前言:要了解set和map,首先需要对搜索树和哈希有一定的了解,才能进一步深入的了解set和map。
1.搜索树
(1)性质:
若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点值都小于根节点的值。
若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点值都大于根节点的值。
它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树。
二叉搜索树中不允许出现相同的值
eg:

(2)相关功能的实现:
前提得实现一个节点类TreeNode,包含left(左子树),right(右子树),val三个属性。
a.查找:
分析:
时间复杂度:
最好情况:
最坏情况:

代码实现:
public TreeNode search(int val) {if(root == null) {return null;}TreeNode cur = root;while(cur != null) {if (cur.val > val) {//进到左边cur = cur.left;} else if (cur.val < val) {//进到右边cur = cur.right;} else {return cur;}}return null;
}b.插入:
分析:
时间复杂度与查找的相同。

代码实现:
public void insert(int val) {if(root == null) {root = new TreeNode(val);return;}TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val);TreeNode cur = root;TreeNode parent = null;while(cur != null) {parent = cur;if (cur.val > node.val) {//进到左边cur = cur.left;} else if (cur.val < node.val) {//进到右边cur = cur.right;} else {return;}}//记录父亲节点的用处if(parent.val > node.val) {parent.left = node;}if(parent.val < node.val) {parent.right = node;}
}c.删除:
分析:
时间复杂度与查找和插入相同。

代码实现:
public void delete(int val) {if(root == null) {return;}TreeNode cur = root;TreeNode parent = null;while(cur != null) {cur = parent;if (cur.val > val) {//进到左边cur = cur.left;} else if (cur.val < val) {//进到右边cur = cur.right;} else {removeNode(parent,cur);}}
}
private void removeNode(TreeNode parent, TreeNode cur) {if(cur.left == null) {if(cur == root) {cur = cur.right;}else if(parent.right == cur) {parent.right = cur.right;}else if(parent.left == cur) {parent.left = cur.right;}}else if(cur.right == null) {if(cur == root) {cur = cur.left;}else if(parent.right == cur) {parent.right = cur.left;}else if(parent.left == cur) {parent.left = cur.left;}}else {TreeNode tmpParent = cur;TreeNode tmp = cur.right;while(tmp.left != null) {tmpParent = tmp;tmp = tmp.left;}cur.val = tmp.val;if(tmpParent.left == tmp) {tmpParent.left = tmp.right;}if(tmpParent.right == tmp) {tmpParent.right = tmp.right;}}
}(3)和集合类的关系:
TreeSet和TreeMap即java中运用二叉搜索树实现的Set和Map;但实际上是一颗红黑树,红黑树是一颗近似平衡的二叉搜索树(不会出现一些单只树的情况)。
2.哈希表
(1)概念:
通过构造一种存储结构,和某种函数(hashFunc)使元素的存储位置与它的关键码之间能够建立一 一映射的关系,从而在查找时候能很快速的查找到对应的元素。构造出来的存储结构就成为哈希表,某种转换函数称为哈希函数,上述这中查找方式称为哈希(散列)方法。
eg:

(2)冲突:
a.概念:
不同关键字通过哈希函数计算出相同的哈希地址。
b.避免:
冲突是不能够完全避免的,我们只能设计一个比较合理的哈希函数来尽量降低哈希冲突率。
直接定制法:Hash(key) = A * key + B 使用场景:适合查找比较小且连续的情况。
除留余数法:Hash(key) = key % p(p <= m,m为哈希表的长度)
c.负载因子调节(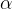 ):
):
= 填入表中的元素/哈希表的长度,
越大,表明冲突的概率越大,反之则越小。
d.解决方式:
闭散列:
有线性探测和二次探测两种方式:
线性探测:

线性探测有个缺陷就是冲突的元素易容易堆积在一起。
二次探测:

研究表明:当表的长度为质数并且负载因子不超过0.5时,新的表项一定能插入,而且任何一个位置都不会被探查两次。因此只要表中有一半的位置,就不存在表满的问题。此时在搜索时可以不考虑装满的情况,但在插入时必须确保表的负载因子不超过0.5,否则需要扩容。
因此闭散列最大的缺陷就是表的利用率比较低。
开散列:(哈希桶,开链法,链地址法)
各个桶中的元素通过一个单链表串起来,各链表头节点存储在哈希表中。
eg:
从上图我们可以看出每个哈希桶中放的都是冲突的元素,此时就可以将开散列认为时是把一个大集合中的搜索问题转化为在小集合中做搜索了。
3.Map和Set
Set和Map都是java中专门用来搜索的容器/数据结构,其搜索的效率与具体的实列类有关。
以前的搜索方式:直接遍历,二分查找......,这些更适合于静态查找。
而Set和Map更适合于动态查找。
搜索的数据:关键字(key)和关键字对应的称为值(value),它们一起称为key-value键值对。一般有两种模型:纯key模型(Set)和纯key-value模型(Map)。
(1)TreeMap,HashMap:
map是一个接口没有继承于Collection接口,存储的是key-value键值对,key是唯一的,不能重复。
a.使用:

关于Map.Entry<K,V>的说明:
Entry也是一个接口,只不过是Map内部实现的接口,它是用来存放key-value键值对的映射关系。
主要有三个使用方法:

Map.Entry<K,V>中没有提供设置key的方法。
b.HashMap源码相关解析:


c.比较:

d.注意:
Map是一个接口,不能够进行实列化对象,要new对象只能通过TreeMap或者HashMap来实现。
Map中key,value的类型可以是所有类型,但TreeMap中的key不能为nul,而HashMap可以。
Map中key是唯一的,value不是唯一的。
Map中的key是不能直接进行修改的,Map.Entry中只提供了setValue方法,并为提供setKey方法,所以要想进行修改key,只能删除这个键值对,重新放入元素。
(2)TreeSet,HashSet:
Set是一个接口,继承与Collection接口,Set集合类可以达到天然去重的效果。
a.使用:

b.比较:

c.注意:
Set是一个接口,不能直接实例化对象,只能通过TreeSet或HashSet来new对象。
Set中的元素是唯一的,所以有天然去重的效果。
TreeSet中的值不能为null,HashSet可以。
Set的底层就是有Map来实现的,其使用key与Object一个默认对象作为键值对插入到Map中的。
Set中的key也是不能修改的,要修改只能删除,重新放入。
Set常见实列化的类有TreeSet和HashSet,此外还有LinkedHashSet,其是在HashSet的基础上维护了一个双向链表来记录元素的插入次序。
4.OJ题:
(1)随机链表的复制
分析:
代码实现:
class Solution {public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {HashMap<Node,Node> map = new HashMap<>();Node cur = head;while(cur != null) {Node node = new Node(cur.val);map.put(cur,node);cur = cur.next;}cur = head;while(cur != null) {map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);cur = cur.next;}return map.get(head);}
}(2)旧键盘
分析:

代码实现:
public static void func(String str1, String str2) {Set<Character> set = new HashSet<>();for (char ch : str2.toUpperCase().toCharArray()) {set.add(ch);}Set<Character> set1 = new HashSet<>();for (char ch : str1.toUpperCase().toCharArray()) {if (!set.contains(ch) && !set1.contains(ch)) {System.out.print(ch);set1.add(ch);}}
}(3)前k个高频单词
分析:
代码实现:
class Solution {public List<String> topKFrequent(String[] words, int k) {HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();for (String word : words) {if (map.get(word) == null) {map.put(word, 1);} else {int val = map.get(word);map.put(word, val + 1);}}// 建立小根堆PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Map.Entry<String, Integer> o1, Map.Entry<String, Integer> o2) {if (o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue()) == 0) {return o2.getKey().compareTo(o1.getKey());}return o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue());}});for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {if (queue.size() < k) {queue.offer(entry);} else {Map.Entry<String, Integer> tmp = queue.peek();if (tmp.getValue().compareTo(entry.getValue()) < 0) {queue.poll();queue.offer(entry);} else {// 按照字符顺序排if (tmp.getValue().compareTo(entry.getValue()) == 0) {if (tmp.getKey().compareTo(entry.getKey()) > 0) {queue.poll();queue.offer(entry);}}}}}List<String> list = new LinkedList<>();for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {Map.Entry<String, Integer> tmp = queue.poll();list.add(tmp.getKey());}Collections.reverse(list);return list;}
}