1. 前言
在将第三方数据源的数据导入到Elasticsearch中时,原始数据长什么样,索引后的文档就是什么样。文档数据结构不统一,导致后续数据分析时变得麻烦,以往需要额外写一个中间程序来读取原始数据,转换加工后再写入到Elasticsearch,比较麻烦,于是官方推出了Ingest pipeline。
Ingest pipeline 允许文档在被索引之前对数据进行预处理,将数据加工处理成我们需要的格式,例如删除或增加一些字段等。有了Ingest pipeline,就不需要我们再额外开发中间程序对数据进行加工转换等操作了,全权交给Elasticsearch即可。
2. 创建Ingest pipeline
Pipeline 由一系列处理器 Processor 组成,每个Processor按照顺序执行,对传入的文档进行加工处理,Elasticsearch再将加工后的文档添加到索引中。
默认情况下,每个节点都具备ingest能力,即文档预处理的能力。如果要预处理大量的文档,建议开启专门的ingest节点,配置如下:
node.roles: [ ingest ]
可以通过Elasticsearch提供的「_ingest/pipeline」端点来创建Ingest pipeline,如下示例,创建了一个名为“test-pipeline”的pipeline,它由三个Processor组成:lowercase负责将字段值改为小写、remove负责删除给定字段、rename负责重命名给定字段。
PUT _ingest/pipeline/test-pipeline
{"description": "测试pipeline","processors": [{"lowercase": {"field": "title"},"remove": {"field": "extended_data"},"rename": {"field": "field_a","target_field": "field_b"}}]
}
然后,我们就可以通过Elasticsearch提供的模拟API,来测试我们的Pipelline,如下示例:
POST _ingest/pipeline/test-pipeline/_simulate
{"docs": [{"_source": {"title": "我是TITLE","extended_data": "我是扩展数据","field_a": "我是要rename的field"}}]
}
Pipeline返回的结果符合我们的预期,字段title的值英文部分改为了等效的小写、extended_data字段被删除了、field_a被重命名为field_b。
{"docs": [{"doc": {"_index": "_index","_version": "-3","_id": "_id","_source": {"title": "我是title","field_b": "我是要rename的field"},"_ingest": {"timestamp": "2024-04-15T07:21:20.521194Z"}}}]
}
3. 内置的Processor
截止Elasticsearch8.13版本,官方内置了40多个的Processor供我们使用,如下是部分Processor示例:
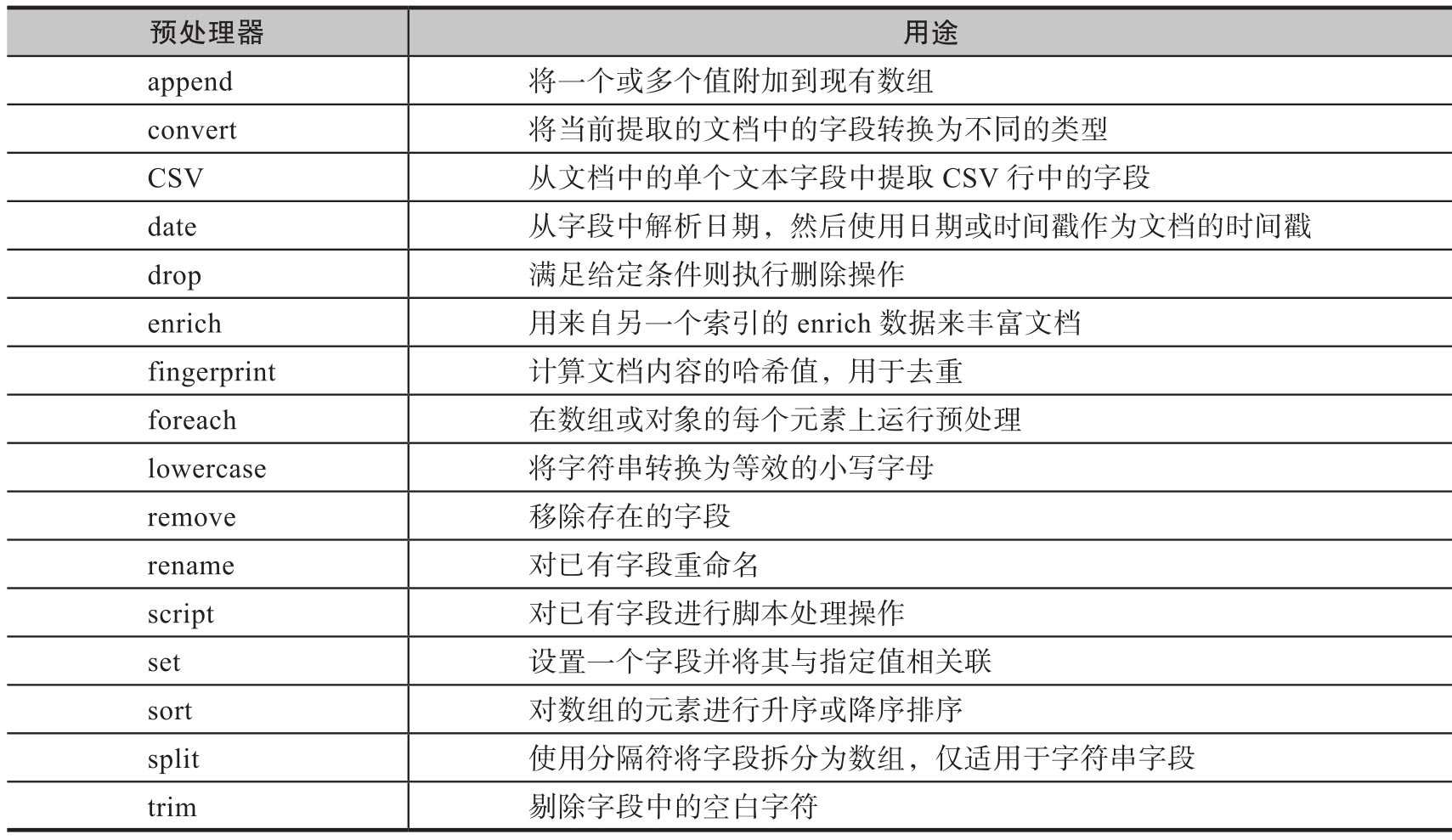
这里介绍几个常用的,其它参考官方文档即可。
append Processor:如果字段已经存在并且是一个数组,则向现有数组追加一个或多个值。
如下示例,如果文档存在tags字段并且是数组,则会自动追加给定的两个tag
PUT _ingest/pipeline/test-pipeline
{"processors": [{"append": {"field": "tags","value": ["年度十佳","Top100"]}}]
}
测试结果
POST _ingest/pipeline/test-pipeline/_simulate
{"docs": [{"_source": {"tags":["热门"]}}]
}{"docs": [{"doc": {"_index": "_index","_version": "-3","_id": "_id","_source": {"tags": ["热门","年度十佳","Top100"]},"_ingest": {"timestamp": "2024-04-15T07:31:23.089093Z"}}}]
}
bytes Processor:将人类可读的字节值(例如1KB)转换为整型字节值(例如1024),如果是数组则转换所有成员。
如下示例,字段memory将会由人类可读的字符串转换为整型字节值
PUT _ingest/pipeline/test-pipeline
{"processors": [{"bytes": {"field": "memory"}}]
}
测试结果
POST _ingest/pipeline/test-pipeline/_simulate
{"docs": [{"_source": {"memory":"132MB"}}]
}{"docs": [{"doc": {"_index": "_index","_version": "-3","_id": "_id","_source": {"memory": 138412032},"_ingest": {"timestamp": "2024-04-15T07:35:07.233976Z"}}}]
}
convert Processor:将文档中的某个字段转换为给定的数据类型,例如将字符串转换为布尔类型。数据类型转换不能随意配置,否则会报错,支持的类型有:integer、long、float、double、string、boolean、ip、auto。
如下示例,将字符串转换为布尔类型
PUT _ingest/pipeline/test-pipeline
{"processors": [{"convert": {"field": "deleted","type": "boolean"}}]
}
测试结果
POST _ingest/pipeline/test-pipeline/_simulate
{"docs": [{"_source": {"deleted":"false"}}]
}{"docs": [{"doc": {"_index": "_index","_version": "-3","_id": "_id","_source": {"deleted": false},"_ingest": {"timestamp": "2024-04-15T07:40:42.066717Z"}}}]
}
date Processor:从文档中的某个字段中解析时间,并将其作为文档的时间戳,默认时间戳的字段名为”@timestamp“。
如下示例,我们将publish_time作为文档的时间戳:
PUT _ingest/pipeline/test-pipeline
{"processors": [{"date": {"field": "publish_time","formats": ["yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"]}}]
}
测试结果:
POST _ingest/pipeline/test-pipeline/_simulate
{"docs": [{"_source": {"publish_time":"2024-01-01 00:00:00"}}]
}{"docs": [{"doc": {"_index": "_index","_version": "-3","_id": "_id","_source": {"publish_time": "2024-01-01 00:00:00","@timestamp": "2024-01-01T00:00:00.000Z"},"_ingest": {"timestamp": "2024-04-15T07:44:28.383089Z"}}}]
}
最后介绍一个功能强大的Processor:script,通过内联的自定义脚本来操作文档,使用起来相当灵活。
如下示例,Processor将从content字段中提取品牌、商品标题和价格,并移除掉content字段。
PUT _ingest/pipeline/test-pipeline
{"processors": [{"script": {"lang": "painless","source": """String[] splits = ctx['content'].splitOnToken(',');ctx['brand'] = splits[0];ctx['title'] = splits[1];ctx['price'] = Integer.parseInt(splits[2]);ctx.remove('content');"""}}]
}
测试结果
POST _ingest/pipeline/test-pipeline/_simulate
{"docs": [{"_source": {"content":"小米,小米汽车SU7,214900"}}]
}{"docs": [{"doc": {"_index": "_index","_version": "-3","_id": "_id","_source": {"title": "小米汽车SU7","brand": "小米","price": 214900},"_ingest": {"timestamp": "2024-04-15T07:58:44.134495Z"}}}]
}
4. 应用Ingest pipeline
Ingest pipeline创建好以后,主要有四类应用场景。
先创建一个名为”set-last-update-time-pipeline“的pipeline,它的目的是给文档设置一个最后修改的时间戳。
PUT _ingest/pipeline/set-last-update-time-pipeline
{"processors": [{"set": {"field": "last_update_time","value": "{{{_ingest.timestamp}}}"}}]
}
4.1 索引时指定pipeline
可以在索引文档时指定Pipeline,文档写入前会先经过管道的预处理。
下面是没指定Pipeline时写入文档和索引结果
POST test-index/_doc/1
{"title":"new doc"
}{"_index": "test-index","_id": "1","_version": 1,"_seq_no": 0,"_primary_term": 1,"found": true,"_source": {"title": "new doc"}
}
下面是指定Pipeline时索引文档和索引结果,发现文档自动添加了last_update_time字段。
POST test-index/_doc/1?pipeline=set-last-update-time-pipeline
{"title":"new doc"
}{"_index": "test-index","_id": "1","_version": 1,"_seq_no": 0,"_primary_term": 1,"found": true,"_source": {"title": "new doc","last_update_time": "2024-04-15T08:11:50.448923Z"}
}
4.2 更新时指定pipeline
在更新文档时,也可以指定Pipeline对要更新的文档执行预处理操作。
如下示例,先索引两个文档
POST test-index/_doc/1
{"title":"new doc1"
}
POST test-index/_doc/2
{"title":"new doc2"
}
然后利用”_update_by_query“端点来批量更新文档,同时指定pipeline,即可给所有文档添加last_update_time
POST test-index/_update_by_query?pipeline=set-last-update-time-pipeline
{"query": {"match_all": {}}
}
下面是更新后的文档结果
{"took": 0,"timed_out": false,"_shards": {"total": 1,"successful": 1,"skipped": 0,"failed": 0},"hits": {"total": {"value": 2,"relation": "eq"},"max_score": 1,"hits": [{"_index": "test-index","_id": "1","_score": 1,"_source": {"title": "new doc1","last_update_time": "2024-04-15T08:17:24.527237Z"}},{"_index": "test-index","_id": "2","_score": 1,"_source": {"title": "new doc2","last_update_time": "2024-04-15T08:17:24.528187Z"}}]}
}
4.3 索引映射指定pipeline
如果不想每次写入和更新时都指定Pipeline,也可以在创建索引时指定Pipeline,如下示例:
PUT test-index
{"settings": {"index":{"default_pipeline":"set-last-update-time-pipeline"}}, "mappings": {"properties": {"title":{"type": "keyword"}}}
}
索引文档或更新文档时,会自动触发对应的Pipeline对文档进行预处理。如下示例,写入两篇文档不指定Pipeline
POST test-index/_doc/1
{"title":"new doc1"
}
POST test-index/_doc/2
{"title":"new doc2"
}
检索文档发现均已添加last_update_time字段
[{"_index": "test-index","_id": "1","_score": 1,"_source": {"title": "new doc1","last_update_time": "2024-04-15T08:21:49.591599Z"}},{"_index": "test-index","_id": "2","_score": 1,"_source": {"title": "new doc2","last_update_time": "2024-04-15T08:21:49.592733Z"}}
]
4.4 reindex指定pipeline
Elasticsearch提供了reindex API用于将一个索引的文档复制到另一个索引,reindex过程也可以指定Pipeline在写入目标索引前进行预处理。
如下示例,先定义源索引以及写入两篇文档
PUT source-index
{"mappings": {"properties": {"title":{"type": "keyword"}}}
}POST source-index/_doc
{"title":"doc1"
}
POST source-index/_doc
{"title":"doc2"
}
接着定义目标索引,映射新增last_update_time字段
PUT dest-index
{"mappings": {"properties": {"title":{"type": "keyword"},"last_update_time":{"type": "date"}}}
}
然后调用reindex API完成文档迁移
POST _reindex
{"source": {"index": "source-index"},"dest": {"index": "dest-index","pipeline": "set-last-update-time-pipeline"}
}
最后查看dest-index文档数据,发现均添加last_update_time字段
[{"_index": "dest-index","_id": "glfh4I4BXAgLe9UUkOwp","_score": 1,"_source": {"title": "doc1","last_update_time": "2024-04-15T08:43:18.905182Z"}},{"_index": "dest-index","_id": "g1fh4I4BXAgLe9UUkuy1","_score": 1,"_source": {"title": "doc2","last_update_time": "2024-04-15T08:43:18.906068Z"}}
]
5. 尾巴
Ingest Pipelines 是Elasticsearch一个非常实用的功能,它类似于大数据中的ETL,在真正索引数据前,先经过Pipeline完成数据的清洗和加工,把原始数据转换成我们想要的格式再索引,利于后续的数据分析。默认情况下,所有节点都具备Ingest能力,如果要预处理大量文档,建议部署专门的ingest节点,避免影响到主数据节点。
