
.exe文件主要包含pingmianF.py文件和read_inp_auto.py文件

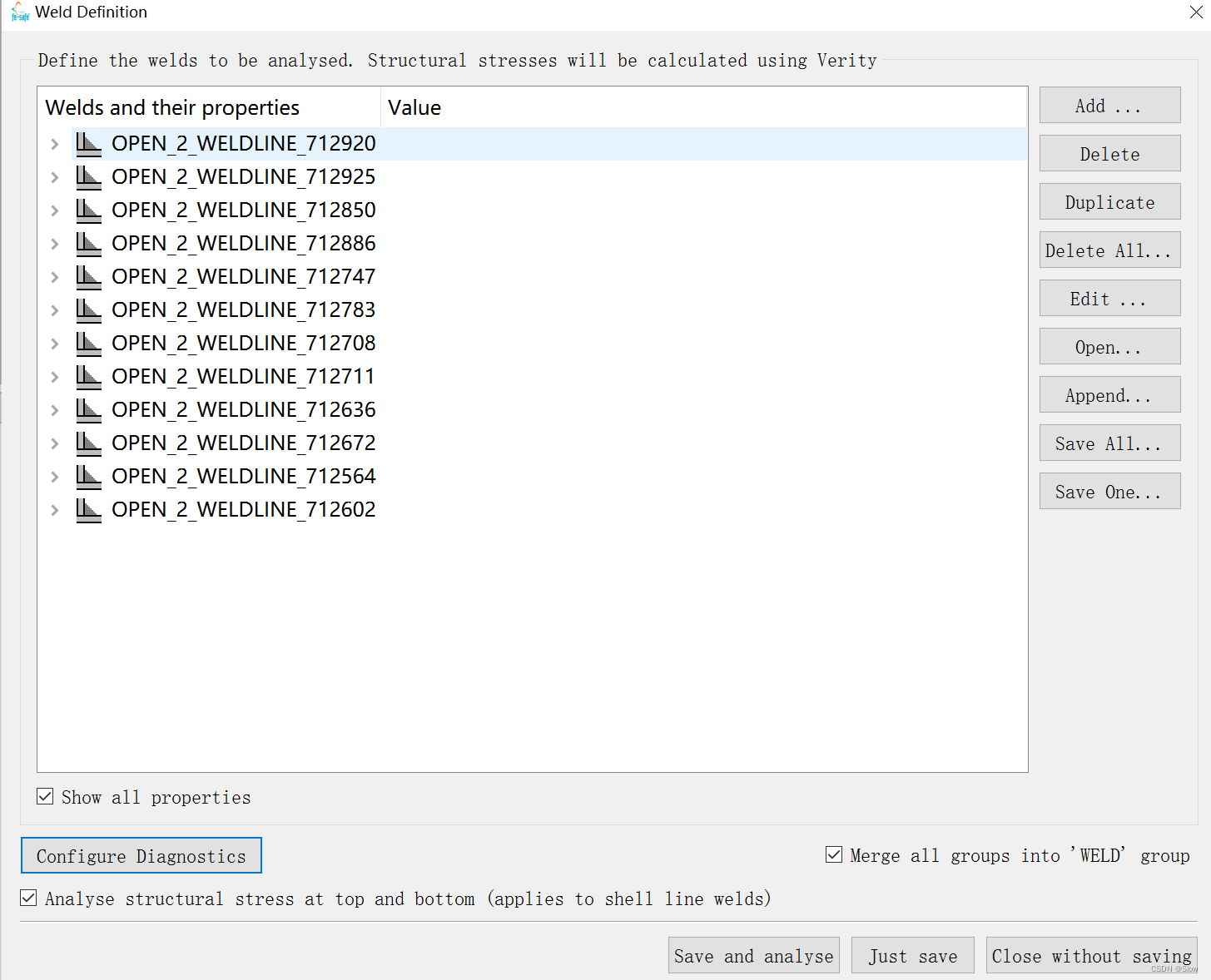
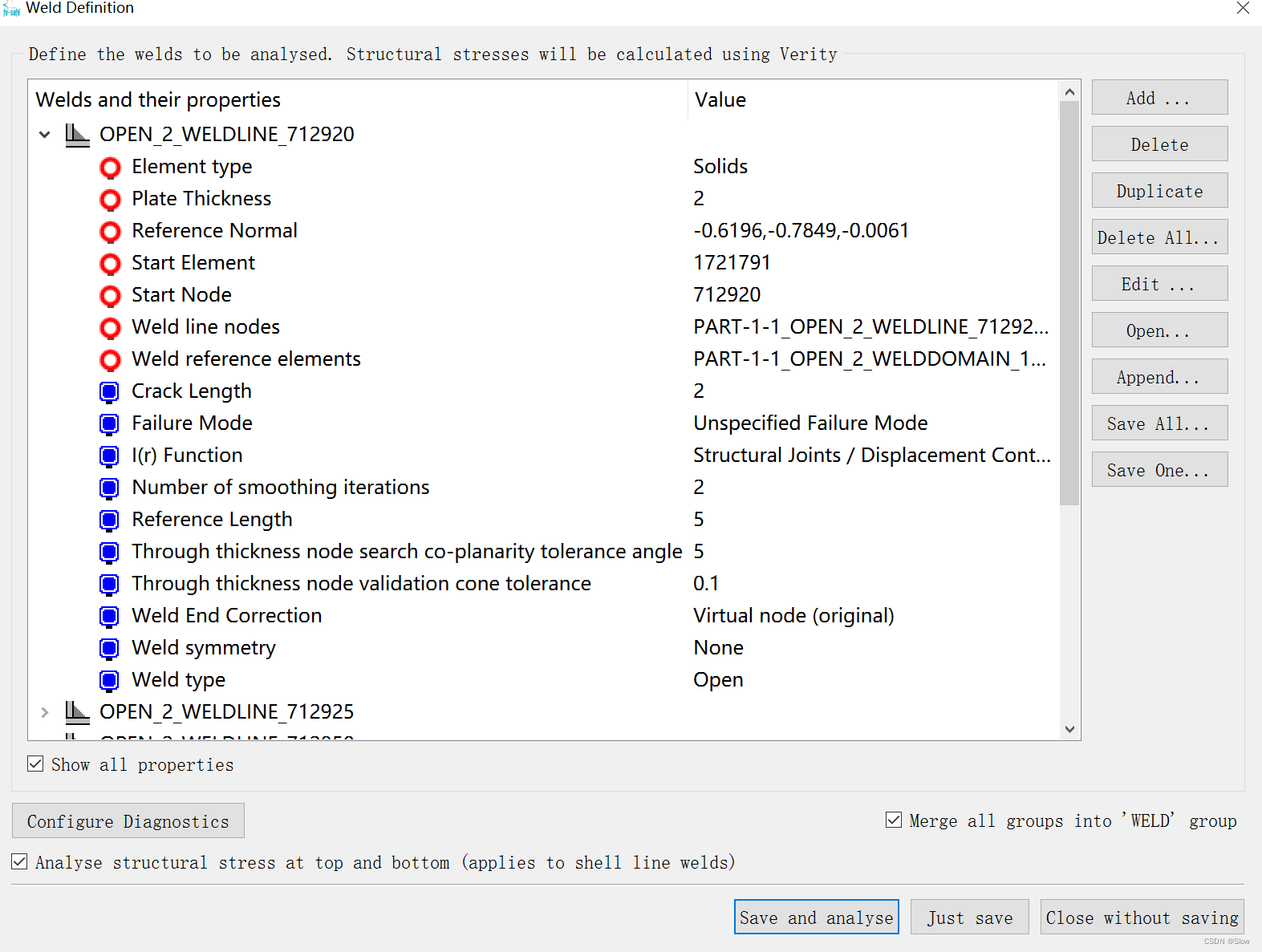
实现效果
代码
read_inp_auto.py
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import re
import sys
import os
import os.path
import time
import pingmianF
from pingmianF import vector
import numpy as np
from tkinter import messagebox
from tkinter import filedialogls_weldline = []
ls_welddomain = []
ls1 = []
ls2 = []
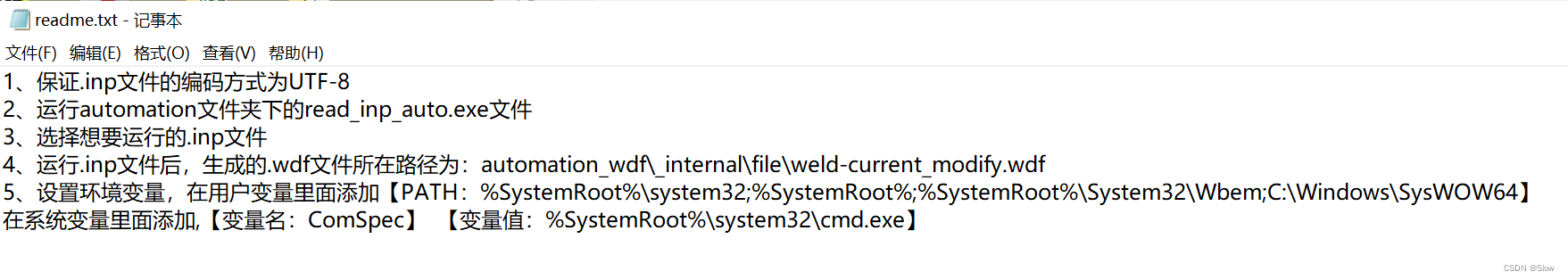
def popupmsg(msg):messagebox.showerror('Warning', msg)#生成资源文件目录访问路径
def resource_path(relative_path):if getattr(sys, 'frozen', False): #是否Bundle Resourcebase_path = sys._MEIPASSelse:base_path = os.path.abspath(".")return os.path.join(base_path, relative_path)
def automation(path_inpname):#访问res文件夹下数据.txt的内容filename = resource_path(os.path.join("file",path_inpname))with open(filename,'r',encoding='utf-8') as fa:for line in fa:if "WELDLINE_" in line:ls1.append(line)if "WELDDOMAIN_" in line:ls2.append(line)print(ls1)print(ls2)# lines = fa.readlines()# print(lines)# f.close()# fa.close()# # with open ('project_incoordinata.txt','r',encoding = 'utf8') as f:# fa = open(r"project_1.inp", 'r',encoding="utf-8")# fb = open("weldline_out.txt",'w')# fc = open("welddomain_out.txt",'w')# # fd = open("all_node_coordinate_out.txt",'w')# for line in fa:## if "WELDLINE_" in line:# ls1.append(line)# if "WELDDOMAIN_"in line:# ls2.append(line)# print(ls1)# print(ls2)# ['*NSET, NSET=Closed_2_weldline_126578_143528\n', '*NSET, NSET=Closed_2_weldline_126051_144027\n', '*NSET, NSET=Open_3_weldline_126776_189374\n']# ['*ELSET, ELSET=Closed_2_welddomain_318468\n', '*ELSET, ELSET=Closed_2_welddomain_318666\n', '*ELSET, ELSET=Open_3_welddomain_628339\n']for i in range(0,len(ls1)):ls_weldline.append(ls1[i].strip('\n').split('=')[-1])#print(ls_weldline)for j in range(0,len(ls2)):# print(ls_welddomain[j])ls_welddomain.append(ls2[j].strip('\n').split('=')[-1])print(ls_welddomain)print(len(ls_welddomain))# ['Closed_2_weldline_126578_143528', 'Closed_2_weldline_126051_144027', 'Open_3_weldline_126776_189374']# ['Closed_2_welddomain_318468', 'Closed_2_welddomain_318666', 'Open_3_welddomain_628339']# fb.write(str(ls_weldline))# fc.write(str(ls_welddomain))# 从inp里面提取出需要的字符串存入,ls_weldline,ls_welddomainwelddomain_element = []ls_element = []for k in range(0,len(ls_welddomain)):welddomain_element.append(ls_welddomain[k].strip('\n').split('_')[-1])print("welddomain_element is"+str(welddomain_element))print(len(welddomain_element))# ['318468', '318666', '628339']# 提取每个热影响区的起始单元welddomain_ele_node = []filename = resource_path(os.path.join("file",path_inpname))print(filename)with open(filename,'r',encoding='utf-8') as f:# with open('project_1.inp', 'r') as f:for line in f:for j in range(0, len(welddomain_element)):if welddomain_element[j] in line:welddomain_ele_node.append(line)print(welddomain_ele_node )print(len(welddomain_ele_node) )# f.close()# print(welddomain_ele_node)# print(len(welddomain_ele_node))welddomain_ele = []welddomain_node = []welddomain_ele = welddomain_ele_node [0:len(welddomain_element)]print(welddomain_ele)print(len(welddomain_ele))# [' 628339, 126776, 189374, 189375, 189198, 189434, 189435, 189433,\n', ' 318666, 144028, 127140, 126051, 144027, 144603, 144602, 144604,\n', ' 318468, 143529, 143528, 126578, 126990, 144519, 144521, 144520,\n']#提取单元所在行包含的八个节点for j in range(0, len(welddomain_ele)):welddomain_ele[j] = welddomain_ele[j].strip( ).strip('\n').split(',')[1:4]# print(welddomain_ele)specprint(len(welddomain_ele))# [[' 126776', ' 189374', ' 189375'], [' 144028', ' 127140', ' 126051'], [' 143529', ' 143528', ' 126578']]# 提取单元所包含节点里面的前三个节点,用来求取法向量# print(welddomain_ele[0][0])#获取节点坐标文档import refilename = resource_path(os.path.join("file",path_inpname))print(filename)node_coordinate = []with open(filename,'r',encoding='utf-8') as fa:# node_coordinate = []# with open('project_1.inp', 'r') as f:data = fa.read().splitlines()idx1 = data.index('*NODE,NSET=NALL')idx2 = data.index('**')output = data[idx1 + 1 : idx2]# fa.close()filename = resource_path(os.path.join("file","project_incoordinata.txt"))print(filename)node_coordinate = []# with open(filename,'r',encoding='utf-8') as fa:with open (filename,'w',encoding = 'utf8') as f:f.write('\n'.join(output))project_incoordinata = []# f.close()with open (filename,'r',encoding = 'utf8') as f:lines = f.readlines()for line in lines:line = line.strip('\n').split(',')project_incoordinata.append(line)print(len(project_incoordinata))print(project_incoordinata)# f.close()#[' 126776', ' 189374', ' 189375', ' 144028', ' 127140', ' 126051', ' 143529', ' 143528', ' 126578']node = []print(len(welddomain_ele))for j in range (0,len(welddomain_ele)):for k in range(0,3):node.append(welddomain_ele[j][k])print(node)#[' 126776', ' 189374', ' 189375', ' 144028', ' 127140', ' 126051', ' 143529', ' 143528', ' 126578']with open (filename,'r',encoding = 'utf8') as f:for line in f.readlines():str1 = line.split(',')[0]int_str1 = int(str1)for j in range(0,len(node)):if int_str1 == int(node[j]):node_coordinate.append(line)# f.close()# print(node_coordinate)#node_coordinate#['126051, -213.32157, -23.94757, 55.92702\n',# '126578, -49.68242, -23.94821, -50.66072\n',# '126776, -114.42335, -23.94608, -46.53174\n',# '127140, -212.51184, -23.98995, 56.26252\n',# '143528, -48.68259, -23.94195, -50.67784\n',# '143529, -48.67345, -23.97157, -50.15527\n',# '144028, -212.89419, -23.97285, 57.18638\n',# '189374, -115.39657, -23.94313, -46.30191\n',# '189375, -115.09989, -23.98079, -45.04446\n']node_list = []print(len(node))print(len(node_coordinate))for i in range (0,len(node)):for j in range (0,len(node_coordinate)):str1 = node_coordinate[j].strip(' ').split(',')[0]str2 = node[i].strip(' ')# print(str1)# print(str2)str3 = node_coordinate[j].strip(' ').strip('\n').split(',')[1:4]if int(str1) == int(str2):node_list.append(str3)print(node_list)# print(node_list[0])# node_list = np.array(node_list)# print(node_list)# for i in range(0,len(node_list)):# node_list[i] = node_list[i].astype(np.float64)## print(node_list)##['126776, -114.42335, -23.94608, -46.53174\n',# '189374, -115.39657, -23.94313, -46.30191\n',# '189375, -115.09989, -23.98079, -45.04446\n',# '144028, -212.89419, -23.97285, 57.18638\n',# '127140, -212.51184, -23.98995, 56.26252\n',# '126051, -213.32157, -23.94757, 55.92702\n',# '143529, -48.67345, -23.97157, -50.15527\n',# '143528, -48.68259, -23.94195, -50.67784\n',# '126578, -49.68242, -23.94821, -50.66072\n']# [[' -114.42335', ' -23.94608', ' -46.53174'],# [' -115.39657', ' -23.94313', ' -46.30191'],# [' -115.09989', ' -23.98079', ' -45.04446'],# [' -212.89419', ' -23.97285', ' 57.18638'],# [' -212.51184', ' -23.98995', ' 56.26252'],# [' -213.32157', ' -23.94757', ' 55.92702'],# [' -48.67345', ' -23.97157', ' -50.15527'],# [' -48.68259', ' -23.94195', ' -50.67784'],# [' -49.68242', ' -23.94821', ' -50.66072']]# fa.close()## f.close()# f1 = open('weld-current - 副本1.txt', 'r')# f1 = open('weld-current - 副本1.txt', 'w')# f2 = open('weld-current_modify.wdf', 'a')filename1 = resource_path(os.path.join("file","weld-current_modify.wdf"))os.remove(filename1)filename2 = resource_path(os.path.join("file","weld_current.txt"))f1 = open(filename1,'a',encoding='utf-8')f1.write('<weld_definition>\n')# f1.close()# f2 = open('weld-current_modify.wdf', 'a')#import os#try:#except# f2.write('<weld_definition>\n')# for line in f1:# def Macro1(test_wdomain,test_wline):j = 0with open(filename2,'r',encoding='utf-8') as f2:# content = f1.read()# f1.seek(0,0)# f1.write('<weld_definition>\n'+content)for i in range(0,len(ls_welddomain)):lines = f2.read()f2.seek(0)# if '%welddomain' in line:# f1.write(line.replace('%welddomain','welddomain1234_4567'))## lines = lines.replace('%Line_Weld','weld_line[i]')# print('weld_line[i]')lines = lines.replace('%New_Line',ls_weldline[i].upper())lines = lines.replace('%plate_thickness', ls_weldline[i].strip('\n').split('_')[1])lines = lines.replace('%welddomain',"PART-1-1_"+ ls_welddomain[i].upper())lines = lines.replace('%start_element', ls_welddomain[i].strip('\n').split('_')[-1])lines = lines.replace('%reference_normal',str(pingmianF.vector(node_list[j],node_list[j+1],node_list[j+2])))print(vector(node_list[j], node_list[j + 1], node_list[j + 2]))# if '%weldline' in line:# f1.write(line.replace('%weldline', 'weldline1234_4567'))lines = lines.replace('%weldline', "PART-1-1_"+ ls_weldline[i].upper()+"_nodal")lines = lines.replace('%start_node', ls_weldline[i].strip('\n').split('_')[-1])lines = lines.replace('%weld_type', ls_welddomain[i].strip('\n').split('_')[0].capitalize())f1.write(lines)j = j+3f1.write('</weld_definition>')f1.close()f2.close()fa.close()f.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':path_inpname = filedialog.askopenfilenames(title="Select Text File",filetypes=[("INP File", "*.inp"), ("All Files", "*.*")])# print(path_inpname)automation(path_inpname[0])# try:# automation(path_inpname[0])# except:# popupmsg('工具运行不成功!')
# f2.close()pingmianF.py
# import numpy as np
#
# def compute_normal_vector(point1, point2, point3):
# vector1 = np.array(point2) - np.array(point1)
# vector2 = np.array(point3) - np.array(point1)
# normal_vector = np.cross(vector1, vector2)
# return normal_vector
#
# # 示例输入
# point1 = [-114.42335, -23.94608, -46.53174]
# point2 = [-115.39657, -23.94313, -46.30191]
# point3 = [-115.09989, -23.98079, -45.04446]
#
# normal_vector = compute_normal_vector(point1, point2, point3)
# print(normal_vector)
# # 在上面的代码示例中,我们使用了numpy库来进行向量的计算。
# # compute_normal_vector函数接受三个点作为输入,然后使用numpy库中的array函数将这些点转换为数组。
# # 接着,我们计算两个向量vector1和vector2,它们分别是point2-point1和point3-point1。
# # 最后,我们使用numpy库中的cross函数计算向量的叉积,得到平面的法向量。# import read_inp_auto as read_inp
import numpy as npp1 =[' -114.42335', ' -23.94608', ' -46.53174']
p2 =[' -115.39657', ' -23.94313', ' -46.30191']
p3 =[' -115.09989', ' -23.98079', ' -45.04446']def vector(p1,p2,p3):# 定义三个点的坐标point1 = np.array(p1)point2 = np.array(p2)point3 = np.array(p3)float_point1 = point1.astype(np.float64)float_point2 = point2.astype(np.float64)float_point3 = point3.astype(np.float64)# 计算两个向量vector1 = float_point2 - float_point1vector2 = float_point3 - float_point1# 计算法向量normal_vector = np.cross(vector1, vector2)# 归一化为单位向量unit_normal_vector = normal_vector / np.linalg.norm(normal_vector)vector_final =",".join(("{:.4f}".format(num) for num in unit_normal_vector))return vector_final
# print(vector(p1,p2,p3))