIZED,
2013 RTNL_LINK_INITIALIZING,
2014 } rtnl_link_state:16;
2015
2016 bool needs_free_netdev;
2017 void (*priv_destructor)(struct net_device *dev);
2018
2019 #ifdef CONFIG_NETPOLL
2020 struct netpoll_info __rcu *npinfo;
2021 #endif
2022
2023 possible_net_t nd_net;
2024
2025 /* mid-layer private */
2026 union {
2027 void *ml_priv;
2028 struct pcpu_lstats __percpu *lstats;
2029 struct pcpu_sw_netstats __percpu *tstats;
2030 struct pcpu_dstats __percpu *dstats;
2031 struct pcpu_vstats __percpu *vstats;
2032 };
2033
2034 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_GARP)
2035 struct garp_port __rcu *garp_port;
2036 #endif
2037 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MRP)
2038 struct mrp_port __rcu *mrp_port;
2039 #endif
2040
2041 struct device dev;
2042 const struct attribute_group *sysfs_groups[4];
2043 const struct attribute_group *sysfs_rx_queue_group;
2044
2045 const struct rtnl_link_ops *rtnl_link_ops;
2046
2047 /* for setting kernel sock attribute on TCP connection setup */
2048 #define GSO_MAX_SIZE 65536
2049 unsigned int gso_max_size;
2050 #define GSO_MAX_SEGS 65535
2051 u16 gso_max_segs;
2052
2053 #ifdef CONFIG_DCB
2054 const struct dcbnl_rtnl_ops *dcbnl_ops;
2055 #endif
2056 s16 num_tc;
2057 struct netdev_tc_txq tc_to_txq[TC_MAX_QUEUE];
2058 u8 prio_tc_map[TC_BITMASK + 1];
2059
2060 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_FCOE)
2061 unsigned int fcoe_ddp_xid;
2062 #endif
2063 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_CGROUP_NET_PRIO)
2064 struct netprio_map __rcu *priomap;
2065 #endif
2066 struct phy_device *phydev;
2067 struct sfp_bus *sfp_bus;
2068 struct lock_class_key *qdisc_tx_busylock;
2069 struct lock_class_key *qdisc_running_key;
2070 bool proto_down;
2071 unsigned wol_enabled:1;
2072
2073 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(1);
2074 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(2);
2075 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(3);
2076 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(4);
2077 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(5);
2078 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(6);
2079 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(7);
2080 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(8);
2081
2082 };2.2 sk_buff
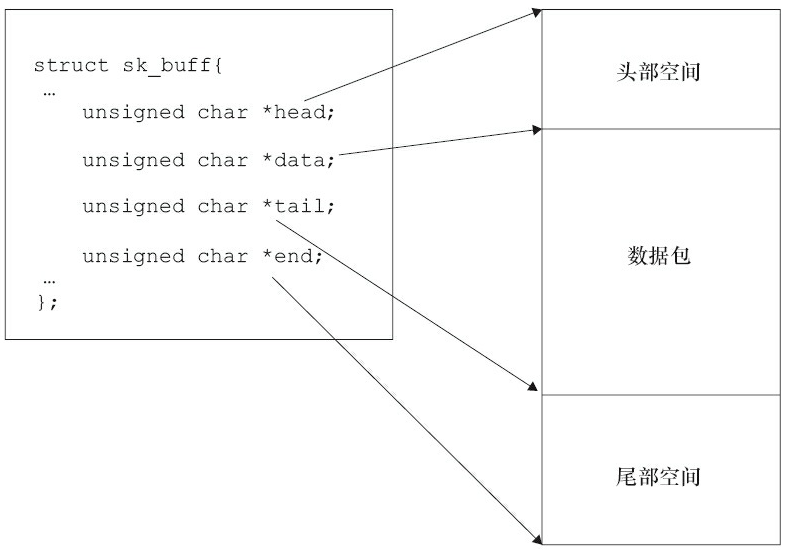
sk_buff结构体非常重要,它定义于include/linux/skbuff.h文件中,含义为“套接字缓冲区”,用于在Linux网络子系统中的各层之间传递数据,是Linux网络子系统数据传递的“中枢神经”。当发送数据包时,Linux内核的网络处理模块必须建立一个包含要传输的数据包的sk_buff,然后将sk_buff递交给下层,各层在sk_buff中添加不同的协议头直至交给网络设备发送。同样地,当网络设备从网络媒介上接收到数据包后,它必须将接收到的数据转换为sk_buff数据结构并传递给上层,各层剥去相应的协议头直至交给用户。
40 struct sk_buff {
241 /* These two members must be first. */
242 struct sk_buff *next;
243 struct sk_buff *prev;
244
245 ktime_t tstamp;
246
247 struct sock *sk;
248 //struct net_device *dev;
249 struct ifnet *dev;
250
251 /*
252 * This is the control buffer. It is free to use for every
253 * layer. Please put your private variables there. If you
254 * want to keep them across layers you have to do a skb_clone()
255 * first. This is owned by whoever has the skb queued ATM.
256 */
257 char cb[48] __aligned(8);
258
259 unsigned long _skb_refdst;
260 #ifdef CONFIG_XFRM
261 struct sec_path *sp;
262 #endif
263 unsigned int len,
264 data_len;
265 u16 mac_len,
266 hdr_len;
267 union {
268 u32 csum;
269 struct {
270 u16 csum_start;
271 u16 csum_offset;
272 }smbol2;
273 }smbol1;
274 u32 priority;
275 kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags1);
276 u8 local_df:1,
277 cloned:1,
278 ip_summed:2,
279 nohdr:1,
280 nfctinfo:3;
281 u8 pkt_type:3,
282 fclone:2,
283 ipvs_property:1,
284 peeked:1,
285 nf_trace:1;
286 kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags1);
287 u16 protocol;
288
289 void (*destructor)(struct sk_buff *skb);
290 #if defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK) || defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK_MODULE)
291 struct nf_conntrack *nfct;
292 struct sk_buff *nfct_reasm;
293 #endif
294 #ifdef CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER
295 struct nf_bridge_info *nf_bridge;
296 #endif
297
298 int skb_iif;
299 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED
300 u16 tc_index; /* traffic control index */
301 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT
302 u16 tc_verd; /* traffic control verdict */
303 #endif
304 #endif
305
306 u32 rxhash;
307
308 kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags2);
309 u16 queue_mapping:16;
310 #ifdef CONFIG_IPV6_NDISC_NODETYPE
311 u8 ndisc_nodetype:2,
312 deliver_no_wcard:1;
313 #else
314 u8 deliver_no_wcard:1;
315 #endif
316 kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags2);
317
318 /* 0/14 bit hole */
319
320 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_DMA
321 dma_cookie_t dma_cookie;
322 #endif
323 #ifdef CONFIG_NETWORK_SECMARK
324 u32 secmark;
325 #endif
326 union {
327 u32 mark;
328 u32 dropcount;
329 }symbol3;
330
331 u16 vlan_tci;
332
333 sk_buff_data_t transport_header;
334 sk_buff_data_t network_header;
335 sk_buff_data_t mac_header;
336 /* These elements must be at the end, see alloc_skb() for details. */
337 sk_buff_data_t tail;
338 sk_buff_data_t end;
339 unsigned char *head,
340 *data;
341 unsigned int truesize;
342 atomic_t users;
343 };
344 struct sk_buff_head {
345 /* These two members must be first. */
346 struct sk_buff *next;
347 struct sk_buff *prev;
348
349 u32 qlen;
350 _lock lock;
351 };尤其值得注意的是head和end指向缓冲区的头部和尾部,而data和tail指向实际数据的头部和尾部。每一层会在head和data之间填充协议头,或者在tail和end之间添加新的协议数据。
2.3 net_device_ops
struct net_device_ops 是 Linux 内核中用于网络设备驱动程序的一个重要结构体,它定义了一组函数指针,这些函数用于处理网络设备的操作和事件。这些操作包括数据包的发送和接收、设备的启动和停止、以及其他与网络设备管理相关的功能。
1253 struct net_device_ops {
1254 int (*ndo_init)(struct net_device *dev);
1255 void (*ndo_uninit)(struct net_device *dev);
1256 int (*ndo_open)(struct net_device *dev);
1257 int (*ndo_stop)(struct net_device *dev);
1258 netdev_tx_t (*ndo_start_xmit)(struct sk_buff *skb,
1259 struct net_device *dev);
1260 netdev_features_t (*ndo_features_check)(struct sk_buff *skb,
1261 struct net_device *dev,
1262 netdev_features_t features);
1263 u16 (*ndo_select_queue)(struct net_device *dev,
1264 struct sk_buff *skb,
1265 struct net_device *sb_dev,
1266 select_queue_fallback_t fallback);
1267 void (*ndo_change_rx_flags)(struct net_device *dev,
1268 int flags);
1269 void (*ndo_set_rx_mode)(struct net_device *dev);
1270 int (*ndo_set_mac_address)(struct net_device *dev,
1271 void *addr);
1272 int (*ndo_validate_addr)(struct net_device *dev);
1273 int (*ndo_do_ioctl)(struct net_device *dev,
1274 struct ifreq *ifr, int cmd);
1275 int (*ndo_set_config)(struct net_device *dev,
1276 struct ifmap *map);
1277 int (*ndo_change_mtu)(struct net_device *dev,
1278 int new_mtu);
1279 int (*ndo_neigh_setup)(struct net_device *dev,
1280 struct neigh_parms *);
1281 void (*ndo_tx_timeout) (struct net_device *dev);
1282
1283 void (*ndo_get_stats64)(struct net_device *dev,
1284 struct rtnl_link_stats64 *storage);
1285 bool (*ndo_has_offload_stats)(const struct net_device *dev, int attr_id);
1286 int (*ndo_get_offload_stats)(int attr_id,
1287 const struct net_device *dev,
1288 void *attr_data);
1289 struct net_device_stats* (*ndo_get_stats)(struct net_device *dev);
1290
1291 int (*ndo_vlan_rx_add_vid)(struct net_device *dev,
1292 __be16 proto, u16 vid);
1293 int (*ndo_vlan_rx_kill_vid)(struct net_device *dev,
1294 __be16 proto, u16 vid);
1295 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_POLL_CONTROLLER
1296 void (*ndo_poll_controller)(struct net_device *dev);
1297 int (*ndo_netpoll_setup)(struct net_device *dev,
1298 struct netpoll_info *info);
1299 void (*ndo_netpoll_cleanup)(struct net_device *dev);
1300 #endif
1301 int (*ndo_set_vf_mac)(struct net_device *dev,
1302 int queue, u8 *mac);
1303 int (*ndo_set_vf_vlan)(struct net_device *dev,
1304 int queue, u16 vlan,
1305 u8 qos, __be16 proto);
1306 int (*ndo_set_vf_rate)(struct net_device *dev,
1307 int vf, int min_tx_rate,
1308 int max_tx_rate);
1309 int (*ndo_set_vf_spoofchk)(struct net_device *dev,
1310 int vf, bool setting);
1311 int (*ndo_set_vf_trust)(struct net_device *dev,
1312 int vf, bool setting);
1313 int (*ndo_get_vf_config)(struct net_device *dev,
1314 int vf,
1315 struct ifla_vf_info *ivf);
1316 int (*ndo_set_vf_link_state)(struct net_device *dev,
1317 int vf, int link_state);
1318 int (*ndo_get_vf_stats)(struct net_device *dev,
1319 int vf,
1320 struct ifla_vf_stats
1321 *vf_stats);
1322 int (*ndo_set_vf_port)(struct net_device *dev,
1323 int vf,
1324 struct nlattr *port[]);
1325 int (*ndo_get_vf_port)(struct net_device *dev,
1326 int vf, struct sk_buff *skb);
1327 int (*ndo_set_vf_guid)(struct net_device *dev,
1328 int vf, u64 guid,
1329 int guid_type);
1330 int (*ndo_set_vf_rss_query_en)(
1331 struct net_device *dev,
1332 int vf, bool setting);
1333 int (*ndo_setup_tc)(struct net_device *dev,
1334 enum tc_setup_type type,
1335 void *type_data);
1336 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_FCOE)
1337 int (*ndo_fcoe_enable)(struct net_device *dev);
1338 int (*ndo_fcoe_disable)(struct net_device *dev);
1339 int (*ndo_fcoe_ddp_setup)(struct net_device *dev,
1340 u16 xid,
1341 struct scatterlist *sgl,
1342 unsigned int sgc);
1343 int (*ndo_fcoe_ddp_done)(struct net_device *dev,
1344 u16 xid);
1345 int (*ndo_fcoe_ddp_target)(struct net_device *dev,
1346 u16 xid,
1347 struct scatterlist *sgl,
1348 unsigned int sgc);
1349 int (*ndo_fcoe_get_hbainfo)(struct net_device *dev,
1350 struct netdev_fcoe_hbainfo *hbainfo);
1351 #endif
1352
1353 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_LIBFCOE)
1354 #define NETDEV_FCOE_WWNN 0
1355 #define NETDEV_FCOE_WWPN 1
1356 int (*ndo_fcoe_get_wwn)(struct net_device *dev,
1357 u64 *wwn, int type);
1358 #endif
1359
1360 #ifdef CONFIG_RFS_ACCEL
1361 int (*ndo_rx_flow_steer)(struct net_device *dev,
1362 const struct sk_buff *skb,
1363 u16 rxq_index,
1364 u32 flow_id);
1365 #endif
1366 int (*ndo_add_slave)(struct net_device *dev,
1367 struct net_device *slave_dev,
1368 struct netlink_ext_ack *extack);
1369 int (*ndo_del_slave)(struct net_device *dev,
1370 struct net_device *slave_dev);
1371 netdev_features_t (*ndo_fix_features)(struct net_device *dev,
1372 netdev_features_t features);
1373 int (*ndo_set_features)(struct net_device *dev,
1374 netdev_features_t features);
1375 int (*ndo_neigh_construct)(struct net_device *dev,
1376 struct neighbour *n);
1377 void (*ndo_neigh_destroy)(struct net_device *dev,
1378 struct neighbour *n);
1379
1380 int (*ndo_fdb_add)(struct ndmsg *ndm,
1381 struct nlattr *tb[],
1382 struct net_device *dev,
1383 const unsigned char *addr,
1384 u16 vid,
1385 u16 flags);
1386 int (*ndo_fdb_del)(struct ndmsg *ndm,
1387 struct nlattr *tb[],
1388 struct net_device *dev,
1389 const unsigned char *addr,
1390 u16 vid);
1391 int (*ndo_fdb_dump)(struct sk_buff *skb,
1392 struct netlink_callback *cb,
1393 struct net_device *dev,
1394 struct net_device *filter_dev,
1395 int *idx);
1396
1397 int (*ndo_bridge_setlink)(struct net_device *dev,
1398 struct nlmsghdr *nlh,
1399 u16 flags);
1400 int (*ndo_bridge_getlink)(struct sk_buff *skb,
1401 u32 pid, u32 seq,
1402 struct net_device *dev,
1403 u32 filter_mask,
1404 int nlflags);
1405 int (*ndo_bridge_dellink)(struct net_device *dev,
1406 struct nlmsghdr *nlh,
1407 u16 flags);
1408 int (*ndo_change_carrier)(struct net_device *dev,
1409 bool new_carrier);
1410 int (*ndo_get_phys_port_id)(struct net_device *dev,
1411 struct netdev_phys_item_id *ppid);
1412 int (*ndo_get_phys_port_name)(struct net_device *dev,
1413 char *name, size_t len);
1414 void (*ndo_udp_tunnel_add)(struct net_device *dev,
1415 struct udp_tunnel_info *ti);
1416 void (*ndo_udp_tunnel_del)(struct net_device *dev,
1417 struct udp_tunnel_info *ti);
1418 void* (*ndo_dfwd_add_station)(struct net_device *pdev,
1419 struct net_device *dev);
1420 void (*ndo_dfwd_del_station)(struct net_device *pdev,
1421 void *priv);
1422
1423 int (*ndo_get_lock_subclass)(struct net_device *dev);
1424 int (*ndo_set_tx_maxrate)(struct net_device *dev,
1425 int queue_index,
1426 u32 maxrate);
1427 int (*ndo_get_iflink)(const struct net_device *dev);
1428 int (*ndo_change_proto_down)(struct net_device *dev,
1429 bool proto_down);
1430 int (*ndo_fill_metadata_dst)(struct net_device *dev,
1431 struct sk_buff *skb);
1432 void (*ndo_set_rx_headroom)(struct net_device *dev,
1433 int needed_headroom);
1434 int (*ndo_bpf)(struct net_device *dev,
1435 struct netdev_bpf *bpf);
1436 int (*ndo_xdp_xmit)(struct net_device *dev, int n,
1437 struct xdp_frame **xdp,
1438 u32 flags);
1439 int (*ndo_xsk_async_xmit)(struct net_device *dev,
1440 u32 queue_id);
1441
1442 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(1);
1443 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(2);
1444 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(3);
1445 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(4);
1446 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(5);
1447 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(6);
1448 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(7);
1449 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(8);
1450 };2.4 ethtool_ops
struct ethtool_ops 是 Linux 内核中用于网络设备驱动程序的一个结构体,定义了一组与以太网设备交互的操作。这些操作允许用户空间工具(如 ethtool)获取和设置网络设备的状态、配置和统计信息。常用的操作包括获取连接状态、驱动信息、设备设置、以及自协商的重置。通过实现这些操作,驱动程序可以提供详细的设备信息和管理功能,使得设备的使用和调试更加方便。
360 struct ethtool_ops {
361 int (*get_settings)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_cmd *);
362 int (*set_settings)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_cmd *);
363 void (*get_drvinfo)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_drvinfo *);
364 int (*get_regs_len)(struct net_device *);
365 void (*get_regs)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_regs *, void *);
366 void (*get_wol)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_wolinfo *);
367 int (*set_wol)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_wolinfo *);
368 u32 (*get_msglevel)(struct net_device *);
369 void (*set_msglevel)(struct net_device *, u32);
370 int (*nway_reset)(struct net_device *);
371 u32 (*get_link)(struct net_device *);
372 int (*get_eeprom_len)(struct net_device *);
373 int (*get_eeprom)(struct net_device *,
374 struct ethtool_eeprom *, u8 *);
375 int (*set_eeprom)(struct net_device *,
376 struct ethtool_eeprom *, u8 *);
377 int (*get_coalesce)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_coalesce *);
378 int (*set_coalesce)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_coalesce *);
379 void (*get_ringparam)(struct net_device *,
380 struct ethtool_ringparam *);
381 int (*set_ringparam)(struct net_device *,
382 struct ethtool_ringparam *);
383 void (*get_pauseparam)(struct net_device *,
384 struct ethtool_pauseparam*);
385 int (*set_pauseparam)(struct net_device *,
386 struct ethtool_pauseparam*);
387 void (*self_test)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_test *, u64 *);
388 void (*get_strings)(struct net_device *, u32 stringset, u8 *);
389 int (*set_phys_id)(struct net_device *, enum ethtool_phys_id_state);
390 void (*get_ethtool_stats)(struct net_device *,
391 struct ethtool_stats *, u64 *);
392 int (*begin)(struct net_device *);
393 void (*complete)(struct net_device *);
394 u32 (*get_priv_flags)(struct net_device *);
395 int (*set_priv_flags)(struct net_device *, u32);
396 int (*get_sset_count)(struct net_device *, int);
397 int (*get_rxnfc)(struct net_device *,
398 struct ethtool_rxnfc *, u32 *rule_locs);
399 int (*set_rxnfc)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_rxnfc *);
400 int (*flash_device)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_flash *);
401 int (*reset)(struct net_device *, u32 *);
402 u32 (*get_rxfh_key_size)(struct net_device *);
403 u32 (*get_rxfh_indir_size)(struct net_device *);
404 int (*get_rxfh)(struct net_device *, u32 *indir, u8 *key,
405 u8 *hfunc);
406 int (*set_rxfh)(struct net_device *, const u32 *indir,
407 const u8 *key, const u8 hfunc);
408 int (*get_rxfh_context)(struct net_device *, u32 *indir, u8 *key,
409 u8 *hfunc, u32 rss_context);
410 int (*set_rxfh_context)(struct net_device *, const u32 *indir,
411 const u8 *key, const u8 hfunc,
412 u32 *rss_context, bool delete);
413 void (*get_channels)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_channels *);
414 int (*set_channels)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_channels *);
415 int (*get_dump_flag)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_dump *);
416 int (*get_dump_data)(struct net_device *,
417 struct ethtool_dump *, void *);
418 int (*set_dump)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_dump *);
419 int (*get_ts_info)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_ts_info *);
420 int (*get_module_info)(struct net_device *,
421 struct ethtool_modinfo *);
422 int (*get_module_eeprom)(struct net_device *,
423 struct ethtool_eeprom *, u8 *);
424 int (*get_eee)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_eee *);
425 int (*set_eee)(struct net_device *, struct ethtool_eee *);
426 int (*get_tunable)(struct net_device *,
427 const struct ethtool_tunable *, void *);
428 int (*set_tunable)(struct net_device *,
429 const struct ethtool_tunable *, const void *);
430 int (*get_per_queue_coalesce)(struct net_device *, u32,
431 struct ethtool_coalesce *);
432 int (*set_per_queue_coalesce)(struct net_device *, u32,
433 struct ethtool_coalesce *);
434 int (*get_link_ksettings)(struct net_device *,
435 struct ethtool_link_ksettings *);
436 int (*set_link_ksettings)(struct net_device *,
437 const struct ethtool_link_ksettings *);
438 int (*get_fecparam)(struct net_device *,
439 struct ethtool_fecparam *);
440 int (*set_fecparam)(struct net_device *,
441 struct ethtool_fecparam *);
442 void (*get_ethtool_phy_stats)(struct net_device *,
443 struct ethtool_stats *, u64 *);
444
445 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(1);
446 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(2);
447 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(3);
448 ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(4);
449 };3 相关函数
3.1 网络协议接口层
3.1.1 dev_queue_xmit
| 函数原型 | int dev_queue_xmit(struct sk_buff *skb) | |
| 参数 | struct sk_buff *skb | 指向一个 sk_buff 结构的指针,包含了要发送的数据包和相关的元数据,如源地址、目标地址、协议类型等。 |
| 返回值 | int | 成功:0 失败:负数 |
| 功能 | Linux 内核中用于发送网络数据包的函数,主要用于将数据包排入网络设备的发送队列 | |
当发送数据包时,Linux内核的网络处理模块必须建立一个包含要传输的数据包的sk_buff,然后将sk_buff递交给下层,各层在sk_buff中添加不同的协议头直至交给网络设备发送
3878 int dev_queue_xmit(struct sk_buff *skb)
3879 {
3880 return __dev_queue_xmit(skb, NULL);
3881 } 3.1.2 netif_rx
| 函数原型 | int netif_rx(struct sk_buff *skb) | |
| 参数 | struct sk_buff *skb | 指向一个 sk_buff 结构的指针,包含了要发送的数据包和相关的元数据,如源地址、目标地址、协议类型等。 |
| 返回值 | int | 成功:0 失败:负数 |
| 功能 | Linux 内核中用于接收网络数据包的函数。它主要负责将接收到的数据包传递到网络协议栈的进一步处理 | |
当网络设备从网络媒介上接收到数据包后,它必须将接收到的数据转换为sk_buff数据结构并传递给上层,各层剥去相应的协议头直至交给用户
4521 int netif_rx(struct sk_buff *skb)
4522 {
4523 trace_netif_rx_entry(skb);
4524
4525 return netif_rx_internal(skb);
4526 } 4471 static int netif_rx_internal(struct sk_buff *skb)
4472 {
4473 int ret;
4474
4475 net_timestamp_check(netdev_tstamp_prequeue, skb);
4476
4477 trace_netif_rx(skb);
4478
4479 #ifdef CONFIG_RPS
4480 if (static_key_false(&rps_needed)) {
4481 struct rps_dev_flow voidflow, *rflow = &voidflow;
4482 int cpu;
4483
4484 preempt_disable();
4485 rcu_read_lock();
4486
4487 cpu = get_rps_cpu(skb->dev, skb, &rflow);
4488 if (cpu < 0)
4489 cpu = smp_processor_id();
4490
4491 ret = enqueue_to_backlog(skb, cpu, &rflow->last_qtail);
4492
4493 rcu_read_unlock();
4494 preempt_enable();
4495 } else
4496 #endif
4497 {
4498 unsigned int qtail;
4499
4500 ret = enqueue_to_backlog(skb, get_cpu(), &qtail);
4501 put_cpu();
4502 }
4503 return ret;
4504 }3.1.3 alloc_skb
| 函数原型 | struct sk_buff *alloc_skb(unsigned int size, gfp_t priority) | |
| 参数 | unsigned int size | 要分配的缓冲区大小,以字节为单位。这个大小应该足够容纳网络数据包的负载及任何额外的元数据。 |
| gfp_t priority | 分配内存时的优先级标志,控制内存分配的行为。常用的标志包括: GFP_KERNEL: 普通内核上下文中的分配,允许睡眠。 GFP_ATOMIC: 在不可睡眠的上下文中进行分配,通常用于中断上下文。 | |
| 返回值 | struct sk_buff * | 指向分配好的 sk_buff 结构的指针,如果内存分配失败,则返回 NULL。 |
| 功能 | Linux 内核中用于分配网络缓冲区的函数,主要用于创建一个新的 sk_buff(socket buffer)结构,该结构用于存储网络数据包 | |
992 static inline struct sk_buff *alloc_skb(unsigned int size, gfp_t priority)994 { 995 return __alloc_skb(size, priority, 0, NUMA_NO_NODE);996 } 3.1.4 kfree_skb
| 函数原型 | void kfree_skb(struct sk_buff *skb) | |
| 参数 | struct sk_buff *skb | 指向要释放的 sk_buff 结构的指针。 |
| 返回值 | ||
| 功能 | Linux 内核中用于释放 sk_buff(socket buffer)结构的函数。该函数主要用于在不再需要网络缓冲区时,释放与之相关联的内存,以避免内存泄漏。 | |
666 void kfree_skb(struct sk_buff *skb)667 { 668 if (!skb_unref(skb))669 return;670 671 trace_kfree_skb(skb, __builtin_return_address(0));672 __kfree_skb(skb);673 }3.1.5 skb_put
| 函数原型 | void *skb_put(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len) | |
| 参数 | struct sk_buff *skb | 指向要操作的 sk_buff 结构的指针。 |
| unsigned int len | 要添加的数据的长度,以字节为单位。 | |
| 返回值 | ||
| 功能 | Linux 内核中用于在 sk_buff(socket buffer)结构中添加数据的函数。它主要用于调整 sk_buff 的数据指针和长度,以便存放新的数据 | |
1704 void *skb_put(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len)
1705 {
1706 void *tmp = skb_tail_pointer(skb);
1707 SKB_LINEAR_ASSERT(skb);
1708 skb->tail += len;
1709 skb->len += len;
1710 if (unlikely(skb->tail > skb->end))
1711 skb_over_panic(skb, len, __builtin_return_address(0));
1712 return tmp;
1713 }3.1.6 skb_push
| 函数原型 | void *skb_push(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len) | |
| 参数 | struct sk_buff *skb | 指向要操作的 sk_buff 结构的指针。 |
| unsigned int len | 要添加的数据的长度,以字节为单位。 | |
| 返回值 | ||
| 功能 | skb_push 是 Linux 内核中用于在 sk_buff(socket buffer)结构的前面添加数据的函数。它主要用于调整 sk_buff 的数据指针,以便在数据包的前面插入新的数据 | |
1725 void *skb_push(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len)
1726 {
1727 skb->data -= len;
1728 skb->len += len;
1729 if (unlikely(skb->data < skb->head))
1730 skb_under_panic(skb, len, __builtin_return_address(0));
1731 return skb->data;
1732 } 3.1.7 skb_reserve
| 函数原型 | void skb_reserve(struct sk_buff *skb, int len) | |
| 参数 | struct sk_buff *skb | 指向要操作的 sk_buff 结构的指针。 |
| unsigned int len | 要添加的数据的长度,以字节为单位。 | |
| 返回值 | ||
| 功能 | Linux 内核中用于在 sk_buff(socket buffer)结构的开头保留一定字节数的函数。它主要用于为将来可能添加的数据预留空间,以避免对已有数据的移动 | |
2233 static inline void skb_reserve(struct sk_buff *skb, int len)
2234 {
2235 skb->data += len;
2236 skb->tail += len;
2237 }3.2 网络设备驱动的注册与注销
3.2.1 register_netdev
| 函数原型 | int register_netdev(struct net_device *dev) | |
| 参数 | struct net_device *dev | 指向要注册的 struct net_device 结构的指针。这个结构包含了网络设备的各种信息,如设备名称、硬件地址、操作函数等 |
| 返回值 | int | 成功:0 失败:负数 |
| 功能 | linux 内核中用于注册网络设备的函数。它将网络设备结构体 (struct net_device) 注册到内核网络子系统,使其能够被系统和应用程序识别和使用。 | |
8879 int register_netdev(struct net_device *dev)
8880 {
8881 int err;
8882
8883 if (rtnl_lock_killable())
8884 return -EINTR;
8885 err = register_netdevice(dev);
8886 rtnl_unlock();
8887 return err;
8888 } 3.2.2 unregister_netdev
| 函数原型 | int unregister_netdev(struct net_device *dev) | |
| 参数 | struct net_device *dev | 指向要注册的 struct net_device 结构的指针。这个结构包含了网络设备的各种信息,如设备名称、硬件地址、操作函数等 |
| 返回值 | int | 成功:0 失败:负数 |
| 功能 | linux 内核中用于注销网络设备的函数 | |
9369 void unregister_netdev(struct net_device *dev)
9370 {
9371 rtnl_lock();
9372 unregister_netdevice(dev);
9373 rtnl_unlock();
9374 } 3.2.3 alloc_netdev
| 函数原型 | struct net_device *alloc_netdev(int sizeof_priv, const char *name,unsigned char name_assign_type,void (*setup)(struct net_device *)); | |
| 参数 | int sizeof_priv | 指定私有数据结构的大小,网络设备通常需要保存特定于设备的信息。 |
| const char *name | 设备名称的格式,例如 "eth%d",表示以 eth 开头,后面跟随一个数字的名称。 | |
| unsigned char name_assign_type | 指定名称分配的类型,常用的值包括动态分配或静态分配。 | |
| void (*setup)(struct net_device *) | 一个指向设置函数的指针,用于进一步配置网络设备。这个函数会在分配完成后被调用 | |
| 返回值 | struct net_device * | 成功时返回一个指向 struct net_device 的指针,失败时返回 NULL。 |
| 功能 | 分配内存: alloc_netdev 会为网络设备分配所需的内存空间。 初始化: 它会初始化网络设备的基本参数,包括设备名称、最大帧大小等。 注册钩子: 此宏通常还会设置一些操作函数的指针,这些函数定义了设备的行为,如发送和接收数据包。 | |
4099 #define alloc_netdev(sizeof_priv, name, name_assign_type, setup) \
4100 alloc_netdev_mqs(sizeof_priv, name, name_assign_type, setup, 1, 1)9148 struct net_device *alloc_netdev_mqs(int sizeof_priv, const char *name,
9149 unsigned char name_assign_type,
9150 void (*setup)(struct net_device *),
9151 unsigned int txqs, unsigned int rxqs)
9152 {
9153 struct net_device *dev;
9154 unsigned int alloc_size;
9155 struct net_device *p;
9156
9157 BUG_ON(strlen(name) >= sizeof(dev->name));
9158
9159 if (txqs < 1) {
9160 pr_err("alloc_netdev: Unable to allocate device with zero queues\n");
9161 return NULL;
9162 }
9163
9164 if (rxqs < 1) {
9165 pr_err("alloc_netdev: Unable to allocate device with zero RX queues\n");
9166 return NULL;
9167 }
9168
9169 alloc_size = sizeof(struct net_device);
9170 if (sizeof_priv) {
9171 /* ensure 32-byte alignment of private area */
9172 alloc_size = ALIGN(alloc_size, NETDEV_ALIGN);
9173 alloc_size += sizeof_priv;
9174 }
9175 /* ensure 32-byte alignment of whole construct */
9176 alloc_size += NETDEV_ALIGN - 1;
9177
9178 p = kvzalloc(alloc_size, GFP_KERNEL | __GFP_RETRY_MAYFAIL);
9179 if (!p)
9180 return NULL;
9181
9182 dev = PTR_ALIGN(p, NETDEV_ALIGN);
9183 dev->padded = (char *)dev - (char *)p;
9184
9185 dev->pcpu_refcnt = alloc_percpu(int);
9186 if (!dev->pcpu_refcnt)
9187 goto free_dev;
9188
9189 if (dev_addr_init(dev))
9190 goto free_pcpu;
9191
9192 dev_mc_init(dev);
9193 dev_uc_init(dev);
9194
9195 dev_net_set(dev, &init_net);
9196
9197 dev->gso_max_size = GSO_MAX_SIZE;
9198 dev->gso_max_segs = GSO_MAX_SEGS;
9199 dev->upper_level = 1;
9200 dev->lower_level = 1;
9201
9202 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->napi_list);
9203 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->unreg_list);
9204 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->close_list);
9205 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->link_watch_list);
9206 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->adj_list.upper);
9207 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->adj_list.lower);
9208 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->ptype_all);
9209 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->ptype_specific);
9210 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED
9211 hash_init(dev->qdisc_hash);
9212 #endif
9213 dev->priv_flags = IFF_XMIT_DST_RELEASE | IFF_XMIT_DST_RELEASE_PERM;
9214 setup(dev);
9215
9216 if (!dev->tx_queue_len) {
9217 dev->priv_flags |= IFF_NO_QUEUE;
9218 dev->tx_queue_len = DEFAULT_TX_QUEUE_LEN;
9219 }
9220
9221 dev->num_tx_queues = txqs;
9222 dev->real_num_tx_queues = txqs;
9223 if (netif_alloc_netdev_queues(dev))
9224 goto free_all;
9225
9226 dev->num_rx_queues = rxqs;
9227 dev->real_num_rx_queues = rxqs;
9228 if (netif_alloc_rx_queues(dev))
9229 goto free_all;
9230
9231 strcpy(dev->name, name);
9232 dev->name_assign_type = name_assign_type;
9233 dev->group = INIT_NETDEV_GROUP;
9234 if (!dev->ethtool_ops)
9235 dev->ethtool_ops = &default_ethtool_ops;
9236
9237 nf_hook_ingress_init(dev);
9238
9239 return dev;
9240
9241 free_all:
9242 free_netdev(dev);
9243 return NULL;
9244
9245 free_pcpu:
9246 free_percpu(dev->pcpu_refcnt);
9247 free_dev:
9248 netdev_freemem(dev);
9249 return NULL;
9250 }3.2.3 free_netdev
| 函数原型 | void free_netdev(struct net_device *dev) | |
| 参数 | struct net_device *dev | 指向 struct net_device 的指针,代表要释放的网络设备。 |
| 返回值 | ||
| 功能 | Linux 内核中用于释放网络设备资源的函数。它主要用于在不再需要某个网络设备时,清理和释放与该设备相关的内存和资源 | |
9262 void free_netdev(struct net_device *dev)
9263 {
9264 struct napi_struct *p, *n;
9265
9266 might_sleep();
9267 netif_free_tx_queues(dev);
9268 netif_free_rx_queues(dev);
9269
9270 kfree(rcu_dereference_protected(dev->ingress_queue, 1));
9271
9272 /* Flush device addresses */
9273 dev_addr_flush(dev);
9274
9275 list_for_each_entry_safe(p, n, &dev->napi_list, dev_list)
9276 netif_napi_del(p);
9277
9278 free_percpu(dev->pcpu_refcnt);
9279 dev->pcpu_refcnt = NULL;
9280
9281 /* Compatibility with error handling in drivers */
9282 if (dev->reg_state == NETREG_UNINITIALIZED) {
9283 netdev_freemem(dev);
9284 return;
9285 }
9286
9287 BUG_ON(dev->reg_state != NETREG_UNREGISTERED);
9288 dev->reg_state = NETREG_RELEASED;
9289
9290 /* will free via device release */
9291 put_device(&dev->dev);
9292 }3.3 网络设备的打开与释放
3.3.1 netif_start_queue
| 函数原型 | void netif_start_queue(struct net_device *dev) | |
| 参数 | struct net_device *dev | 指向 struct net_device 的指针,表示要启动发送队列的网络设备。 |
| 返回值 | ||
| 功能 | Linux 内核中用于启动网络设备发送队列的函数。它允许网络驱动程序通知内核,网络设备可以开始处理发送数据包 | |
3103 static inline void netif_start_queue(struct net_device *dev)
3104 {
3105 netif_tx_start_queue(netdev_get_tx_queue(dev, 0));
3106 }2133 struct netdev_queue *netdev_get_tx_queue(const struct net_device *dev,
2134 unsigned int index)
2135 {
2136 return &dev->_tx[index];
2137 }3092 static __always_inline void netif_tx_start_queue(struct netdev_queue *dev_queue)
3093 {
3094 clear_bit(__QUEUE_STATE_DRV_XOFF, &dev_queue->state);
3095 }58 clear_bit(unsigned long nr, volatile void * addr)59 {60 unsigned long temp;61 int *m = ((int *) addr) + (nr >> 5);62 63 __asm__ __volatile__(64 "1: ldl_l %0,%3\n"65 " bic %0,%2,%0\n"66 " stl_c %0,%1\n"67 " beq %0,2f\n"68 ".subsection 2\n"69 "2: br 1b\n"70 ".previous" 71 :"=&r" (temp), "=m" (*m)72 :"Ir" (1UL << (nr & 31)), "m" (*m));73 }3.3.2 netif_stop_queue
| 函数原型 | void netif_stop_queue(struct net_device *dev) | |
| 参数 | struct net_device *dev | 指向 struct net_device 的指针,表示要停止发送队列的网络设备。 |
| 返回值 | ||
| 功能 | Linux 内核中用于停止网络设备发送队列的函数。它允许网络驱动程序通知内核,网络设备暂时无法处理发送数据包。这是网络设备驱动中的一个重要功能,用于管理数据传输的状态 | |
3154 static inline void netif_stop_queue(struct net_device *dev)
3155 {
3156 netif_tx_stop_queue(netdev_get_tx_queue(dev, 0));
3157 } 3142 static __always_inline void netif_tx_stop_queue(struct netdev_queue *dev_queue)
3143 {
3144 set_bit(__QUEUE_STATE_DRV_XOFF, &dev_queue->state);
3145 } 29 set_bit(unsigned long nr, volatile void * addr)30 {31 unsigned long temp;32 int *m = ((int *) addr) + (nr >> 5);33 34 __asm__ __volatile__(35 "1: ldl_l %0,%3\n"36 " bis %0,%2,%0\n"37 " stl_c %0,%1\n"38 " beq %0,2f\n"39 ".subsection 2\n"40 "2: br 1b\n"41 ".previous"42 :"=&r" (temp), "=m" (*m)43 :"Ir" (1UL << (nr & 31)), "m" (*m));44 }3.3.3 模板
1static int xxx_open(struct net_device *dev)
2{
3 /* 申请端口、IRQ等,类似于fops->open */
4 ret = request_irq(dev->irq, &xxx_interrupt, 0, dev->name, dev);
5 ...
6 netif_start_queue(dev);
7 ...
8}
9
10static int xxx_release(struct net_device *dev)
11{
12 /* 释放端口、IRQ等,类似于fops->close */
13 free_irq(dev->irq, dev);
14 ...
15 netif_stop_queue(dev); /* can't transmit any more */
16 ...
17}3.4 网络连接状态
3.4.1 netif_carrier_on
| 函数原型 | void netif_carrier_on(struct net_device *dev) | |
| 参数 | struct net_device *dev | 指向 struct net_device 的指针,表示要设置连接状态的网络设备 |
| 返回值 | ||
| 功能 | 设置网络设备连接状态 | |
511 void netif_carrier_on(struct net_device *dev)512 { 513 if (test_and_clear_bit(__LINK_STATE_NOCARRIER, &dev->state)) {514 if (dev->reg_state == NETREG_UNINITIALIZED)515 return;516 atomic_inc(&dev->carrier_up_count);517 linkwatch_fire_event(dev);518 if (netif_running(dev))519 __netdev_watchdog_up(dev);520 }521 } 3.4.2 netif_carrier_off
| 函数原型 | void netif_carrier_off(struct net_device *dev) | |
| 参数 | struct net_device *dev | 指向 struct net_device 的指针,表示要更新连接状态的网络设备。 |
| 返回值 | ||
| 功能 | 用于设置网络设备断开连接状态 | |
530 void netif_carrier_off(struct net_device *dev)531 { 532 if (!test_and_set_bit(__LINK_STATE_NOCARRIER, &dev->state)) {533 if (dev->reg_state == NETREG_UNINITIALIZED)534 return;535 atomic_inc(&dev->carrier_down_count);536 linkwatch_fire_event(dev);537 }538 }3.4.3 netif_carrier_ok
| 函数原型 | bool netif_carrier_ok(const struct net_device *dev) | |
| 参数 | struct net_device *dev | 指向 struct net_device 的指针,表示要检查的网络设备。 |
| 返回值 | ||
| 功能 | 用于检查网络设备的连接状态 | |
3757 static inline bool netif_carrier_ok(const struct net_device *dev)
3758 {
3759 return !test_bit(__LINK_STATE_NOCARRIER, &dev->state);
3760 } 3.4.4 模板
在网络设备驱动程序中可采取一定的手段来检测和报告链路状态,最常见的方法是采用中断,其次可以设置一个定时器来对链路状态进行周期性的检查。当定时器到期之后,在定时器处理函数中读取物理设备的相关寄存器以获得载波状态,从而更新设备的连接状态网络设备驱动用定时器周期性检查链路状态
1static int xxx_open(struct net_device *dev)
2{
3 struct xxx_priv *priv = netdev_priv(dev);
4
5 ...
6 priv->timer.expires = jiffies + 3* Hz;
7 priv->timer.data = (unsigned long)dev;
8 priv->timer.function = &xxx_timer; /* 定时器处理函数 */
9 add_timer(&priv->timer);
10 ...
11}1static void xxx_timer(unsigned long data)
2{
3 struct net_device *dev = (struct net_device*)data;
4 u16 link;
5 …
6 if (!(dev->flags &IFF_UP))
7 goto set_timer;
8
9 /* 获得物理上的连接状态 */
10 if (link = xxx_chk_link(dev)) {
11 if (!(dev->flags &IFF_RUNNING)) {
12 netif_carrier_on(dev);
13 dev->flags |= IFF_RUNNING;
14 printk(KERN_DEBUG "%s: link up\n", dev->name);
15 }
16 } else {
17 if (dev->flags &IFF_RUNNING) {
18 netif_carrier_off(dev);
19 dev->flags &= ~IFF_RUNNING;
20 printk(KERN_DEBUG "%s: link down\n", dev->name);
21 }
22 }
24 set_timer:
25 priv->timer.expires = jiffies + 1* Hz;
26 priv->timer.data = (unsigned long)dev;
27 priv->timer.function = &xxx_timer; /* timer handler */
28 add_timer(&priv->timer);
29 }上述代码第10行调用xxx_chk_link()函数来读取网络适配器硬件的相关寄存器,以获得链路连接状态,具体实现由硬件决定。当链路连接上时,第12行的netif_carrier_on()函数显式地通知内核链路正常;反之,第18行的netif_carrier_off()同样显式地通知内核链路失去连接。
4 dm9000驱动解读
dm9000.c
dm9000.h
drivers/net/ethernet/davicom/dm9000.c
static const struct ethtool_ops dm9000_ethtool_ops = {.get_drvinfo = dm9000_get_drvinfo,.get_msglevel = dm9000_get_msglevel,.set_msglevel = dm9000_set_msglevel,.nway_reset = dm9000_nway_reset,.get_link = dm9000_get_link,.get_wol = dm9000_get_wol,.set_wol = dm9000_set_wol,.get_eeprom_len = dm9000_get_eeprom_len,.get_eeprom = dm9000_get_eeprom,.set_eeprom = dm9000_set_eeprom,.get_link_ksettings = dm9000_get_link_ksettings,.set_link_ksettings = dm9000_set_link_ksettings,
};static void dm9000_poll_work(struct work_struct *w)
{struct delayed_work *dw = to_delayed_work(w);struct board_info *db = container_of(dw, struct board_info, phy_poll);struct net_device *ndev = db->ndev;if (db->flags & DM9000_PLATF_SIMPLE_PHY &&!(db->flags & DM9000_PLATF_EXT_PHY)) {unsigned nsr = dm9000_read_locked(db, DM9000_NSR);unsigned old_carrier = netif_carrier_ok(ndev) ? 1 : 0;unsigned new_carrier;new_carrier = (nsr & NSR_LINKST) ? 1 : 0;if (old_carrier != new_carrier) {if (netif_msg_link(db))dm9000_show_carrier(db, new_carrier, nsr);if (!new_carrier)netif_carrier_off(ndev);elsenetif_carrier_on(ndev);}} elsemii_check_media(&db->mii, netif_msg_link(db), 0);if (netif_running(ndev))dm9000_schedule_poll(db);
}static int dm9000_start_xmit(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev)
{unsigned long flags;struct board_info *db = netdev_priv(dev);dm9000_dbg(db, 3, "%s:\n", __func__);if (db->tx_pkt_cnt > 1)return NETDEV_TX_BUSY;spin_lock_irqsave(&db->lock, flags);/* Move data to DM9000 TX RAM */writeb(DM9000_MWCMD, db->io_addr);(db->outblk)(db->io_data, skb->data, skb->len);dev->stats.tx_bytes += skb->len;db->tx_pkt_cnt++;/* TX control: First packet immediately send, second packet queue */if (db->tx_pkt_cnt == 1) {dm9000_send_packet(dev, skb->ip_summed, skb->len);} else {/* Second packet */db->queue_pkt_len = skb->len;db->queue_ip_summed = skb->ip_summed;netif_stop_queue(dev);}spin_unlock_irqrestore(&db->lock, flags);/* free this SKB */dev_consume_skb_any(skb);return NETDEV_TX_OK;
}/** DM9000 interrupt handler* receive the packet to upper layer, free the transmitted packet*/static void dm9000_tx_done(struct net_device *dev, struct board_info *db)
{int tx_status = ior(db, DM9000_NSR); /* Got TX status */if (tx_status & (NSR_TX2END | NSR_TX1END)) {/* One packet sent complete */db->tx_pkt_cnt--;dev->stats.tx_packets++;if (netif_msg_tx_done(db))dev_dbg(db->dev, "tx done, NSR %02x\n", tx_status);/* Queue packet check & send */if (db->tx_pkt_cnt > 0)dm9000_send_packet(dev, db->queue_ip_summed,db->queue_pkt_len);netif_wake_queue(dev);}
}
/** Received a packet and pass to upper layer*/
static void dm9000_rx(struct net_device *dev)
{struct board_info *db = netdev_priv(dev);struct dm9000_rxhdr rxhdr;struct sk_buff *skb;u8 rxbyte, *rdptr;bool GoodPacket;int RxLen;/* Check packet ready or not */do {ior(db, DM9000_MRCMDX); /* Dummy read *//* Get most updated data */rxbyte = readb(db->io_data);/* Status check: this byte must be 0 or 1 */if (rxbyte & DM9000_PKT_ERR) {dev_warn(db->dev, "status check fail: %d\n", rxbyte);iow(db, DM9000_RCR, 0x00); /* Stop Device */return;}if (!(rxbyte & DM9000_PKT_RDY))return;/* A packet ready now & Get status/length */GoodPacket = true;writeb(DM9000_MRCMD, db->io_addr);(db->inblk)(db->io_data, &rxhdr, sizeof(rxhdr));RxLen = le16_to_cpu(rxhdr.RxLen);if (netif_msg_rx_status(db))dev_dbg(db->dev, "RX: status %02x, length %04x\n",rxhdr.RxStatus, RxLen);/* Packet Status check */if (RxLen < 0x40) {GoodPacket = false;if (netif_msg_rx_err(db))dev_dbg(db->dev, "RX: Bad Packet (runt)\n");}if (RxLen > DM9000_PKT_MAX) {dev_dbg(db->dev, "RST: RX Len:%x\n", RxLen);}/* rxhdr.RxStatus is identical to RSR register. */if (rxhdr.RxStatus & (RSR_FOE | RSR_CE | RSR_AE |RSR_PLE | RSR_RWTO |RSR_LCS | RSR_RF)) {GoodPacket = false;if (rxhdr.RxStatus & RSR_FOE) {if (netif_msg_rx_err(db))dev_dbg(db->dev, "fifo error\n");dev->stats.rx_fifo_errors++;}if (rxhdr.RxStatus & RSR_CE) {if (netif_msg_rx_err(db))dev_dbg(db->dev, "crc error\n");dev->stats.rx_crc_errors++;}if (rxhdr.RxStatus & RSR_RF) {if (netif_msg_rx_err(db))dev_dbg(db->dev, "length error\n");dev->stats.rx_length_errors++;}}/* Move data from DM9000 */if (GoodPacket &&((skb = netdev_alloc_skb(dev, RxLen + 4)) != NULL)) {skb_reserve(skb, 2);rdptr = skb_put(skb, RxLen - 4);/* Read received packet from RX SRAM */(db->inblk)(db->io_data, rdptr, RxLen);dev->stats.rx_bytes += RxLen;/* Pass to upper layer */skb->protocol = eth_type_trans(skb, dev);if (dev->features & NETIF_F_RXCSUM) {if ((((rxbyte & 0x1c) << 3) & rxbyte) == 0)skb->ip_summed = CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY;elseskb_checksum_none_assert(skb);}netif_rx(skb);dev->stats.rx_packets++;} else {/* need to dump the packet's data */(db->dumpblk)(db->io_data, RxLen);}} while (rxbyte & DM9000_PKT_RDY);
}static int dm9000_open(struct net_device *dev)
{struct board_info *db = netdev_priv(dev);unsigned int irq_flags = irq_get_trigger_type(dev->irq);if (netif_msg_ifup(db))dev_dbg(db->dev, "enabling %s\n", dev->name);/* If there is no IRQ type specified, tell the user that this is a* problem*/if (irq_flags == IRQF_TRIGGER_NONE)dev_warn(db->dev, "WARNING: no IRQ resource flags set.\n");irq_flags |= IRQF_SHARED;/* GPIO0 on pre-activate PHY, Reg 1F is not set by reset */iow(db, DM9000_GPR, 0); /* REG_1F bit0 activate phyxcer */mdelay(1); /* delay needs by DM9000B *//* Initialize DM9000 board */dm9000_init_dm9000(dev);if (request_irq(dev->irq, dm9000_interrupt, irq_flags, dev->name, dev))return -EAGAIN;/* Now that we have an interrupt handler hooked up we can unmask* our interrupts*/dm9000_unmask_interrupts(db);/* Init driver variable */db->dbug_cnt = 0;mii_check_media(&db->mii, netif_msg_link(db), 1);netif_start_queue(dev);/* Poll initial link status */schedule_delayed_work(&db->phy_poll, 1);return 0;
}static void dm9000_shutdown(struct net_device *dev)
{struct board_info *db = netdev_priv(dev);/* RESET device */dm9000_phy_write(dev, 0, MII_BMCR, BMCR_RESET); /* PHY RESET */iow(db, DM9000_GPR, 0x01); /* Power-Down PHY */dm9000_mask_interrupts(db);iow(db, DM9000_RCR, 0x00); /* Disable RX */
}/** Stop the interface.* The interface is stopped when it is brought.*/
static int dm9000_stop(struct net_device *ndev)
{struct board_info *db = netdev_priv(ndev);if (netif_msg_ifdown(db))dev_dbg(db->dev, "shutting down %s\n", ndev->name);cancel_delayed_work_sync(&db->phy_poll);netif_stop_queue(ndev);netif_carrier_off(ndev);/* free interrupt */free_irq(ndev->irq, ndev);dm9000_shutdown(ndev);return 0;
}static const struct net_device_ops dm9000_netdev_ops = {.ndo_open = dm9000_open,.ndo_stop = dm9000_stop,.ndo_start_xmit = dm9000_start_xmit,.ndo_tx_timeout = dm9000_timeout,.ndo_set_rx_mode = dm9000_hash_table,.ndo_do_ioctl = dm9000_ioctl,.ndo_set_features = dm9000_set_features,.ndo_validate_addr = eth_validate_addr,.ndo_set_mac_address = eth_mac_addr,
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_POLL_CONTROLLER.ndo_poll_controller = dm9000_poll_controller,
#endif
};static int dm9000_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{struct dm9000_plat_data *pdata = dev_get_platdata(&pdev->dev);struct board_info *db; /* Point a board information structure */struct net_device *ndev;struct device *dev = &pdev->dev;/* Init network device */ndev = alloc_etherdev(sizeof(struct board_info));if (!ndev) {ret = -ENOMEM;goto out_regulator_disable;}SET_NETDEV_DEV(ndev, &pdev->dev);INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&db->phy_poll, dm9000_poll_work);ndev->netdev_ops = &dm9000_netdev_ops;ndev->watchdog_timeo = msecs_to_jiffies(watchdog);ndev->ethtool_ops = &dm9000_ethtool_ops;if (!is_valid_ether_addr(ndev->dev_addr) && pdata != NULL) {mac_src = "platform data";memcpy(ndev->dev_addr, pdata->dev_addr, ETH_ALEN);}if (!is_valid_ether_addr(ndev->dev_addr)) {/* try reading from mac */mac_src = "chip";for (i = 0; i < 6; i++)ndev->dev_addr[i] = ior(db, i+DM9000_PAR);}if (!is_valid_ether_addr(ndev->dev_addr)) {inv_mac_addr = true;eth_hw_addr_random(ndev);mac_src = "random";}platform_set_drvdata(pdev, ndev);ret = register_netdev(ndev);if (ret == 0) {if (inv_mac_addr)dev_warn(db->dev, "%s: Invalid ethernet MAC address. Please set using ip\n",ndev->name);printk(KERN_INFO "%s: dm9000%c at %p,%p IRQ %d MAC: %pM (%s)\n",ndev->name, dm9000_type_to_char(db->type),db->io_addr, db->io_data, ndev->irq,ndev->dev_addr, mac_src);}return 0;out:dev_err(db->dev, "not found (%d).\n", ret);dm9000_release_board(pdev, db);free_netdev(ndev);out_regulator_disable:if (!IS_ERR(power))regulator_disable(power);return ret;
}static int dm9000_drv_suspend(struct device *dev)
{struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);struct net_device *ndev = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);struct board_info *db;if (ndev) {db = netdev_priv(ndev);db->in_suspend = 1;if (!netif_running(ndev))return 0;netif_device_detach(ndev);/* only shutdown if not using WoL */if (!db->wake_state)dm9000_shutdown(ndev);}return 0;
}static int dm9000_drv_resume(struct device *dev)
{struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);struct net_device *ndev = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);struct board_info *db = netdev_priv(ndev);if (ndev) {if (netif_running(ndev)) {/* reset if we were not in wake mode to ensure if* the device was powered off it is in a known state */if (!db->wake_state) {dm9000_init_dm9000(ndev);dm9000_unmask_interrupts(db);}netif_device_attach(ndev);}db->in_suspend = 0;}return 0;
}static const struct dev_pm_ops dm9000_drv_pm_ops = {.suspend = dm9000_drv_suspend,.resume = dm9000_drv_resume,
};static int dm9000_drv_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{struct net_device *ndev = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);struct board_info *dm = to_dm9000_board(ndev);unregister_netdev(ndev);dm9000_release_board(pdev, dm);free_netdev(ndev); /* free device structure */if (dm->power_supply)regulator_disable(dm->power_supply);dev_dbg(&pdev->dev, "released and freed device\n");return 0;
}#ifdef CONFIG_OF
static const struct of_device_id dm9000_of_matches[] = {{ .compatible = "davicom,dm9000", },{ /* sentinel */ }
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, dm9000_of_matches);
#endifstatic struct platform_driver dm9000_driver = {.driver = {.name = "dm9000",.pm = &dm9000_drv_pm_ops,.of_match_table = of_match_ptr(dm9000_of_matches),},.probe = dm9000_probe,.remove = dm9000_drv_remove,
};module_platform_driver(dm9000_driver);