背景
我们继续分析EurekaClient的两个自动化配置类:
| 自动化配置类 | 功能 | 职责 |
| EurekaClientAutoConfiguration | 配置EurekaClient | 确保了Eureka客户端能够正确地: - 注册到Eureka服务端 - 周期性地发送心跳信息来更新服务租约 - 下线时通知Eureka服务端 - 获取服务实例列表; 更侧重于Eureka客户端的基本配置和功能实现 |
| EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration | 配置EurekaDiscoveryClient | 创建RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent事件的监听类,用于重启注册; 更多地涉及到服务的自动注册、健康检查以及事件处理等方面 |
CloudEurekaClient分析
原理
客户端本质就是4个动作:
获取服务列表
注册服务实例
租约续约
取消租约
源码
让我们继续关注 第一个自动装配类 EurekaClientAutoConfiguration 对CloudEurekaClient 的构造封装,即如下代码块:
@Bean(destroyMethod = "shutdown")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EurekaClient.class,search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public EurekaClient eurekaClient(ApplicationInfoManager manager,EurekaClientConfig config) {return new CloudEurekaClient(manager, config, this.optionalArgs,this.context);
}分析代码:
CloudEurekaClient对象,并交给容器管理bean
CloudEurekaClient
public class CloudEurekaClient extends DiscoveryClient {public CloudEurekaClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager,EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs<?> args,ApplicationEventPublisher publisher) {super(applicationInfoManager, config, args);this.applicationInfoManager = applicationInfoManager;this.publisher = publisher;this.eurekaTransportField = ReflectionUtils.findField(DiscoveryClient.class,"eurekaTransport");ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(this.eurekaTransportField);}
}分析代码:
实际上CloudEurekaClient调用了父类DiscoveryClient的构造器
DiscoveryClient
经历了多个重载构造器的嵌套,我们进入了最终的构造器:
private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler;
// additional executors for supervised subtasks
private final ThreadPoolExecutor heartbeatExecutor;
private final ThreadPoolExecutor cacheRefreshExecutor;@Inject
DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args,Provider<BackupRegistry> backupRegistryProvider, EndpointRandomizer endpointRandomizer) {// .... 一些初始化工作logger.info("Initializing Eureka in region {}", clientConfig.getRegion());try {// default size of 2 - 1 each for heartbeat and cacheRefreshscheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2,new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-%d").setDaemon(true).build());heartbeatExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-HeartbeatExecutor-%d").setDaemon(true).build()); // use direct handoffcacheRefreshExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-CacheRefreshExecutor-%d").setDaemon(true).build()); // use direct handoffeurekaTransport = new EurekaTransport();scheduleServerEndpointTask(eurekaTransport, args);AzToRegionMapper azToRegionMapper;if (clientConfig.shouldUseDnsForFetchingServiceUrls()) {azToRegionMapper = new DNSBasedAzToRegionMapper(clientConfig);} else {azToRegionMapper = new PropertyBasedAzToRegionMapper(clientConfig);}if (null != remoteRegionsToFetch.get()) {azToRegionMapper.setRegionsToFetch(remoteRegionsToFetch.get().split(","));}instanceRegionChecker = new InstanceRegionChecker(azToRegionMapper, clientConfig.getRegion());} catch (Throwable e) {throw new RuntimeException("Failed to initialize DiscoveryClient!", e);}// .......if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka() && clientConfig.shouldEnforceRegistrationAtInit()) {try {if (!register() ) {throw new IllegalStateException("Registration error at startup. Invalid server response.");}} catch (Throwable th) {logger.error("Registration error at startup: {}", th.getMessage());throw new IllegalStateException(th);}}// finally, init the schedule tasks (e.g. cluster resolvers, heartbeat, instanceInfo replicator, fetchinitScheduledTasks();// ...其他初始化工作
}代码分析:
这里初始化了3个异步线程池:scheduler、heartbeatExecutor、cacheRefreshExecutor
scheduler:coreSize=2的周期任务线程池,线程名命名是DiscoveryClient-%s
heartbeatExecutor:coreSize=1的异步线程池,线程名命名是DiscoveryClient-HeartbeatExecutor-%d
cacheRefreshExecutor:coreSize=1的异步线程池,线程名命名是DiscoveryClient-CacheRefreshExecutor-%d
这三个线程池,是怎么配合工作的呢?不着急,慢慢往下看
initScheduledTasks()的代码如下:
private void initScheduledTasks() {if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) {// registry cache refresh timerint registryFetchIntervalSeconds = clientConfig.getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds();int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();cacheRefreshTask = new TimedSupervisorTask("cacheRefresh",scheduler,cacheRefreshExecutor,registryFetchIntervalSeconds,TimeUnit.SECONDS,expBackOffBound,new CacheRefreshThread());// 【1】scheduler.schedule(cacheRefreshTask,registryFetchIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);}if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) {int renewalIntervalInSecs = instanceInfo.getLeaseInfo().getRenewalIntervalInSecs();int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();logger.info("Starting heartbeat executor: " + "renew interval is: {}", renewalIntervalInSecs);// Heartbeat timerheartbeatTask = new TimedSupervisorTask("heartbeat",scheduler,heartbeatExecutor,renewalIntervalInSecs,TimeUnit.SECONDS,expBackOffBound,new HeartbeatThread());// 【2】scheduler.schedule(heartbeatTask,renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS);} else {logger.info("Not registering with Eureka server per configuration");}
}分析代码:
【1】检查是否需要获取注册表信息(配置项eureka.client.fetchRegistry默认=true)
用注入的异步线程池cacheRefreshExecutor,按指定时间间隔registryFetchIntervalSeconds,去执行CacheRefreshThread,即缓存刷新refreshRegistry()任务
缓存刷新任务cacheRefreshTask
使用调度器 scheduler 安排任务
【2】检查是否需要注册入Eureka(配置项eureka.client.registerWithEureka默认=true)
用注入的异步线程池heartbeatExecutor,按指定时间间隔renewalIntervalInSecs,去执行HeartbeatThread,即执行续租renew()任务
心跳续租任务heartbeatTask
使用调度器 scheduler 安排任务
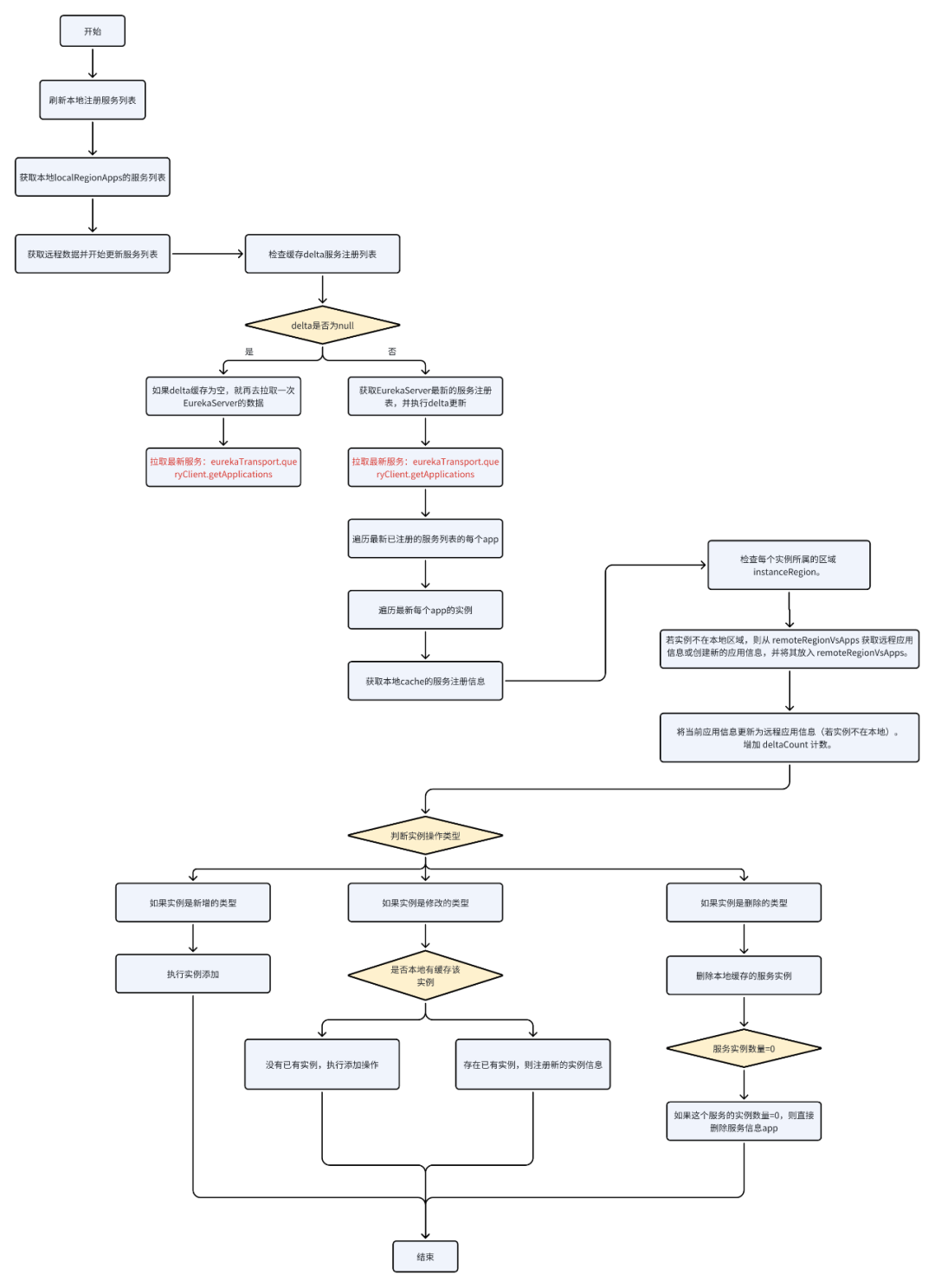
CacheRefreshThread - 缓存刷新
class CacheRefreshThread implements Runnable {public void run() {refreshRegistry();}
}@VisibleForTesting
void refreshRegistry() {try {//.....//【1】刷新本地注册服务列表boolean success = fetchRegistry(remoteRegionsModified);//.....} catch (Throwable e) {logger.error("Cannot fetch registry from server", e);}
}private boolean fetchRegistry(boolean forceFullRegistryFetch) {try {// 【2】获取本地localRegionApps的服务列表Applications applications = getApplications();// 【3】获取远程数据并更新服务列表getAndUpdateDelta(applications);}// registry was fetched successfully, so return truereturn true;
}private void getAndUpdateDelta(Applications applications) throws Throwable {// .....//【4】检查缓存delta的服务注册列表Applications delta = null;if (delta == null) {// 【4.1】如果缓存为空,就再去拉取一次EurekaServer的数据getAndStoreFullRegistry();} else {if (fetchRegistryUpdateLock.tryLock()) {try {//【5】获取EurekaServer最新的服务注册表,并执行delta更新getAndStoreFullRegistry()updateDelta(delta);} finally {fetchRegistryUpdateLock.unlock();}} }
} private void getAndStoreFullRegistry() throws Throwable {long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get();Applications apps = null;EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress() == null? eurekaTransport.queryClient.getApplications(remoteRegionsRef.get()): eurekaTransport.queryClient.getVip(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress(), remoteRegionsRef.get());if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()) {apps = httpResponse.getEntity();}
}private void updateDelta(Applications delta) {int deltaCount = 0;//【6】遍历服务注册列表的每个appfor (Application app : delta.getRegisteredApplications()) {//【7】遍历每个服务的所有实例instancefor (InstanceInfo instance : app.getInstances()) {//【8】获取本地cache的服务注册信息Applications applications = getApplications();String instanceRegion = instanceRegionChecker.getInstanceRegion(instance);if (!instanceRegionChecker.isLocalRegion(instanceRegion)) {Applications remoteApps = remoteRegionVsApps.get(instanceRegion);if (null == remoteApps) {remoteApps = new Applications();remoteRegionVsApps.put(instanceRegion, remoteApps);}applications = remoteApps;}++deltaCount;//【9】如果实例是新增的类型if (ActionType.ADDED.equals(instance.getActionType())) {Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());if (existingApp == null) {//【10】执行实例添加applications.addApplication(app);}applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).addInstance(instance);} //【11】如果实例是修改的类型else if (ActionType.MODIFIED.equals(instance.getActionType())) {Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());if (existingApp == null) {//【12】没有已有实例,执行添加操作applications.addApplication(app);}//【13】存在已有实例,则注册新的实例信息applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).addInstance(instance);} //【14】如果实例是删除的类型else if (ActionType.DELETED.equals(instance.getActionType())) {Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());if (existingApp != null) {//【15】删除这个服务的实例existingApp.removeInstance(instance);//【16】如果这个服务的实例数量=0,则直接删除服务信息appif (existingApp.getInstancesAsIsFromEureka().isEmpty()) {applications.removeApplication(existingApp);}}}}}
}代码分析:见下面流程图
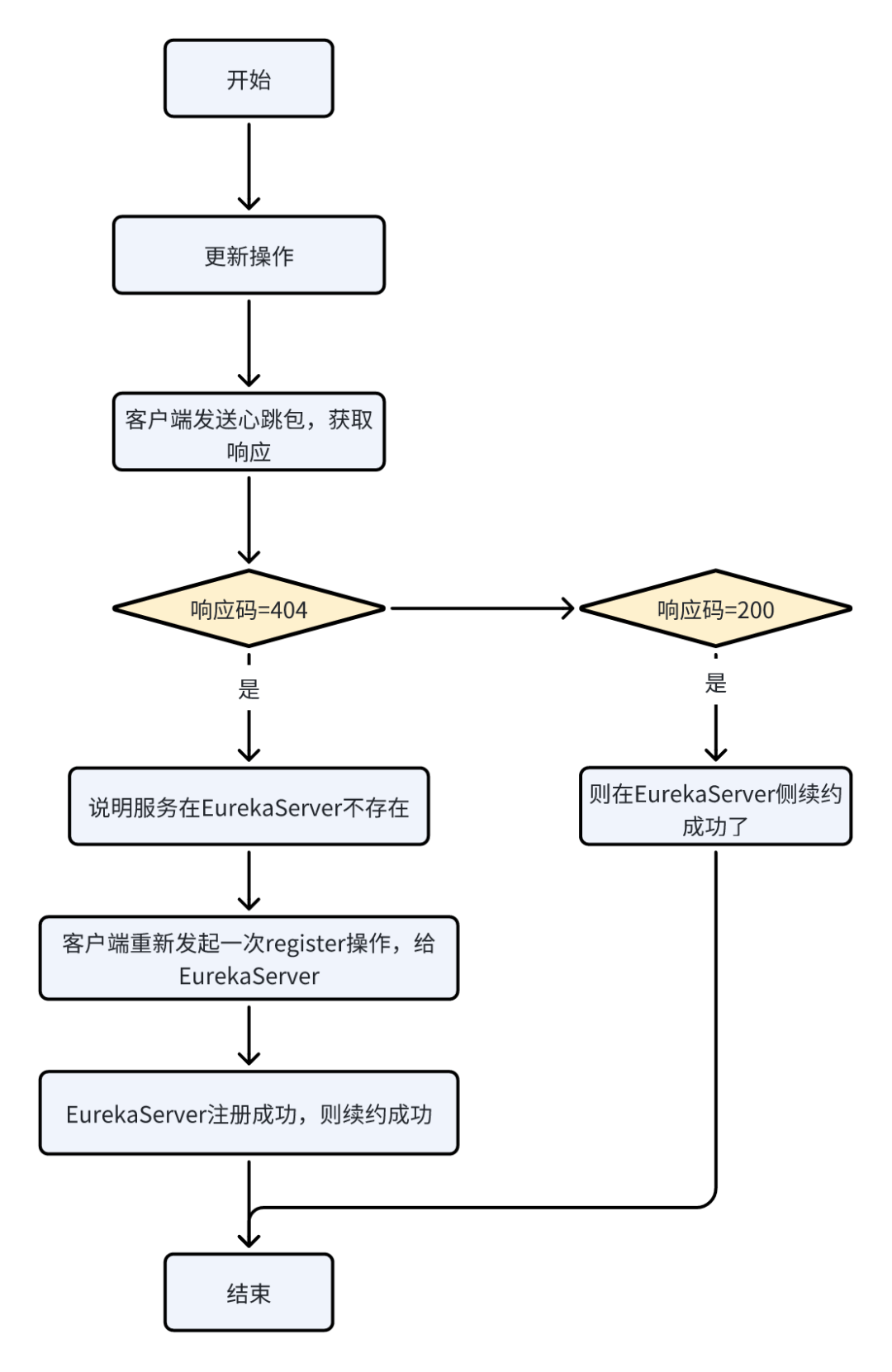
HeartbeatThread - 心跳续租
private final Counter REREGISTER_COUNTER = Monitors.newCounter(PREFIX+ "Reregister");private class HeartbeatThread implements Runnable {public void run() {//【1】更新操作if (renew()) {lastSuccessfulHeartbeatTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();}}
}boolean renew() {EurekaHttpResponse<InstanceInfo> httpResponse;try {//【2】客户端发送心跳包,获取响应httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.sendHeartBeat(instanceInfo.getAppName(), instanceInfo.getId(), instanceInfo, null);//【3】响应码=404,说明服务在EurekaServer不存在if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.NOT_FOUND.getStatusCode()) {REREGISTER_COUNTER.increment();long timestamp = instanceInfo.setIsDirtyWithTime();//【4】客户端重新发起一次register操作,给EurekaServerboolean success = register();if (success) {instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(timestamp);}//【5】EurekaServer注册成功,则续约成功return success;}//【6】响应码=200,则在EurekaServer侧续约成功了return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode();} catch (Throwable e) {logger.error(PREFIX + "{} - was unable to send heartbeat!", appPathIdentifier, e);return false;}
}代码分析:见下面流程图
取消租约
@Bean(destroyMethod = "shutdown")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EurekaClient.class,search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public EurekaClient eurekaClient(ApplicationInfoManager manager,EurekaClientConfig config) {return new CloudEurekaClient(manager, config, this.optionalArgs,this.context);
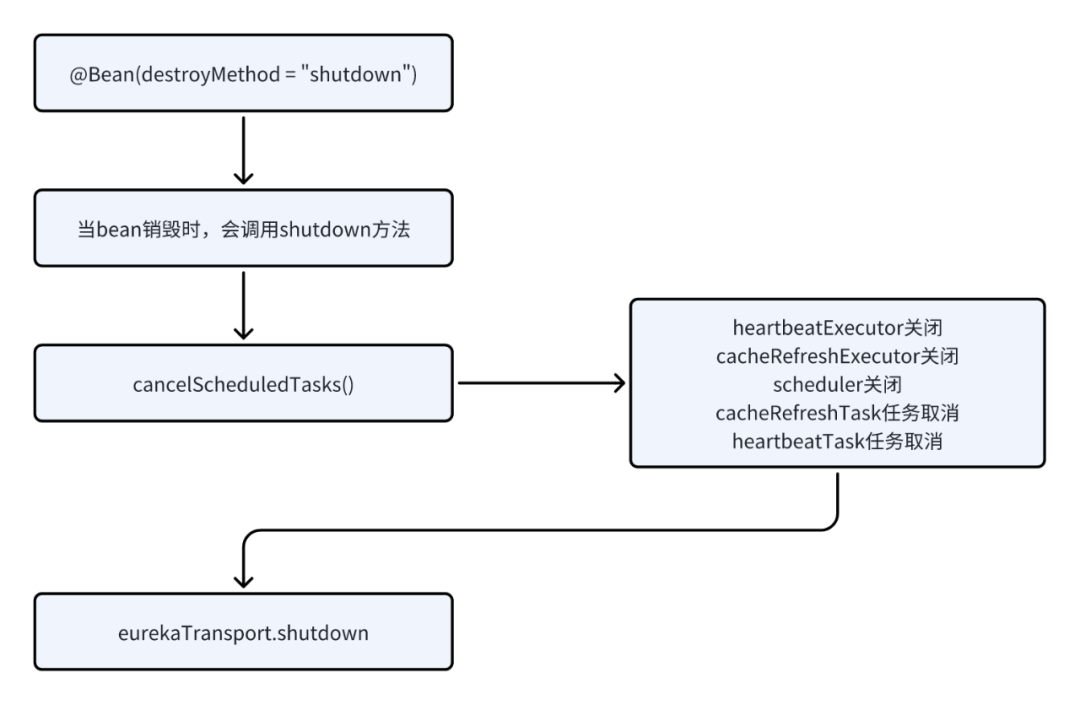
}@PreDestroy
@Override
public synchronized void shutdown() {if (isShutdown.compareAndSet(false, true)) {logger.info("Shutting down DiscoveryClient ...");if (statusChangeListener != null && applicationInfoManager != null) {applicationInfoManager.unregisterStatusChangeListener(statusChangeListener.getId());}cancelScheduledTasks();// If APPINFO was registeredif (applicationInfoManager != null&& clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()&& clientConfig.shouldUnregisterOnShutdown()) {applicationInfoManager.setInstanceStatus(InstanceStatus.DOWN);unregister();}if (eurekaTransport != null) {eurekaTransport.shutdown();}heartbeatStalenessMonitor.shutdown();registryStalenessMonitor.shutdown();Monitors.unregisterObject(this);logger.info("Completed shut down of DiscoveryClient");}
}private void cancelScheduledTasks() {if (instanceInfoReplicator != null) {instanceInfoReplicator.stop();}if (heartbeatExecutor != null) {heartbeatExecutor.shutdownNow();}if (cacheRefreshExecutor != null) {cacheRefreshExecutor.shutdownNow();}if (scheduler != null) {scheduler.shutdownNow();}if (cacheRefreshTask != null) {cacheRefreshTask.cancel();}if (heartbeatTask != null) {heartbeatTask.cancel();}
}代码分析:见下面流程图
小结
我们回到开头的原理,知道EurekaClient客户端本质就是4个动作:
获取服务列表:在CacheRefreshThread里有实现,即CacheRefreshThread的【4.1】步骤的eurekaTransport.queryClient.getApplications
注册服务实例:在HeartbeatThread里有实现,即HeartbeatThread的【4】步骤的eurekaTransport.registrationClient.register
租约续约:在HeartbeatThread里有实现,即HeartbeatThread的【2】步骤的eurekaTransport.registrationClient.sendHeartBeat
取消租约:在定义CloudEurekaClient的@Bean(destroyMethod = "shutdown")注解有生命
但我们还想知道,CacheRefreshThread 和 HeartbeatThread的背后通信,以及在EurekaServer的原理细节。可以,我们放到下一个章节再讲。
其他文章
Kafka消息堆积问题排查
基于SpringMVC的API灰度方案
理解到位:灾备和只读数据库
SQL治理经验谈:索引覆盖
Mybatis链路分析:JDK动态代理和责任链模式的应用
大模型安装部署、测试、接入SpringCloud应用体系
Mybatis插件-租户ID的注入&拦截应用