Conveyor Belts
题面翻译
传送带
题目描述
传送带 $ m_n $ 是一个大小为 $ n \times n $ 的矩阵,其中 $ n $ 是一个偶数。矩阵由顺时针移动的同心带组成。
换句话说,当 n = 2 n=2 n=2 时,传送带矩阵就是一个 2 × 2 2 \times 2 2×2 的矩阵,其单元格形成顺时针长度为 4 4 4 的循环。对于任何自然数 k ≥ 2 k \ge 2 k≥2,矩阵 m 2 k m_{2k} m2k 是通过向矩阵 m 2 k − 2 m_{2k-2} m2k−2 添加形成顺时针循环的外层而获得的。
你站在坐标为 ( x 1 , y 1 ) (x_1,y_1) (x1,y1) 的单元格上,想要到达坐标为 ( x 2 , y 2 ) (x_2,y_2) (x2,y2) 的单元格。每秒钟你会移动到你所在的带子上的下一个单元格。你也可以通过花费一单位能量移动到相邻的单元格。移动是即时发生的,你可以随时进行无限次移动。
你的任务是找到从坐标为 ( x 1 , y 1 ) (x_1,y_1) (x1,y1) 的单元格到坐标为 ( x 2 , y 2 ) (x_2,y_2) (x2,y2) 的单元格所需的最小能量。
例如,当 n = 8 n=8 n=8 时,你最初在坐标为 ( 1 , 3 ) (1,3) (1,3) 的单元格中,并且你想要进入坐标为 ( 6 , 4 ) (6,4) (6,4) 的单元格。你可以立即进行 2 2 2 次移动
题目描述
Conveyor matrix $ m_n $ is matrix of size $ n \times n $ , where $ n $ is an even number. The matrix consists of concentric ribbons moving clockwise.
In other words, the conveyor matrix for $ n = 2 $ is simply a matrix $ 2 \times 2 $ , whose cells form a cycle of length $ 4 $ clockwise. For any natural $ k \ge 2 $ , the matrix $ m_{2k} $ is obtained by adding to the matrix $ m_{2k - 2} $ an outer layer forming a clockwise cycle.
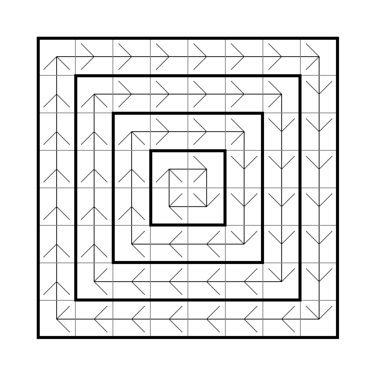 The conveyor matrix $ 8 \times 8 $ . You are standing in a cell with coordinates $ x_1, y_1 $ and you want to get into a cell with coordinates $ x_2, y_2 $ . A cell has coordinates $ x, y $ if it is located at the intersection of the $ x $ th row and the $ y $ th column.
The conveyor matrix $ 8 \times 8 $ . You are standing in a cell with coordinates $ x_1, y_1 $ and you want to get into a cell with coordinates $ x_2, y_2 $ . A cell has coordinates $ x, y $ if it is located at the intersection of the $ x $ th row and the $ y $ th column.
Standing on some cell, every second you will move to the cell next in the direction of movement of the tape on which you are. You can also move to a neighboring cell by spending one unit of energy. Movements happen instantly and you can make an unlimited number of them at any time.
Your task is to find the minimum amount of energy that will have to be spent to get from the cell with coordinates $ x_1, y_1 $ to the cell with coordinates $ x_2, y_2 $ .
For example, $ n=8 $ initially you are in a cell with coordinates $ 1,3 $ and you want to get into a cell with coordinates $ 6, 4 $ . You can immediately make $ 2 $ movements, once you are in a cell with coordinates $ 3, 3 $ , and then after $ 8 $ seconds you will be in the right cell.
输入格式
The first line contains an integer $ t $ ( $ 1 \le t \le 2 \cdot 10^5 $ ) — the number of test cases.
The descriptions of the test cases follow.
The description of each test case consists of one string containing five integers $ n $ , $ x_1 $ , $ y_1 $ , $ x_2 $ and $ y_2 $ ( $ 1 \le x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2 \le n \le 10^9 $ ) — matrix size and the coordinates of the start and end cells. It is guaranteed that the number $ n $ is even.
输出格式
For each test case, print one integer in a separate line — the minimum amount of energy that will have to be spent to get from the cell with coordinates $ x_1, y_1 $ to the cell with coordinates $ x_2, y_2 $ .
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
5
2 1 1 2 2
4 1 4 3 3
8 1 3 4 6
100 10 20 50 100
1000000000 123456789 987654321 998244353 500000004
样例输出 #1
0
1
2
9
10590032
思路:将物件放在同一区域在进行计算更好
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e6 + 10;
const int M = 1e9 + 7;
const int MOD = 998244353;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll>PII;
typedef pair<double, double>PDD;int dx[] = {1, 1, -1, -1, 2, 2, -2, -2};
int dy[] = {2, -2, 2, -2, 1, -1, 1, -1};int t;
int main()
{cin >> t;while(t --){ll n, a, b, c, d;cin >> n >> a >> b >> c >> d;if(a > n / 2) a = n - a + 1;if(b > n / 2) b = n - b + 1;if(c > n / 2) c = n - c + 1;if(d > n / 2) d = n - d + 1;//让两个物件处于左上角//处在第几层ll o1 = min(a, b), o2 = min(c, d);cout << abs(o1 - o2) << endl;}return 0;
}
