LLM 中什么是Prompts?如何使用LangChain 快速实现Prompts 一
Prompt是一种基于自然语言处理的交互方式,它通过机器对自然语言的解析,实现用户与机器之间的沟通。 Prompt主要实现方式是通过建立相应的语料库和语义解析模型,来将自然语言转换为机器可识别的指令。 Prompt是一种计算机编程语言,它被广泛用于自然语言处理(NLP)和人工智能(AI)领域。

Prompt templage 是用于生成语言模型提示的预定义方案。
模板可以包括说明、少量示例以及适合给定任务的特定上下文和问题。
LangChain 提供了创建和使用提示模板的工具。
LangChain 致力于创建与模型无关的模板,以便能够轻松地跨不同语言模型重用现有模板。
通常LLM 期望提示是字符串或聊天消息列表。
PromptTemplate
用于PromptTemplate创建字符串提示的模板。
默认情况下,PromptTemplate使用 Python 的 str.format 语法进行模板化。
该模板支持任意数量的变量,包括无变量:
python复制代码 from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplateprompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template("Tell me a {adjective} joke about {content}.")prompt_template.format(adjective="funny", content="chickens")# > 'Tell me a funny joke about chickens.'
python复制代码 # 无变量prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template("Tell me a joke")prompt_template.format()# > 'Tell me a joke'
PromptTemplate 一般使用在单轮对话中。不需要历史记忆的场景.
😝有需要的小伙伴,可以V扫描下方二维码免费领取🆓
 ## `ChatPromptTemplate`
## `ChatPromptTemplate`
ChatPromptTemplate 聊天消息列表,每条聊天消息都与内容以及附加参数相关联role。例如聊天消息可以与 AI 助手、人类或系统角色相关联。
创建一个这样的聊天提示模板:
python复制代码 from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplatechat_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system", "You are a helpful AI bot. Your name is {name}."),("human", "Hello, how are you doing?"),("ai", "I'm doing well, thanks!"),("human", "{user_input}"),])messages = chat_template.format_messages(name="Bob", user_input="What is your name?")
ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages接受各种消息表示形式。
例如除了使用上面使用的 (type, content) 的二元组表示之外,我们还可以传入 MessagePromptTemplate的实例BaseMessage。
python复制代码 chat_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([# 这里跟上面的 system 的作用是一致的SystemMessage(content=("You are a helpful assistant that re-writes the user's text to ""sound more upbeat.")),HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"),])messages = chat_template.format_messages(text="I don't like eating tasty things")print(messages)
这样为我们构建聊天提示的方式提供了很大的灵活性。
LECL 方式
PromptTemplate 与 ChatPromptTemplate都实现Runnable接口。这意味着它们支持invoke、 ainvoke、stream、astream、batch、abatch、astream_log 函数的调用。
PromptTemplate接受(提示变量的)字典并返回一个StringPromptValue. ChatPromptTemplate接受一个字典并返回一个ChatPromptValue。
python复制代码 prompt_val = prompt_template.invoke({"adjective": "funny", "content": "chickens"})# StringPromptValue(text='Tell me a funny joke about chickens.')prompt_val.to_string()# > Tell me a funny joke about chickens.prompt_val.to_messages()#> [HumanMessage(content='Tell me a joke')]另一个例子
python复制代码 chat_val = chat_template.invoke({"text": "i dont like eating tasty things."})chat_val.to_messages()#> [SystemMessage(content="You are a helpful assistant that re-writes the user's text to sound more upbeat."),HumanMessage(content='i dont like eating tasty things.')]# 转换为字符串chat_val.to_string()#> "System: You are a helpful assistant that re-writes the user's text to sound more upbeat.\nHuman: i dont like eating tasty things."
使用类型消息
聊天提示由消息列表组成。纯粹为了创建这些提示方便我们开发人员添加的一种的便捷方法。在此管道中,每个新元素都是最终提示中的一条新消息。
python复制代码 from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage, HumanMessage, SystemMessage
首先,让我们使用系统消息初始化基本 ChatPromptTemplate。不一定要从系统开始,但这通常是比较好的做法。
python复制代码 prompt = SystemMessage(content="You are a nice pirate")
然后我们可以轻松创建将其与其他消息或消息模板相结合的管道 。
当没有要格式化的变量时使用Message,当有要格式化的变量时使用MessageTemplate。还可以仅使用一个字符串(注意:这将自动推断为 HumanMessagePromptTemplate)
python复制代码 new_prompt = (prompt + HumanMessage(content="hi") + AIMessage(content="what?") + "{input}")
这样LangChain会创建 ChatPromptTemplate 类的一个实例,因此我们可以像以前一样使用它!
python复制代码 new_prompt.format_messages(input="i said hi")# 输出[SystemMessage(content='You are a nice pirate', additional_kwargs={}),HumanMessage(content='hi', additional_kwargs={}, example=False),AIMessage(content='what?', additional_kwargs={}, example=False),HumanMessage(content='i said hi', additional_kwargs={}, example=False)]
也可以在LLMChain一样在使用它。
python复制代码 from langchain.chains import LLMChainfrom langchain_openai import ChatOpenAIllm = ChatOpenAI()chain = LLMChain(prompt=new_prompt, llm=llm)chain.run("I said HI!")
选择器
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 相似 similarity | 使用输入和示例之间的语义相似性来决定选择哪些示例。 |
| MMR | 使用输入和示例之间的最大边际相关性来决定选择哪些示例。 |
| length_based | 根据一定长度内可以容纳的数量来选择示例 |
| Ngram | 使用输入和示例之间的 ngram 重叠来决定选择哪些示例。 |
长度选择
长度选择器根据长度选择要使用的示例。当我们担心构建的提示会超过上下文窗口的长度时,这非常有用。对于较长的输入,它将选择较少的示例来包含,而对于较短的输入,它将选择更多的示例。
python复制代码 from langchain.prompts import FewShotPromptTemplate, PromptTemplatefrom langchain.prompts.example_selector import LengthBasedExampleSelector# 制作反义词的任务示例。examples = [{"input": "happy", "output": "sad"},{"input": "tall", "output": "short"},{"input": "energetic", "output": "lethargic"},{"input": "sunny", "output": "gloomy"},{"input": "windy", "output": "calm"},]example_prompt = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["input", "output"],template="Input: {input}\nOutput: {output}",)example_selector = LengthBasedExampleSelector(# 可供选择的示例。examples=examples,#用于格式化示例的PromptTemplate。example_prompt=example_prompt,# 格式化示例的最大长度。长度由下面的get_text_length函数来衡量。max_length=25,# 用于获取字符串长度的函数,用于确定要包含哪些示例。因为如果未指定,默认值将会提供。# get_text_length: Callable[[str], int] = lambda x: len(re.split("\n| ", x)))dynamic_prompt = FewShotPromptTemplate(# 我们提供一个示例选择器example_selector=example_selector,example_prompt=example_prompt,prefix="Give the antonym of every input",suffix="Input: {adjective}\nOutput:",input_variables=["adjective"],)
python复制代码 print(dynamic_prompt.format(adjective="big"))
python复制代码 Give the antonym of every inputInput: happyOutput: sadInput: tallOutput: shortInput: energeticOutput: lethargicInput: sunnyOutput: gloomyInput: windyOutput: calmInput: bigOutput:
一个包含长输入的示例,所以它只选择了一个示例。
python复制代码 long_string = "big and huge and massive and large and gigantic and tall and much much much much much bigger than everything else"print(dynamic_prompt.format(adjective=long_string))
yaml复制代码 Give the antonym of every inputInput: happyOutput: sadInput: big and huge and massive and large and gigantic and tall and much much much much much bigger than everything elseOutput:
(MMR) 选择
MaxMarginalRelevanceExampleSelector根据与输入最相似的示例的组合来选择示例,同时还针对多样性进行优化。它通过查找与输入具有最大余弦相似度的嵌入示例来实现这一点,然后迭代地添加它们,同时排除它们与已选择示例的接近程度。
看个例子:
python复制代码 from langchain.prompts import FewShotPromptTemplate, PromptTemplatefrom langchain.prompts.example_selector import (MaxMarginalRelevanceExampleSelector,SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector,)from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISSfrom langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddingsexample_prompt = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["input", "output"],template="Input: {input}\nOutput: {output}",)#创建反义词的假装任务的示例。examples = [{"input": "happy", "output": "sad"},{"input": "tall", "output": "short"},{"input": "energetic", "output": "lethargic"},{"input": "sunny", "output": "gloomy"},{"input": "windy", "output": "calm"},]
python复制代码 example_selector = MaxMarginalRelevanceExampleSelector.from_examples(# 可以选择的示例列表。examples,# 用于生成嵌入的嵌入类,用于衡量语义相似性。OpenAIEmbeddings(),# 用于存储嵌入并进行相似度搜索的VectorStore类。FAISS,# 需要生成的示例数量。k=2,)mmr_prompt = FewShotPromptTemplate(#我们提供 ExampleSelectorexample_selector=example_selector,example_prompt=example_prompt,prefix="Give the antonym of every input",suffix="Input: {adjective}\nOutput:",input_variables=["adjective"],)
输入worried 是一种感觉类的词汇,所以应该选择愉快/悲伤的例子作为第一个。
ini复制代码 print(mmr_prompt.format(adjective="worried"))
python复制代码 # 让我们将这与仅仅基于相似性得到的结果进行比较。请使用SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector代替MaxMarginalRelevanceExampleSelector。example_selector = SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector.from_examples(# 可供选择的示例列表。examples,#向量相似性检索OpenAIEmbeddings(),#用于存储嵌入并进行相似性搜索的 VectorStore 类。FAISS,k=2,)similar_prompt = FewShotPromptTemplate(# 供了一个示例选择器,而不仅仅是具体的示例。example_selector=example_selector,example_prompt=example_prompt,prefix="Give the antonym of every input",suffix="Input: {adjective}\nOutput:",input_variables=["adjective"],)print(similar_prompt.format(adjective="worried"))
Ngram重叠选择
NGramOverlapExampleSelector根据 ngram 重叠分数,根据与输入最相似的示例来选择示例并对其进行排序。ngram 重叠分数是 0.0 到 1.0 之间的浮点数(含 0.0 和 1.0)。
选择器允许设置阈值分数。ngram 重叠分数小于或等于阈值的示例被排除。默认情况下,阈值设置为 -1.0,因此不会排除任何示例,只会对它们重新排序。将阈值设置为 0.0 将排除与输入没有 ngram 重叠的示例。
python复制代码 from langchain.prompts import FewShotPromptTemplate, PromptTemplatefrom langchain.prompts.example_selector.ngram_overlap import NGramOverlapExampleSelectorexample_prompt = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["input", "output"],template="Input: {input}\nOutput: {output}",)# 翻译任务的示例examples = [{"input": "See Spot run.", "output": "Ver correr a Spot."},{"input": "My dog barks.", "output": "Mi perro ladra."},{"input": "Spot can run.", "output": "Spot puede correr."},]
python复制代码 example_selector = NGramOverlapExampleSelector(# 可以选择的示例。examples=examples,# 正在使用的 PromptTemplate 用于格式化示例。example_prompt=example_prompt,# 选择器停止的阈值。默认是 -1.0threshold=-1.0,)dynamic_prompt = FewShotPromptTemplate(# 我们提供一个示例选择器。example_selector=example_selector,example_prompt=example_prompt,prefix="Give the Spanish translation of every input",suffix="Input: {sentence}\nOutput:",input_variables=["sentence"],)
对于负阈值:Selector按ngram重叠分数对示例进行排序,不排除任何示例。对于大于1.0的阈值:选择器排除所有示例,并返回一个空列表。对于等于0.0的阈值:Selector根据ngram重叠分数对示例进行排序,并且排除与输入没有ngram重叠的那些。
similarity 选择器
该对象根据与输入的相似性来选择示例。它通过查找与输入具有最大余弦相似度的嵌入示例来实现这一点。
python复制代码 from langchain.prompts import FewShotPromptTemplate, PromptTemplatefrom langchain.prompts.example_selector import SemanticSimilarityExampleSelectorfrom langchain_community.vectorstores import Chromafrom langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddingsexample_prompt = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["input", "output"],template="Input: {input}\nOutput: {output}",)#创建反义词的任务的示例。examples = [{"input": "happy", "output": "sad"},{"input": "tall", "output": "short"},{"input": "energetic", "output": "lethargic"},{"input": "sunny", "output": "gloomy"},{"input": "windy", "output": "calm"},]
python复制代码 example_selector = SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector.from_examples(# 可供选择的示例列表。examples,# 用于生成嵌入的嵌入类,这些嵌入类用于衡量语义相似性。OpenAIEmbeddings(),#用于存储嵌入并进行相似度搜索的VectorStore类。Chroma,k=1,)similar_prompt = FewShotPromptTemplate(# 我们提供一个 ExampleSelectorexample_selector=example_selector,example_prompt=example_prompt,prefix="Give the antonym of every input",suffix="Input: {adjective}\nOutput:",input_variables=["adjective"],)
总结:
本篇文章我们主要介绍了一下内容:
- 什么是
prompt,prompt template - Langchain 中 构建
prompt template的方式以及类型:PromptTemplate,ChatPromptTemplate。 - 使用 langchain 构建消息类型。
- prompt 选择器的类型,以及为什么需要选择器。
那么,我们该如何学习大模型?
作为一名热心肠的互联网老兵,我决定把宝贵的AI知识分享给大家。 至于能学习到多少就看你的学习毅力和能力了 。我已将重要的AI大模型资料包括AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频免费分享出来。
一、大模型全套的学习路线
学习大型人工智能模型,如GPT-3、BERT或任何其他先进的神经网络模型,需要系统的方法和持续的努力。既然要系统的学习大模型,那么学习路线是必不可少的,下面的这份路线能帮助你快速梳理知识,形成自己的体系。
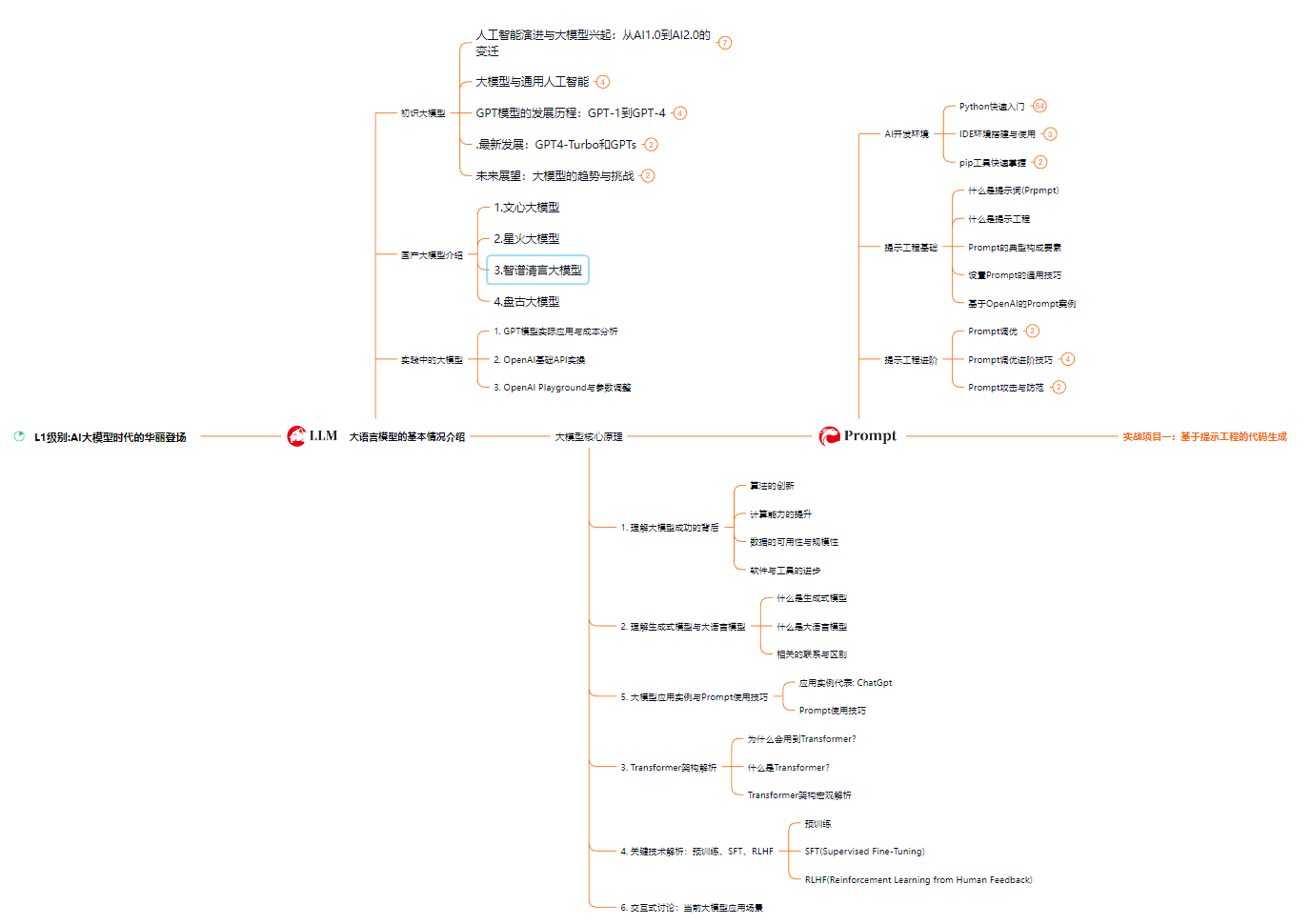
L1级别:AI大模型时代的华丽登场
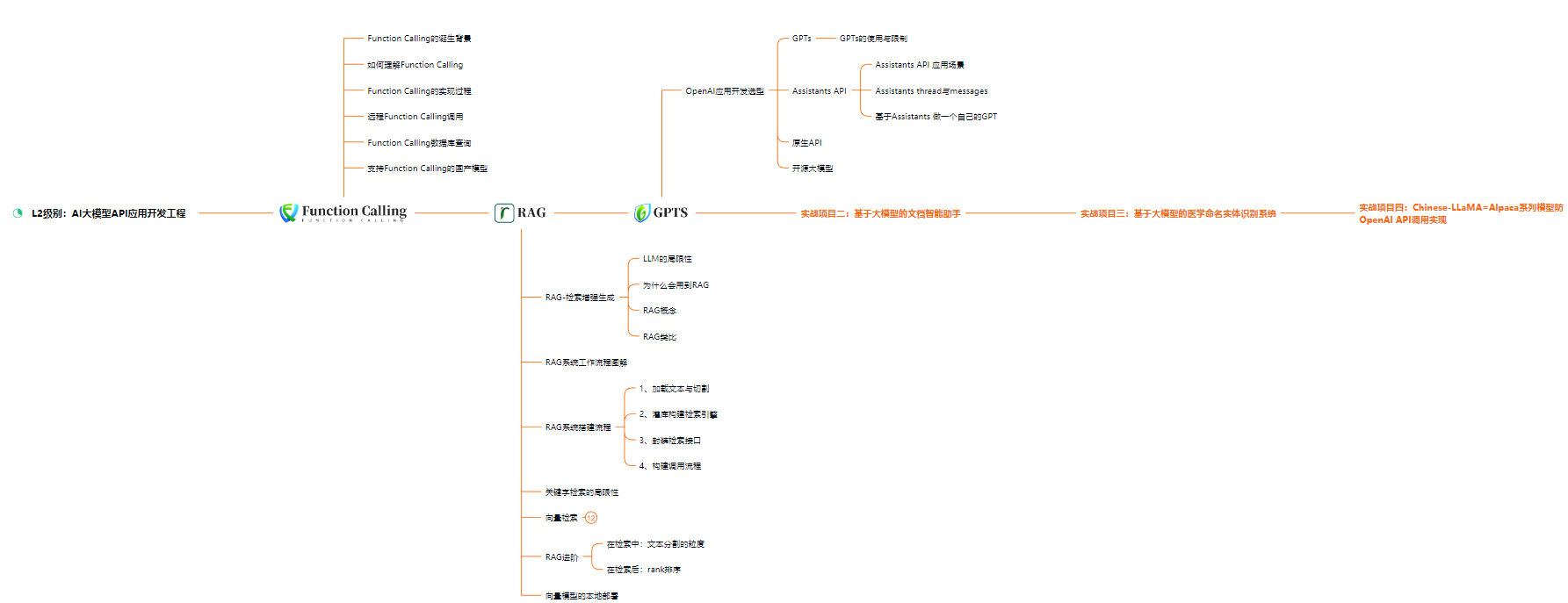
L2级别:AI大模型API应用开发工程
L3级别:大模型应用架构进阶实践

L4级别:大模型微调与私有化部署

一般掌握到第四个级别,市场上大多数岗位都是可以胜任,但要还不是天花板,天花板级别要求更加严格,对于算法和实战是非常苛刻的。建议普通人掌握到L4级别即可。
以上的AI大模型学习路线,不知道为什么发出来就有点糊,高清版可以微信扫描下方CSDN官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】

二、640套AI大模型报告合集
这套包含640份报告的合集,涵盖了AI大模型的理论研究、技术实现、行业应用等多个方面。无论您是科研人员、工程师,还是对AI大模型感兴趣的爱好者,这套报告合集都将为您提供宝贵的信息和启示。

三、大模型经典PDF籍
随着人工智能技术的飞速发展,AI大模型已经成为了当今科技领域的一大热点。这些大型预训练模型,如GPT-3、BERT、XLNet等,以其强大的语言理解和生成能力,正在改变我们对人工智能的认识。 那以下这些PDF籍就是非常不错的学习资源。
四、AI大模型商业化落地方案

作为普通人,入局大模型时代需要持续学习和实践,不断提高自己的技能和认知水平,同时也需要有责任感和伦理意识,为人工智能的健康发展贡献力量。
