530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
给你一棵所有节点为非负值的二叉搜索树,请你计算树中任意两节点的差的绝对值的最小值。
示例:

提示:树中至少有 2 个节点。
思路:
递归三部曲:
- 参数和返回值:参数是传入节点,没有返回值,是None。
- 终止条件:节点为空时,直接返回。
- 递归逻辑:因为是二叉搜索树,中序遍历,每次遍历前记录father变量为前一个遍历的节点,处理节点的时候计算本节点和father节点的绝对差。
# 附上一个错误代码,仅供记录。理解错题意,以为是父子节点的最小绝对差
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def getMinimumDifference(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
self.mini = float('inf')
self.father = None
self.getminabs(root)
return self.mini
def getminabs(self, node: Optional[TreeNode]) -> None:
if not node:
return
if self.father and (diff := abs(self.father.val - node.val)) < self.mini:
self.mini = diff
self.father = node
self.getminabs(node.left)
self.getminabs(node.right)
以上代码使用的是前序遍历,所以不行,但由于题目所给的是二叉搜索树,所以使用中序遍历的顺序应该是从小到大的有序遍历,所以使用中序遍历修改以上代码就可以得到正解,因为最小绝对差一定发生在有序数组的其中两个相邻元素之间。
正确代码实现如下:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def getMinimumDifference(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
self.mini = float('inf')
self.father = None
self.getminabs(root)
return self.mini
def getminabs(self, node: Optional[TreeNode]) -> None:
if not node:
return
self.getminabs(node.left)
if self.father and (diff := abs(self.father.val-node.val)) < self.mini:
self.mini = diff
self.father = node
self.getminabs(node.right)
规范代码:
递归法(版本一)利用中序递增,结合数组:
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.vec = []
def traversal(self, root):
if root is None:
return
self.traversal(root.left)
self.vec.append(root.val) # 将二叉搜索树转换为有序数组
self.traversal(root.right)
def getMinimumDifference(self, root):
self.vec = []
self.traversal(root)
if len(self.vec) < 2:
return 0
result = float('inf')
for i in range(1, len(self.vec)):
# 统计有序数组的最小差值
result = min(result, self.vec[i] - self.vec[i - 1])
return result
迭代法:
class Solution:
def getMinimumDifference(self, root):
stack = []
cur = root
pre = None
result = float('inf')
while cur is not None or len(stack) > 0:
if cur is not None:
stack.append(cur) # 将访问的节点放进栈
cur = cur.left # 左
else:
cur = stack.pop()
if pre is not None: # 中
result = min(result, cur.val - pre.val)
pre = cur
cur = cur.right # 右
return result
501.二叉搜索树中的众数
给定一个有相同值的二叉搜索树(BST),找出 BST 中的所有众数(出现频率最高的元素)。
假定 BST 有如下定义:
- 结点左子树中所含结点的值小于等于当前结点的值
- 结点右子树中所含结点的值大于等于当前结点的值
- 左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树
例如:
给定 BST [1,null,2,2],

返回[2].
提示:如果众数超过1个,不需考虑输出顺序
进阶:你可以不使用额外的空间吗?(假设由递归产生的隐式调用栈的开销不被计算在内)
思路:
- 参数和返回值:参数是传入节点,没有返回值,是None
- 终止条件:节点为空时return
- 递归逻辑:一样是二叉搜索树,所以中序遍历。递归遍历前,记录全局变量的father节点,为前一个遍历的节点。处理节点时,如果本节点和father节点相同,说明当前计数应该+1,全局变量count++,同时需要判断此时count是否与当前所记录的最大maxcount值相等,如果相等将该节点数值加入结果数组;如果count大于记录的maxcount,说明最大数值众数需要更新,将结果数组清零之后再将该节点压入结果数组。如果不同,需要重新计数,count重置为1。
代码实现如下:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def findMode(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
self.father = None
self.count = 1
self.maxcount = 1
self.result = []
self.findmostnum(root)
return self.result
def findmostnum(self, node: Optional[TreeNode]) -> None:
if not node:
return
self.findmostnum(node.left)
if self.father and self.father.val == node.val:
self.count += 1
else: # 由于是二叉搜索树,如果遍历到不同的数值后,必然不会再出现前面出现过的数值,计数应该重新开始,这里不能忘记重置
self.count = 1
if self.count == self.maxcount:
self.result.append(node.val)
elif self.count > self.maxcount:
self.maxcount = self.count
self.result = [node.val]
self.father = node
self.findmostnum(node.right)
规范代码:
递归法(版本一)利用字典:
# Definition for a binary tree node.# class TreeNode:# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):# self.val = val# self.left = left# self.right = rightfrom collections import defaultdict
class Solution:
def searchBST(self, cur, freq_map):
if cur is None:
return
freq_map[cur.val] += 1 # 统计元素频率
self.searchBST(cur.left, freq_map)
self.searchBST(cur.right, freq_map)
def findMode(self, root):
freq_map = defaultdict(int) # key:元素,value:出现频率
result = []
if root is None:
return result
self.searchBST(root, freq_map)
max_freq = max(freq_map.values())
for key, freq in freq_map.items():
if freq == max_freq:
result.append(key)
return result
迭代法:
class Solution:
def findMode(self, root):
st = []
cur = root
pre = None
maxCount = 0 # 最大频率
count = 0 # 统计频率
result = []
while cur is not None or st:
if cur is not None: # 指针来访问节点,访问到最底层
st.append(cur) # 将访问的节点放进栈
cur = cur.left # 左
else:
cur = st.pop()
if pre is None: # 第一个节点
count = 1
elif pre.val == cur.val: # 与前一个节点数值相同
count += 1
else: # 与前一个节点数值不同
count = 1
if count == maxCount: # 如果和最大值相同,放进result中
result.append(cur.val)
if count > maxCount: # 如果计数大于最大值频率
maxCount = count # 更新最大频率
result = [cur.val] # 很关键的一步,不要忘记清空result,之前result里的元素都失效了
pre = cur
cur = cur.right # 右
return result
236.二叉树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
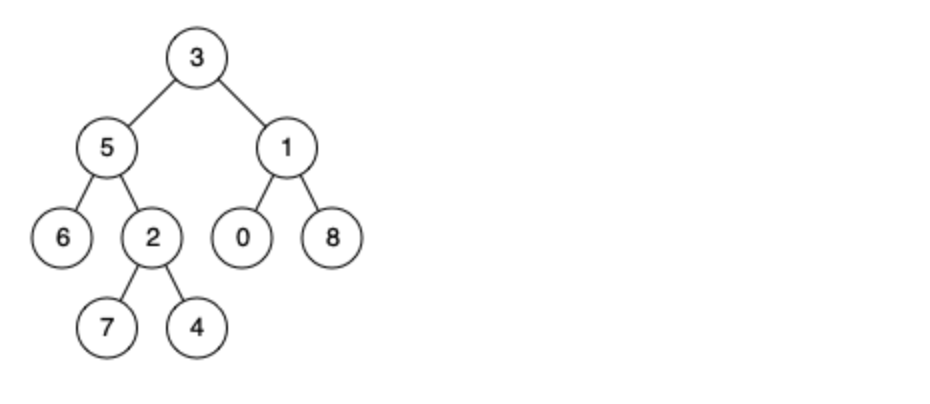
示例 1: 输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 输出: 3 解释: 节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3。
示例 2: 输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4 输出: 5 解释: 节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
说明:
- 所有节点的值都是唯一的。
- p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉树中。
思路:核心思路是找到两个节点的路径,使用递归,找到目标节点后,回溯过程中目标节点的每一个父亲节点都记录在数组中,这样两个节点就会得到两个父亲数组。这两个父亲数组最后一个父亲一定都是根节点,所以这个两个数组可能重叠的部分(公共祖先)一定是数组倒序的那几个节点,找到所有公共祖先中下标最小的那个节点就是他们的最近公共祖先。
代码实现如下:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
result1 = []
result2 = []
self.findnode(root, p, result1)
self.findnode(root, q, result2)
i, j = len(result1)-1, len(result2)-1
while i-1>=0 and j-1>=0 and result1[i-1] == result2[j-1]:
i -= 1
j -= 1
return result1[i]
def findnode(self, node, target, result):
if not node:
return False
if node == target:
result.append(node)
return True
if node.left:
if (left := self.findnode(node.left, target, result)):
result.append(node)
return left
if node.right:
if (right := self.findnode(node.right, target, result)):
result.append(node)
return right
return False
规范代码:
递归法(版本一):
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
if root == q or root == p or root is None:
return root
left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if left is not None and right is not None:
return root
if left is None and right is not None:
return right
elif left is not None and right is None:
return left
else:
return None
递归法(版本二)精简:
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
if root == q or root == p or root is None:
return root
left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if left is not None and right is not None:
return root
if left is None:
return right
return left
