在这篇文章中,我将介绍如何使用 Google Colab 中的 Landcover.ai 数据集实现 UNet 架构进行地理空间图像分割
什么是 UNet?
UNet 是一种卷积神经网络架构,专为生物医学图像分割而设计。其结构类似于“U”形(因此得名),其中收缩路径(编码器)和扩张路径(解码器)通过跳跃连接连接。这些跳跃连接可帮助网络保留在下采样过程中可能丢失的空间信息。
虽然 UNet 最初是为生物医学应用而开发的,但已被证明对各种图像分割任务非常有效,包括卫星和航空图像分析。
项目概况
该项目实现了一个 UNet 模型,对 Landcover.ai 数据集执行语义分割,该数据集包含标有五类的高分辨率航空图像:
- 背景
- 建筑
- 兀兰
- 水
- 道路
目标是训练一个模型,可以从航空图像中自动识别和分类这些不同的土地覆盖类型。
实施步骤
- 准备步骤
我们首先安装项目所需的库:
- 数据库(用于数据增强)
- torch、torchinfo、torchmetrics(PyTorch 和相关工具)
- kornia(计算机视觉库)
- opencv-python(图像处理)
# Install required packages !pip install albumentations !pip install torch torchinfo torchmetrics kornia opencv-python import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib from matplotlib import pyplot as pltimport os import cv2 import albumentations as Aimport torch import torch.nn as nn from torch.nn import functional as F from torch.utils.data.dataset import Dataset from torch.utils.data import DataLoaderfrom torchinfo import summary import torchmetrics as tm from kornia import losses# Check if CUDA is available and set device device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") print(f"Using device: {device}")2. 下载并准备数据集 Landcover.ai 数据集由高分辨率正射影像和相应的分割掩模组成。下载数据集后,我们将其分割成 512×512 像素的较小图像芯片,以使其更易于训练:
# Create directories !mkdir -p landcover_data/images !mkdir -p landcover_data/masks !mkdir -p landcover_data/chips# Download the Landcover.ai dataset !wget -q https://landcover.ai.linuxpolska.com/download/landcover.ai.v1.zip !unzip -q landcover.ai.v1.zip -d landcover_data# Check if files were downloaded successfully print("Files in landcover_data directory:") !ls -la landcover_data3. 创建芯片生成脚本
原始正射影像非常大,因此我们将其分割成更小的 512×512 像素芯片。这不仅使训练更有效率,而且还创建了更多的训练样本:
import glob import os import cv2# Define directories IMGS_DIR = "landcover_data/images/" MASKS_DIR = "landcover_data/masks/" OUTPUT_DIR = "landcover_data/chips/"TARGET_SIZE = 512# Find all image and mask files img_paths = glob.glob(os.path.join(IMGS_DIR, "*.tif")) mask_paths = glob.glob(os.path.join(MASKS_DIR, "*.tif"))img_paths.sort() mask_paths.sort()# Check if we found images and masks print(f"Found {len(img_paths)} images and {len(mask_paths)} masks")# Create output directory if it doesn't exist os.makedirs(OUTPUT_DIR, exist_ok=True)# Define a function to process a limited number of images for testing, for less number of orthophotos change value of limit def process_images(img_paths, mask_paths, limit=41):for i, (img_path, mask_path) in enumerate(zip(img_paths[:limit], mask_paths[:limit])):img_filename = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(img_path))[0]mask_filename = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(mask_path))[0]img = cv2.imread(img_path)mask = cv2.imread(mask_path)# Skip if either image or mask couldn't be readif img is None or mask is None:print(f"Warning: Could not read {img_path} or {mask_path}")continueassert img_filename == mask_filename and img.shape[:2] == mask.shape[:2]k = 0for y in range(0, img.shape[0], TARGET_SIZE):for x in range(0, img.shape[1], TARGET_SIZE):img_tile = img[y:y + TARGET_SIZE, x:x + TARGET_SIZE]mask_tile = mask[y:y + TARGET_SIZE, x:x + TARGET_SIZE]if img_tile.shape[0] == TARGET_SIZE and img_tile.shape[1] == TARGET_SIZE:out_img_path = os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, "{}_{}.jpg".format(img_filename, k))cv2.imwrite(out_img_path, img_tile)out_mask_path = os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, "{}_{}_m.png".format(mask_filename, k))cv2.imwrite(out_mask_path, mask_tile)k += 1print(f"Processed {img_filename} ({i + 1}/{min(limit, len(img_paths))})")# Process a limited number of images first to test # process_images(img_paths, mask_paths, limit=2) # Process all images since test worked well process_images(img_paths, mask_paths)# Check if chips were created print("Generated chips:") !ls -la landcover_data/chips/ | head4. 创建自定义训练/验证/测试分割 我们将数据集分为训练集(70%)、验证集(15%)和测试集(15%):
# Create our own train/val/test splits based on generated chips import random# Get list of all image files (not masks) all_files_in_chips_folder=[f for f in os.listdir(OUTPUT_DIR)] print(f"Total files found in {OUTPUT_DIR} folder: {len(all_files_in_chips_folder)}") all_image_chips = [f for f in os.listdir(OUTPUT_DIR) if f.endswith('.jpg')] print(f"Total image chips found: {len(all_image_chips)}") all_mask_chips = [f for f in os.listdir(OUTPUT_DIR) if f.endswith('_m.png')] print(f"Total mask chips found: {len(all_mask_chips)}")# Shuffle the list for randomization random.seed(42) # For reproducibility random.shuffle(all_image_chips)# Split into train/val/test (70%/15%/15%) train_size = int(0.7 * len(all_image_chips)) val_size = int(0.15 * len(all_image_chips))train_files = all_image_chips[:train_size] val_files = all_image_chips[train_size:train_size+val_size] test_files = all_image_chips[train_size+val_size:]print(f"Split sizes - Train: {len(train_files)}, Val: {len(val_files)}, Test: {len(test_files)}")# Create new txt files with our splits with open("landcover_data/train.txt", "w") as f:for file in train_files:f.write(f"{os.path.splitext(file)[0]}\n")with open("landcover_data/val.txt", "w") as f:for file in val_files:f.write(f"{os.path.splitext(file)[0]}\n")with open("landcover_data/test.txt", "w") as f:for file in test_files:f.write(f"{os.path.splitext(file)[0]}\n")print("Created new train/val/test split files")5. 创建数据集类别列表并处理训练/验证/测试分割
# Define our class names CLASSES = ['background', 'building', 'woodlands', 'water', 'road'] OUTPUT_DIR = "landcover_data/chips/"# Check if the train/val/test split files exist in the downloaded dataset !ls -la landcover_data/*.txt# Now read these files into DataFrames trainDF = pd.read_csv("landcover_data/train.txt", header=None, names=["file"]) trainDF["img"] = OUTPUT_DIR + trainDF['file'] + ".jpg" trainDF["mask"] = OUTPUT_DIR + trainDF['file'] + "_m.png"valDF = pd.read_csv("landcover_data/val.txt", header=None, names=["file"]) valDF["img"] = OUTPUT_DIR + valDF['file'] + ".jpg" valDF["mask"] = OUTPUT_DIR + valDF['file'] + "_m.png"testDF = pd.read_csv("landcover_data/test.txt", header=None, names=["file"]) testDF["img"] = OUTPUT_DIR + testDF['file'] + ".jpg" testDF["mask"] = OUTPUT_DIR + testDF['file'] + "_m.png"# Display the first few rows of the training DataFrame print("Training DataFrame sample:") print(trainDF.head())# Check if the image and mask files exist print("\nChecking if files exist:") print(f"First training image exists: {os.path.exists(trainDF['img'].iloc[0])}") print(f"First training mask exists: {os.path.exists(trainDF['mask'].iloc[0])}") # Function to display a few samples from the training data def display_samples(df, num_samples=3):plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5*num_samples))for i in range(min(num_samples, len(df))):# Read image and maskimg_path = df['img'].iloc[i]mask_path = df['mask'].iloc[i]try:# Read and convert imageimage = cv2.imread(img_path)image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)# Read maskmask = cv2.imread(mask_path, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)if mask is not None:mask = mask[:,:,0] # Take first channel# Displayplt.subplot(num_samples, 2, 2*i+1)plt.title(f"Image {i+1}: {os.path.basename(img_path)}")plt.imshow(image)plt.axis('off')plt.subplot(num_samples, 2, 2*i+2)plt.title(f"Mask {i+1}")if mask is not None:plt.imshow(mask)else:plt.text(0.5, 0.5, "Mask not found", horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center')plt.axis('off')except Exception as e:plt.subplot(num_samples, 2, 2*i+1)plt.text(0.5, 0.5, f"Error loading image: {str(e)}", horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center')plt.axis('off')plt.subplot(num_samples, 2, 2*i+2)plt.text(0.5, 0.5, f"Error loading mask: {str(e)}", horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center')plt.axis('off')plt.tight_layout()plt.show()# Display samples from the training set print("Displaying samples from the training dataset:") display_samples(trainDF, num_samples=4)
让我们检查一下 Landcover.ai 数据集中不同的掩膜颜色及其含义:
# Let's examine the mask values and their meanings
def explore_mask_values(df, num_samples=5):# Define the class names and colors for visualizationclass_names = ['background', 'building', 'woodland', 'water', 'road']class_colors = [(255, 255, 255), (255, 0, 0), (0, 255, 0), (0, 0, 255), (255, 255, 0)]unique_values = set()print("Examining mask values in sample images:")for i in range(min(num_samples, len(df))):mask_path = df['mask'].iloc[i]try:# Read maskmask = cv2.imread(mask_path, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)if mask is not None:# Take first channel (since masks are single-channel)mask_channel = mask[:,:,0]# Get unique valuesvalues = np.unique(mask_channel)unique_values.update(values)print(f"Mask {i+1}: {os.path.basename(mask_path)}")print(f" Unique values: {values}")# Count pixels for each classfor val in values:if val < len(class_names):class_name = class_names[val]count = np.sum(mask_channel == val)percentage = (count / mask_channel.size) * 100print(f" Class {val} ({class_name}): {count} pixels ({percentage:.2f}%)")print()# Display the mask with color-codingplt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))# Original maskplt.subplot(1, 2, 1)plt.title(f"Original Mask {i+1}")plt.imshow(mask_channel)plt.colorbar(label='Class ID')# Colored maskplt.subplot(1, 2, 2)plt.title(f"Color-coded Mask {i+1}")# Create RGB mask for visualizationh, w = mask_channel.shapergb_mask = np.zeros((h, w, 3), dtype=np.uint8)for cls_id, color in enumerate(class_colors):if cls_id < len(class_colors): # Ensure we don't go out of boundsrgb_mask[mask_channel == cls_id] = colorplt.imshow(rgb_mask)# Add legendlegend_elements = [plt.Rectangle((0, 0), 1, 1, color=np.array(color)/255)for color in class_colors[:len(class_names)]]plt.legend(legend_elements, class_names, loc='upper right')plt.tight_layout()plt.show()except Exception as e:print(f"Error processing mask {mask_path}: {str(e)}")print(f"All unique values found across {num_samples} masks: {sorted(unique_values)}")# Explore the mask values
explore_mask_values(trainDF, num_samples=3)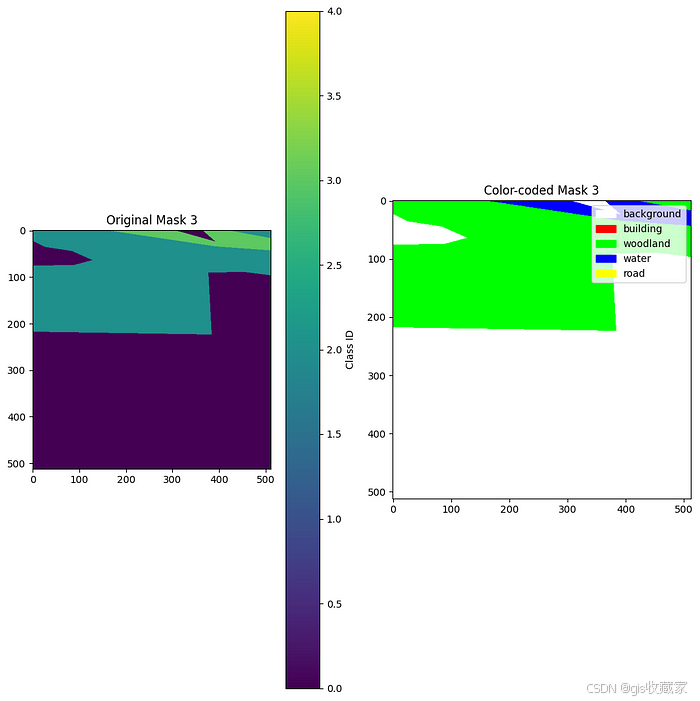
6. 创建自定义数据集、DataLoader 类和数据增强 现在,让我们实现自定义数据集类和数据增强的转换:
# Define the custom dataset class with better error handling
class MultiClassSegDataset(Dataset):def __init__(self, df, transform=None):# Filter out rows with non-existent filesvalid_rows = []for i, row in df.iterrows():if os.path.exists(row['img']) and os.path.exists(row['mask']):valid_rows.append(i)self.df = df.iloc[valid_rows].reset_index(drop=True)print(f"Found {len(self.df)} valid image-mask pairs out of {len(df)} entries")self.transform = transformdef __getitem__(self, idx):image_name = self.df.iloc[idx, 1]mask_name = self.df.iloc[idx, 2]# Read image and mask with error checkingimage = cv2.imread(image_name)if image is None:raise ValueError(f"Failed to read image: {image_name}")image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)mask = cv2.imread(mask_name, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)if mask is None:raise ValueError(f"Failed to read mask: {mask_name}")# Convert to appropriate typesimage = image.astype('uint8')mask = mask[:,:,0] # Take first channel of mask# Apply transformations if providedif self.transform is not None:transformed = self.transform(image=image, mask=mask)image = transformed["image"]mask = transformed["mask"]# Convert to tensorsimage = torch.from_numpy(image)mask = torch.from_numpy(mask)# Convert image to channels-first format and normalizeimage = image.permute(2, 0, 1)image = image.float()/255# Convert mask to long typemask = mask.long()return image, maskdef __len__(self):return len(self.df)# Verify that the file paths in the DataFrames are correct
print("Checking file paths in DataFrames:")
print(f"Example training image path: {trainDF['img'].iloc[0]}")
print(f"Example training mask path: {trainDF['mask'].iloc[0]}")
print(f"File exists: {os.path.exists(trainDF['img'].iloc[0])}")# Check and perhaps modify file paths if needed
# For example, if paths have double slashes or other issues:
trainDF['img'] = trainDF['img'].apply(lambda x: os.path.normpath(x))
trainDF['mask'] = trainDF['mask'].apply(lambda x: os.path.normpath(x))
valDF['img'] = valDF['img'].apply(lambda x: os.path.normpath(x))
valDF['mask'] = valDF['mask'].apply(lambda x: os.path.normpath(x))
testDF['img'] = testDF['img'].apply(lambda x: os.path.normpath(x))
testDF['mask'] = testDF['mask'].apply(lambda x: os.path.normpath(x))# Define transforms for validation and test sets
test_transform = A.Compose([A.PadIfNeeded(min_height=512, min_width=512, border_mode=4),A.Resize(512, 512),
])# Define transforms for training set (with augmentations)
train_transform = A.Compose([A.PadIfNeeded(min_height=512, min_width=512, border_mode=4),A.Resize(512, 512),A.RandomBrightnessContrast(brightness_limit=0.3, contrast_limit=0.3, p=0.5),A.HorizontalFlip(p=0.5),A.VerticalFlip(p=0.5),A.MedianBlur(blur_limit=3, p=0.1), # Removed 'always_apply' parameter
])# Initialize datasets with error handling
trainDS = MultiClassSegDataset(trainDF, transform=train_transform)
valDS = MultiClassSegDataset(valDF, transform=test_transform)
testDS = MultiClassSegDataset(testDF, transform=test_transform)# Print dataset sizes
print(f"Final Training Samples: {len(trainDS)}")
print(f"Final Validation Samples: {len(valDS)}")
print(f"Final Testing Samples: {len(testDS)}")# Initialize DataLoaders with small batch size initially
trainDL = DataLoader(trainDS, batch_size=4, shuffle=True, num_workers=0, pin_memory=False, drop_last=True)
valDL = DataLoader(valDS, batch_size=4, shuffle=False, num_workers=0, pin_memory=False, drop_last=True)
testDL = DataLoader(testDS, batch_size=4, shuffle=False, num_workers=0, pin_memory=False, drop_last=True)# Try to get a single batch
try:batch = next(iter(trainDL))images, labels = batchprint(f"Successfully loaded a batch!")print(f"Batch shapes - Images: {images.shape}, Labels: {labels.shape}")print(f"Data types - Images: {images.dtype}, Labels: {labels.dtype}")# Display a sample image and maskplt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)plt.title("Sample Image")plt.imshow(images[0].permute(1, 2, 0)) # Convert back to channels-last for displayplt.subplot(1, 2, 2)plt.title("Sample Mask")plt.imshow(labels[0])plt.show()
except Exception as e:print(f"Error loading batch: {str(e)}")# If we failed, try to identify the issueprint("\nInvestigating the issue:")sample_idx = 0print(f"Trying to load image: {trainDS.df['img'].iloc[sample_idx]}")try:img = cv2.imread(trainDS.df['img'].iloc[sample_idx])if img is None:print(f"cv2.imread returned None - file might not exist or has format issues")else:print(f"Successfully loaded image with shape: {img.shape}")except Exception as e:print(f"Error: {str(e)}")
O/P 检查 DataFrames 中的文件路径:示例训练图像路径:landcover_data/chips/M-34–65-Da-4–4_57.jpg 示例训练掩码路径:landcover_data/chips/M-34–65-Da-4–4_57_m.png 文件存在:True 在 7471 个条目中发现 7471 个有效图像掩码对 在 1601 个条目中发现 1601 个有效图像掩码对 在 1602 个条目中发现 1602 个有效图像掩码对 最终训练样本:7471 最终验证样本:1601 最终测试样本:1602 成功加载批次!批次形状 — 图像:torch.Size([4, 3, 512, 512]),标签:torch.Size([4, 512, 512]) 数据类型 — 图像:torch.float32,标签:torch.int64
 7. 定义 UNet 架构
7. 定义 UNet 架构
# Helper functions for UNet architecture
def double_conv(inChannels, outChannels):return nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(inChannels, outChannels, kernel_size=(3,3), stride=1, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(outChannels),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(outChannels, outChannels, kernel_size=(3,3), stride=1, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(outChannels),nn.ReLU(inplace=True))def up_conv(inChannels, outChannels):return nn.Sequential(nn.ConvTranspose2d(inChannels, outChannels, kernel_size=(2,2), stride=2),nn.BatchNorm2d(outChannels),nn.ReLU(inplace=True))# UNet model architecture
class myUNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, encoderChn, decoderChn, inChn, botChn, nCls):super().__init__()self.encoderChn = encoderChnself.decoderChn = decoderChnself.botChn = botChnself.nCls = nCls# Encoder pathself.encoder1 = double_conv(inChn, encoderChn[0])self.encoder2 = nn.Sequential(nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),double_conv(encoderChn[0], encoderChn[1]))self.encoder3 = nn.Sequential(nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),double_conv(encoderChn[1], encoderChn[2]))self.encoder4 = nn.Sequential(nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),double_conv(encoderChn[2], encoderChn[3]))# Bottleneckself.bottleneck = nn.Sequential(nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),double_conv(encoderChn[3], botChn))# Decoder path with skip connectionsself.decoder1up = up_conv(botChn, botChn)self.decoder1 = double_conv(encoderChn[3]+botChn, decoderChn[0])self.decoder2up = up_conv(decoderChn[0], decoderChn[0])self.decoder2 = double_conv(encoderChn[2]+decoderChn[0], decoderChn[1])self.decoder3up = up_conv(decoderChn[1], decoderChn[1])self.decoder3 = double_conv(encoderChn[1]+decoderChn[1], decoderChn[2])self.decoder4up = up_conv(decoderChn[2], decoderChn[2])self.decoder4 = double_conv(encoderChn[0]+decoderChn[2], decoderChn[3])# Final classifierself.classifier = nn.Conv2d(decoderChn[3], nCls, kernel_size=(1,1))def forward(self, x):# Encoderencoder1 = self.encoder1(x)encoder2 = self.encoder2(encoder1)encoder3 = self.encoder3(encoder2)encoder4 = self.encoder4(encoder3)# Bottleneckx = self.bottleneck(encoder4)# Decoder with skip connectionsx = self.decoder1up(x)x = torch.concat([x, encoder4], dim=1)x = self.decoder1(x)x = self.decoder2up(x)x = torch.concat([x, encoder3], dim=1)x = self.decoder2(x)x = self.decoder3up(x)x = torch.concat([x, encoder2], dim=1)x = self.decoder3(x)x = self.decoder4up(x)x = torch.concat([x, encoder1], dim=1)x = self.decoder4(x)# Classifier headx = self.classifier(x)return x# Instantiate the model
model = myUNet(encoderChn=[16, 32, 64, 128],decoderChn=[128, 64, 32, 16],inChn=3,botChn=512,nCls=5
).to(device)# Print model summary
summary(model, (4, 3, 512, 512)) # Match our batch size of 48.设置损失函数、优化器和指标
# Define loss function - Dice Loss from kornia
criterion = losses.DiceLoss(average="macro")# Define optimizer with AdamW and initial learning rate
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=0.0001)# Define learning rate scheduler
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.OneCycleLR(optimizer,max_lr=0.01,epochs=50,steps_per_epoch=len(trainDL),three_phase=True
)# Define evaluation metrics
acc = tm.Accuracy(task="multiclass", num_classes=5, average="micro").to(device)
f1 = tm.F1Score(task="multiclass", num_classes=5, average="macro").to(device)
kappa = tm.CohenKappa(task="multiclass", num_classes=5).to(device)# Define the number of epochs and save folder
epochs = 50
save_folder = "model_checkpoints/"
os.makedirs(save_folder, exist_ok=True)# Initialize lists to store metrics
eNum = []
t_loss = []
t_acc = []
t_f1 = []
t_kappa = []
v_loss = []
v_acc = []
v_f1 = []
v_kappa = []# Initialize best validation F1 score
f1VMax = 0.0print("Setup complete for training!")
print(f"Training for {epochs} epochs")
print(f"Model checkpoints will be saved to: {save_folder}")
print(f"Loss function: {criterion.__class__.__name__}")
print(f"Optimizer: {optimizer.__class__.__name__}")
print(f"Learning rate scheduler: {scheduler.__class__.__name__}")输出
训练设置完成!;训练 50 个时期模型检查点将保存到:model_checkpoints/损失函数:DiceLoss优化器:AdamW学习率调度程序:OneCycleLR
9. 训练循环
# For demonstration purposes, let's set a smaller number of epochs
demo_epochs = 20 # You can increase this if you want to train longerprint(f"Starting training for {demo_epochs} epochs...")# Loop over epochs
for epoch in range(1, demo_epochs + 1):# Initialize running loss for epochrunning_loss = 0.0# Make sure model is in training modemodel.train()# Loop over training batchesfor batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(trainDL):# Get data and move to deviceinputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)# Clear gradientsoptimizer.zero_grad()# Forward passoutputs = model(inputs)# Calculate lossloss = criterion(outputs, targets)# Calculate metricsacc_val = acc(outputs, targets)f1_val = f1(outputs, targets)kappa_val = kappa(outputs, targets)# Backward passloss.backward()# Update parametersoptimizer.step()# Update learning ratescheduler.step()# Update running loss with batch resultsrunning_loss += loss.item()# Print progress every 5 batchesif (batch_idx + 1) % 5 == 0:print(f'Epoch: {epoch}, Batch: {batch_idx + 1}/{len(trainDL)}, Loss: {loss.item():.4f}')# Accumulate loss and metrics at end of training epochepoch_loss = running_loss / len(trainDL)acc_train = acc.compute()f1_train = f1.compute()kappa_train = kappa.compute()# Print losses and metrics at end of each training epochprint(f'Epoch: {epoch}, Training Loss: {epoch_loss:.4f}, Training Accuracy: {acc_train:.4f}, Training F1: {f1_train:.4f}, Training Kappa: {kappa_train:.4f}')# Append resultseNum.append(epoch)t_loss.append(epoch_loss)t_acc.append(acc_train.detach().cpu().numpy())t_f1.append(f1_train.detach().cpu().numpy())t_kappa.append(kappa_train.detach().cpu().numpy())# Reset metricsacc.reset()f1.reset()kappa.reset()# Make sure model is in eval modemodel.eval()# Loop over validation batcheswith torch.no_grad():# Initialize running validation lossrunning_loss_v = 0.0for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(valDL):# Get data and move to deviceinputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)# Forward passoutputs = model(inputs)# Calculate validation lossloss_v = criterion(outputs, targets)# Update running loss with batch resultsrunning_loss_v += loss_v.item()# Calculate metricsacc_val = acc(outputs, targets)f1_val = f1(outputs, targets)kappa_val = kappa(outputs, targets)# Accumulate loss and metrics at end of validation epochepoch_loss_v = running_loss_v / len(valDL)acc_val = acc.compute()f1_val = f1.compute()kappa_val = kappa.compute()# Print validation loss and metricsprint(f'Validation Loss: {epoch_loss_v:.4f}, Validation Accuracy: {acc_val:.4f}, Validation F1: {f1_val:.4f}, Validation Kappa: {kappa_val:.4f}')# Append resultsv_loss.append(epoch_loss_v)v_acc.append(acc_val.detach().cpu().numpy())v_f1.append(f1_val.detach().cpu().numpy())v_kappa.append(kappa_val.detach().cpu().numpy())# Reset metricsacc.reset()f1.reset()kappa.reset()# Save model if validation F1-score improvesf1_val_np = f1_val.detach().cpu().numpy()if f1_val_np > f1VMax:f1VMax = f1_val_nptorch.save(model.state_dict(), os.path.join(save_folder, 'landcoverai_unet_model.pt'))print(f'Model saved for epoch {epoch}.')# Save the training metrics to a CSV
results_df = pd.DataFrame({"epoch": eNum,"training_loss": t_loss,"training_accuracy": t_acc,"training_f1": t_f1,"training_kappa": t_kappa,"val_loss": v_loss,"val_accuracy": v_acc,"val_f1": v_f1,"val_kappa": v_kappa
})results_df.to_csv(os.path.join(save_folder, "training_results.csv"), index=False)
print(f"Training completed. Results saved to {os.path.join(save_folder, 'training_results.csv')}")10.可视化训练结果
# Load the training results
results_df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(save_folder, "training_results.csv"))# Plot training and validation loss
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(results_df['epoch'], results_df['training_loss'], label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(results_df['epoch'], results_df['val_loss'], label='Validation Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)# Plot training and validation F1 scores
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(results_df['epoch'], results_df['training_f1'], label='Training F1')
plt.plot(results_df['epoch'], results_df['val_f1'], label='Validation F1')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('F1 Score')
plt.title('Training and Validation F1 Score')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()# Print the epoch with the best validation F1 score
best_epoch = results_df.loc[results_df['val_f1'].idxmax()]
print(f"Best model was saved at epoch {int(best_epoch['epoch'])} with validation F1 score of {best_epoch['val_f1']:.4f}")由于 GPU 限制,我只测试了 20 个 epoch 的训练,Maxwell 教授测试了 50 个 epoch,您可以在我介绍中分享的原始文章中查看结果。
挑战与经验
在整个项目中,我遇到了几个挑战: 1.数据预处理:处理大型正射影像需要仔细的平铺和预处理。2.类别不平衡:一些土地覆盖类型(如水)出现的频率低于其他类型,这需要适当的损失函数。3.模型调整:找到合适的学习率和其他超参数需要进行实验,需要高 GPU 使用率,这是昂贵的。
