一、list的介绍及其使用
1.1 list的使用
https://cplusplus.com/reference/list/list/?kw=list
1.2 list的使用
list中的接口比较多,以此类似,只需要掌握如何正确的使用,然后再去深入背后的原理,已达到可扩展的能力。以下为list中一些常见的重要接口
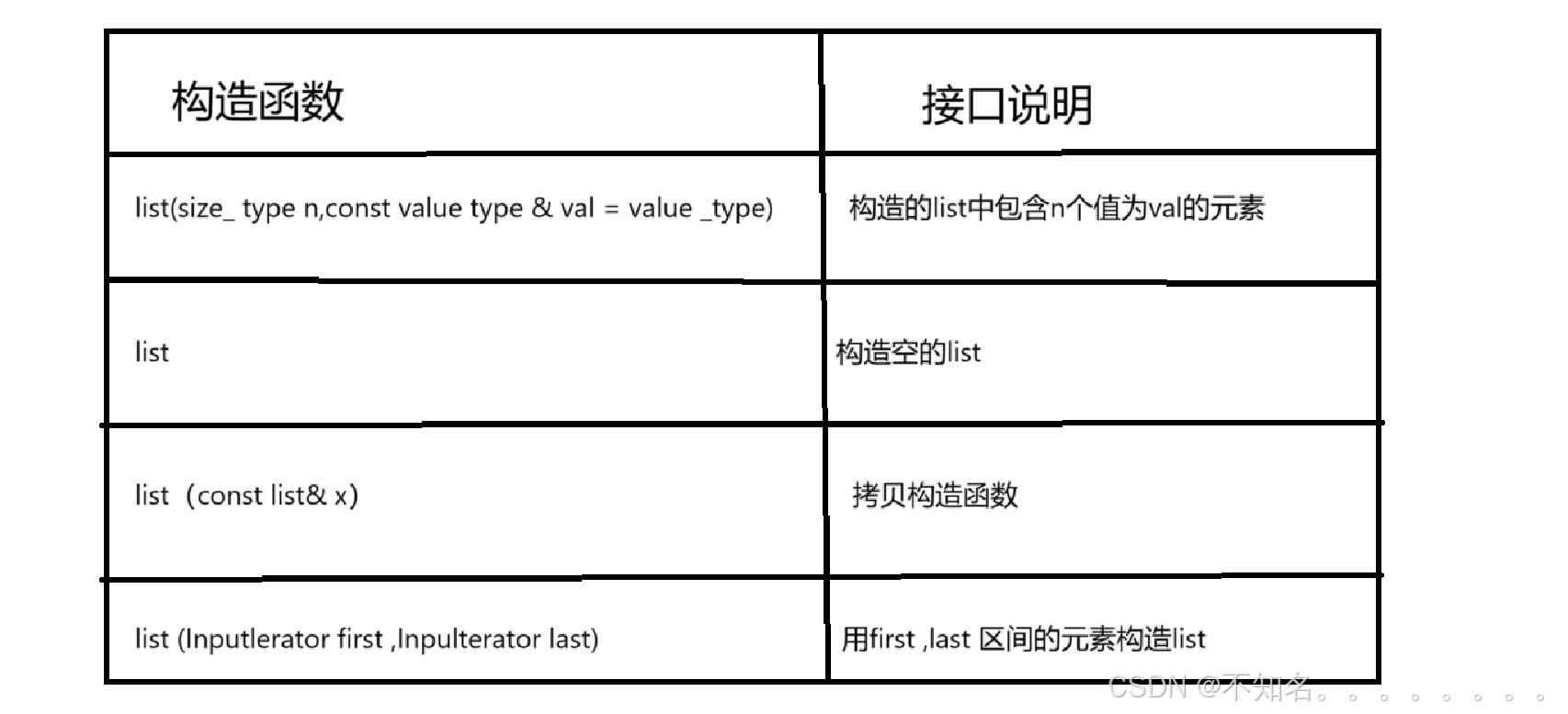
1.21 list的构造
https://cplusplus.com/reference/list/list/list/
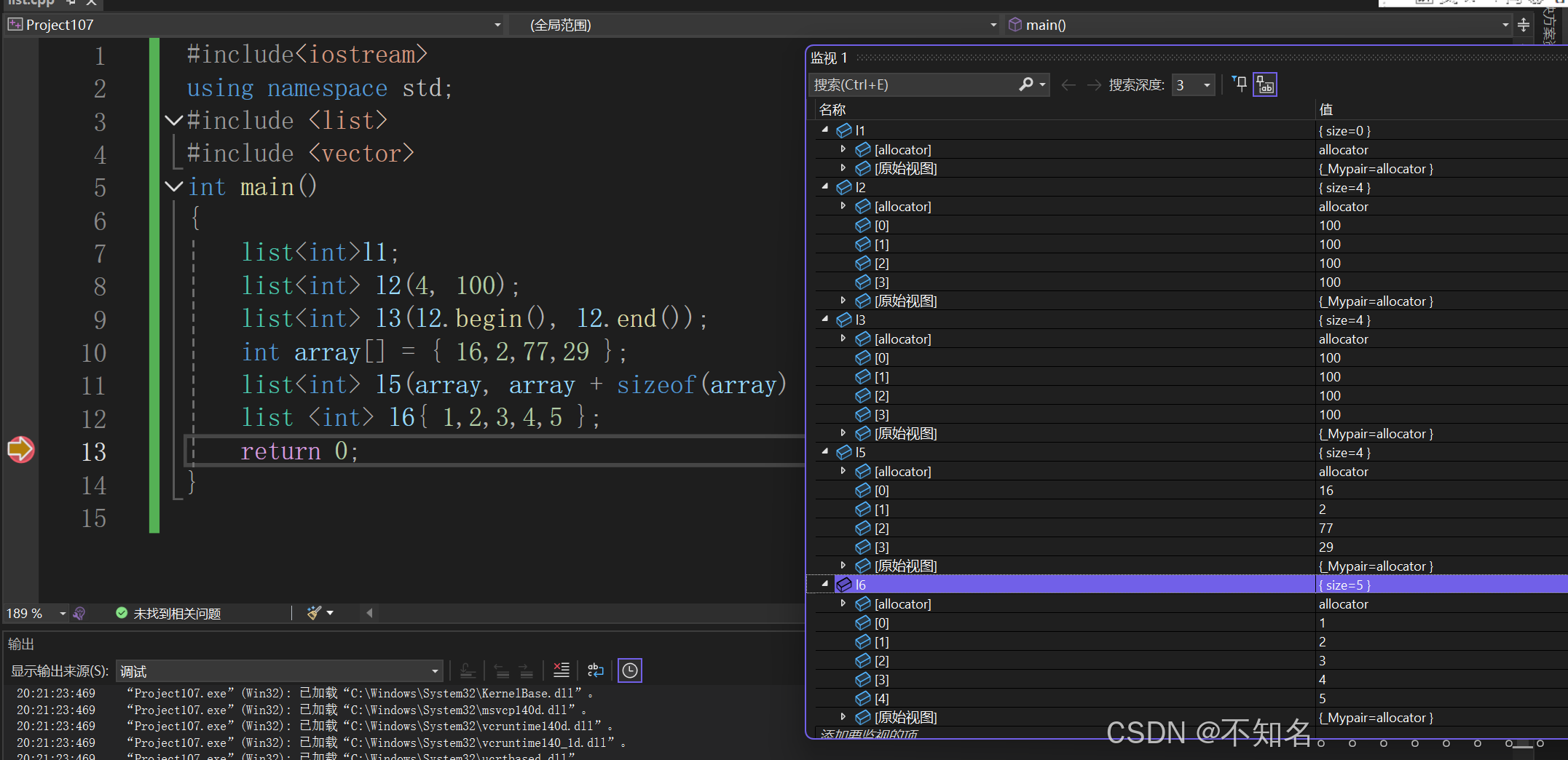
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <list>
#include <vector>
int main()
{list<int>l1;list<int> l2(4, 100);list<int> l3(l2.begin(), l2.end());int array[] = { 16,2,77,29 };list<int> l5(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(int));list <int> l6{ 1,2,3,4,5 };return 0;
}1.2.2 list iterator的使用
此处,大家可暂时将迭代器理解成一个指针,该指针指向list的某个节点
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <list>
#include <vector>
int main()
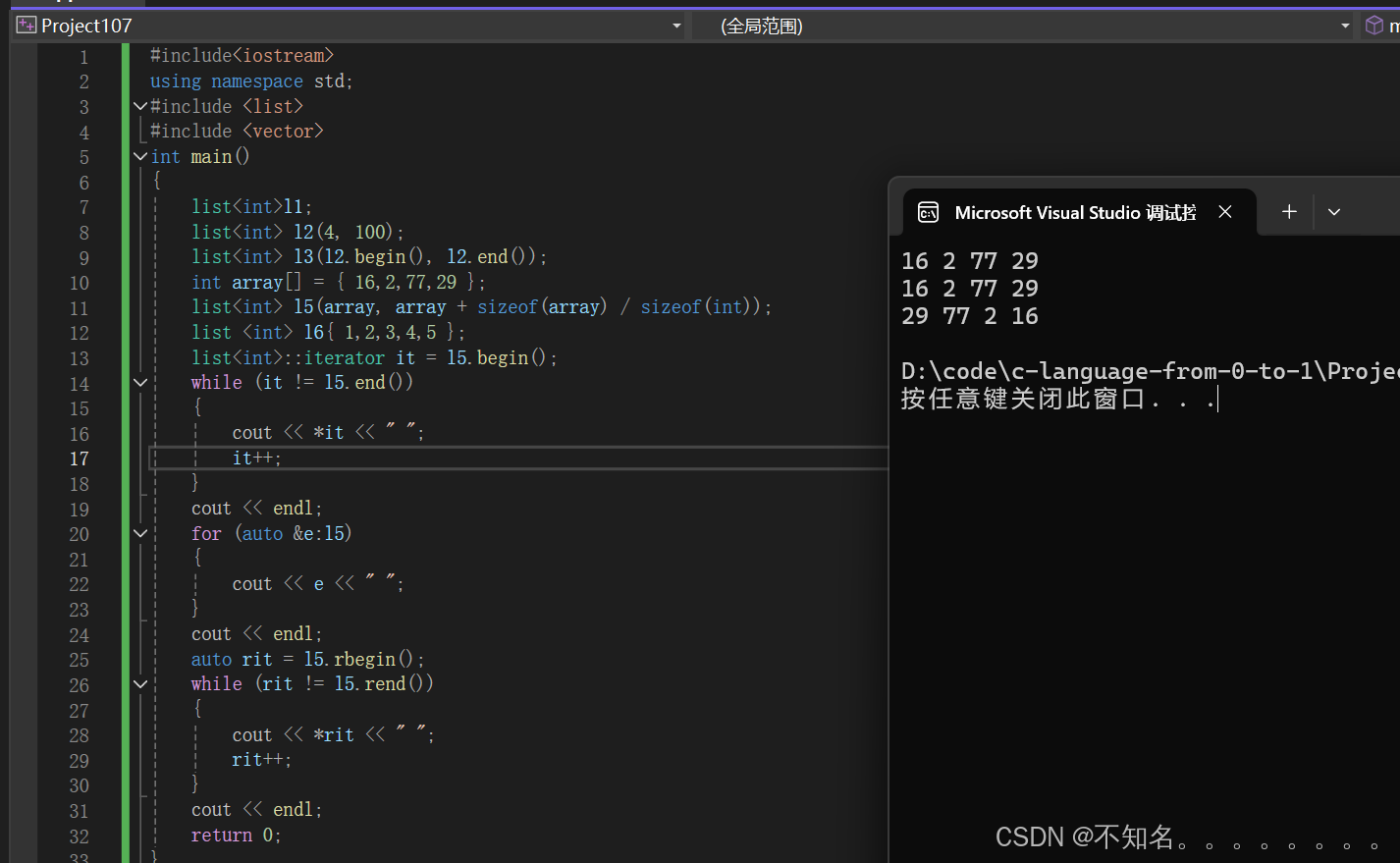
{list<int>l1;list<int> l2(4, 100);list<int> l3(l2.begin(), l2.end());int array[] = { 16,2,77,29 };list<int> l5(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(int));list <int> l6{ 1,2,3,4,5 };list<int>::iterator it = l5.begin();while (it != l5.end()){cout << *it << " ";it++;}cout << endl;for (auto &e:l5){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;auto rit = l5.rbegin();while (rit != l5.rend()){cout << *rit << " ";rit++;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
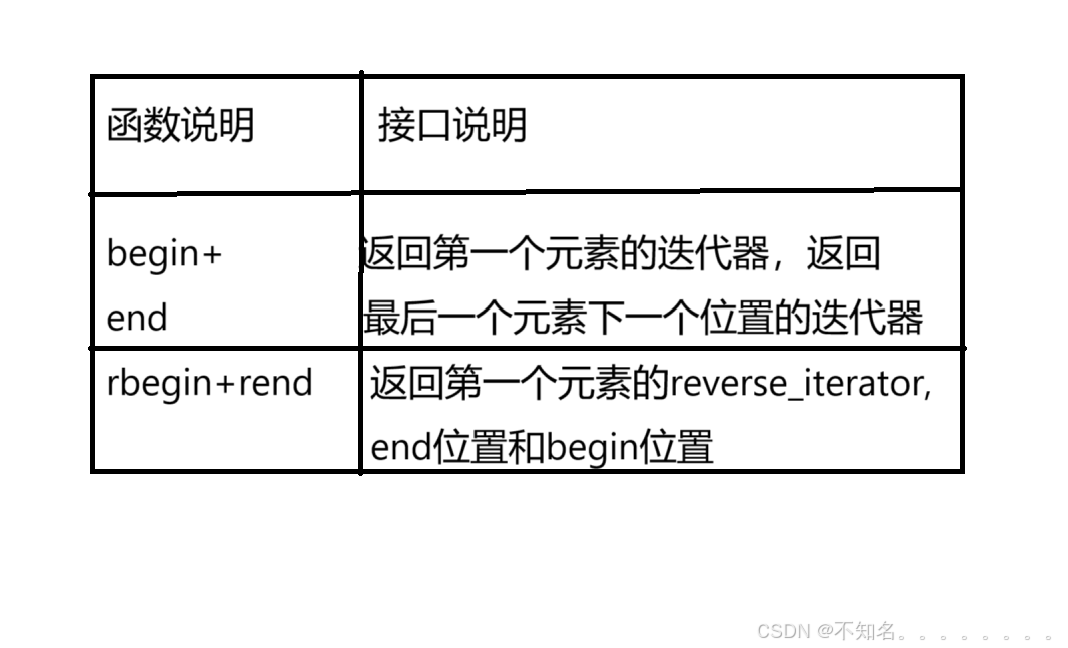
注意:begin和end为正向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向后移动
rbegin(end)和rend(begin)为反向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向前移动
1.2.3 list capacity
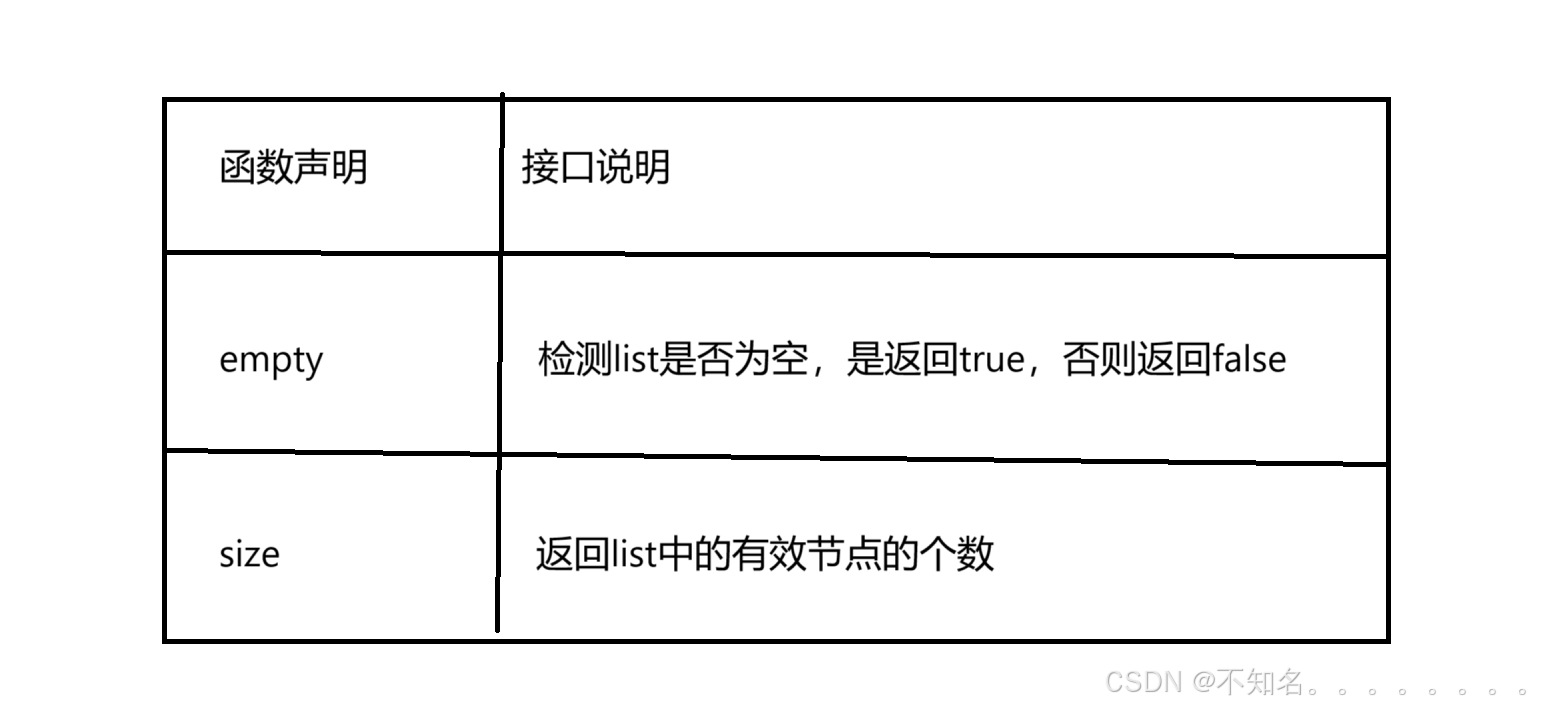
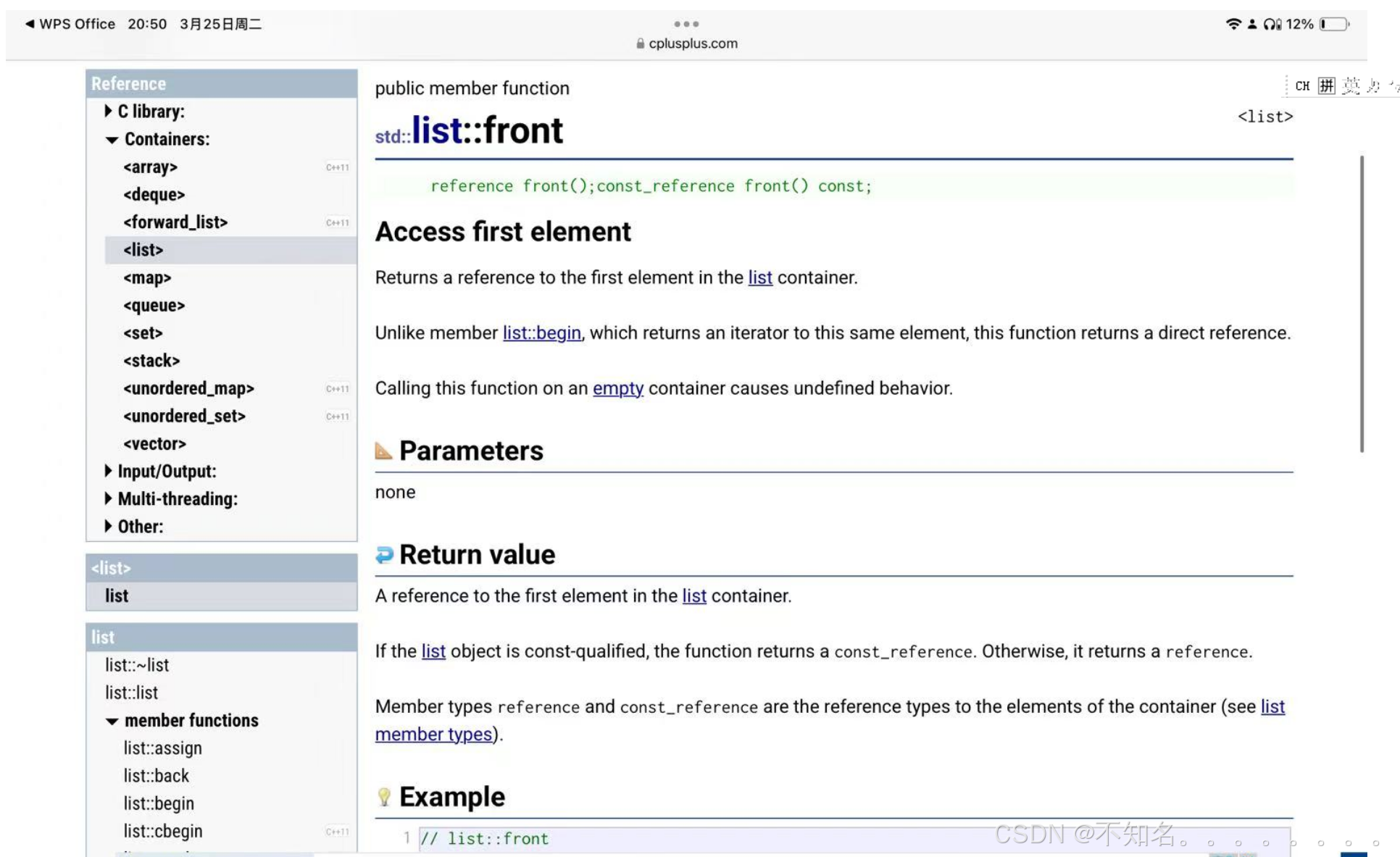
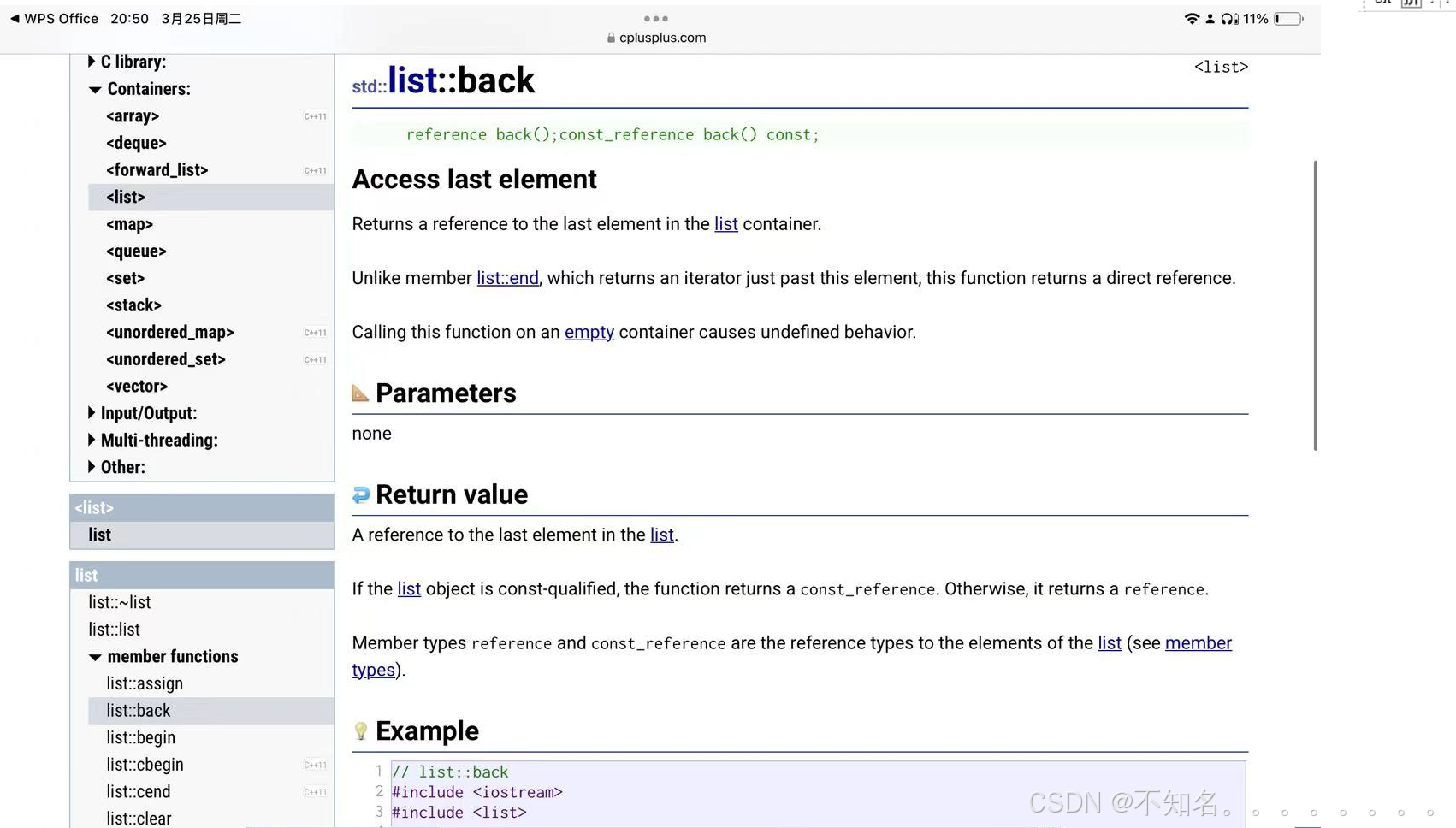
1.2.4 list element access
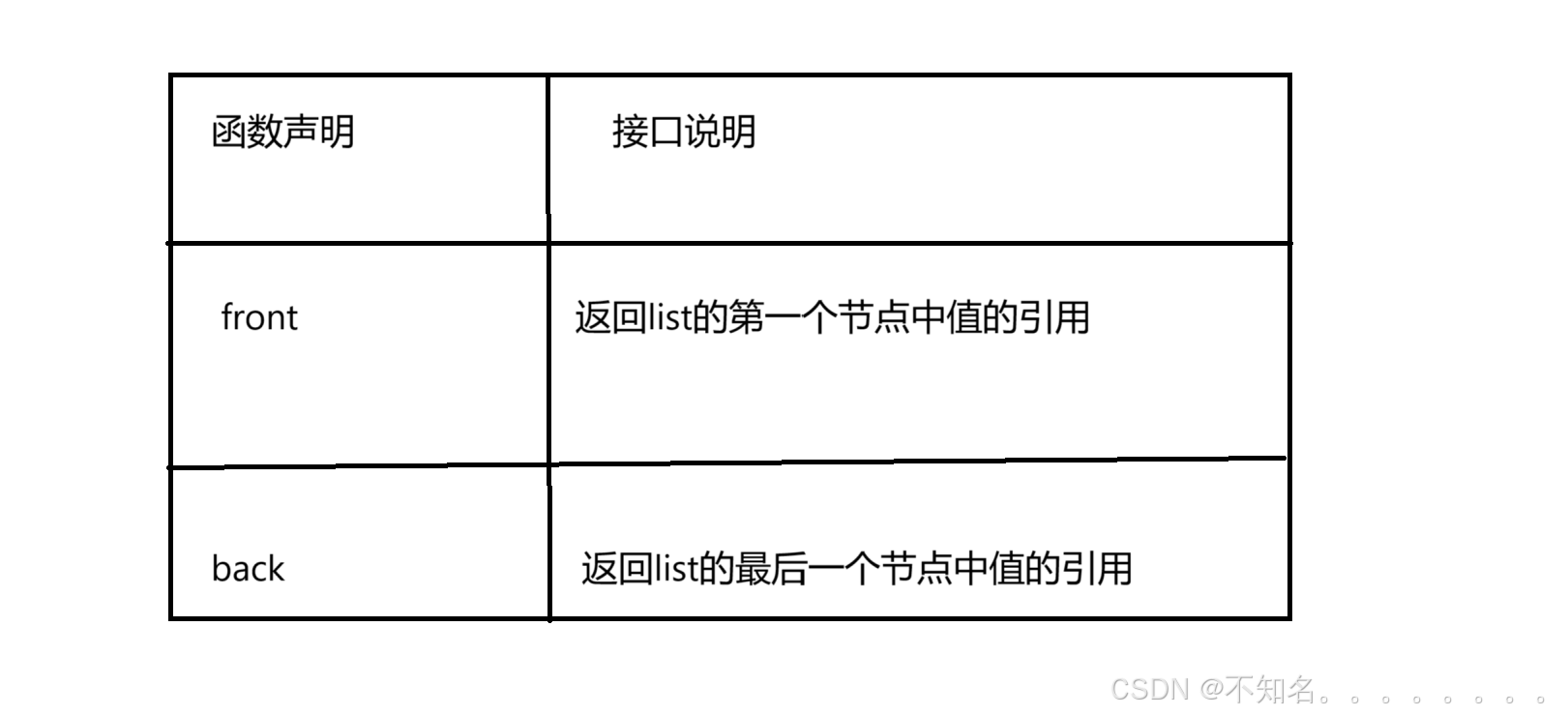
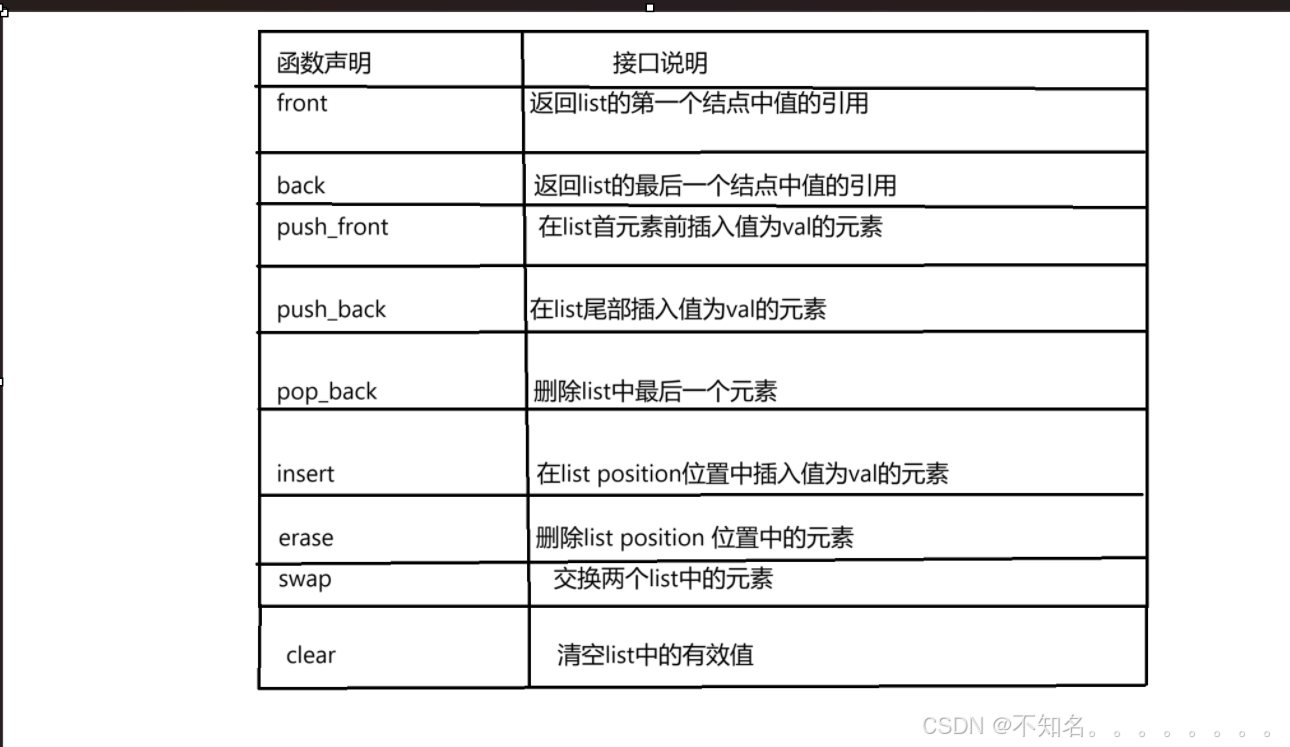
1.2.5 list modifiers
举例:
int array1[] = { 1,2,3 };list<int> L(array1, array1 + sizeof(array1) / sizeof(array1[0]));auto pos = L.begin();cout << *pos << endl;L.insert(pos, 3);for (auto e : L){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;L.insert(pos, 5, 5);for (auto e : L){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;vector<int> v{ 7,8,9 };L.insert(pos, v.begin(), v.end());for (auto e : L){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;L.erase(pos);for (auto e : L){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;L.erase(L.begin(), L.end());for (auto e : L){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;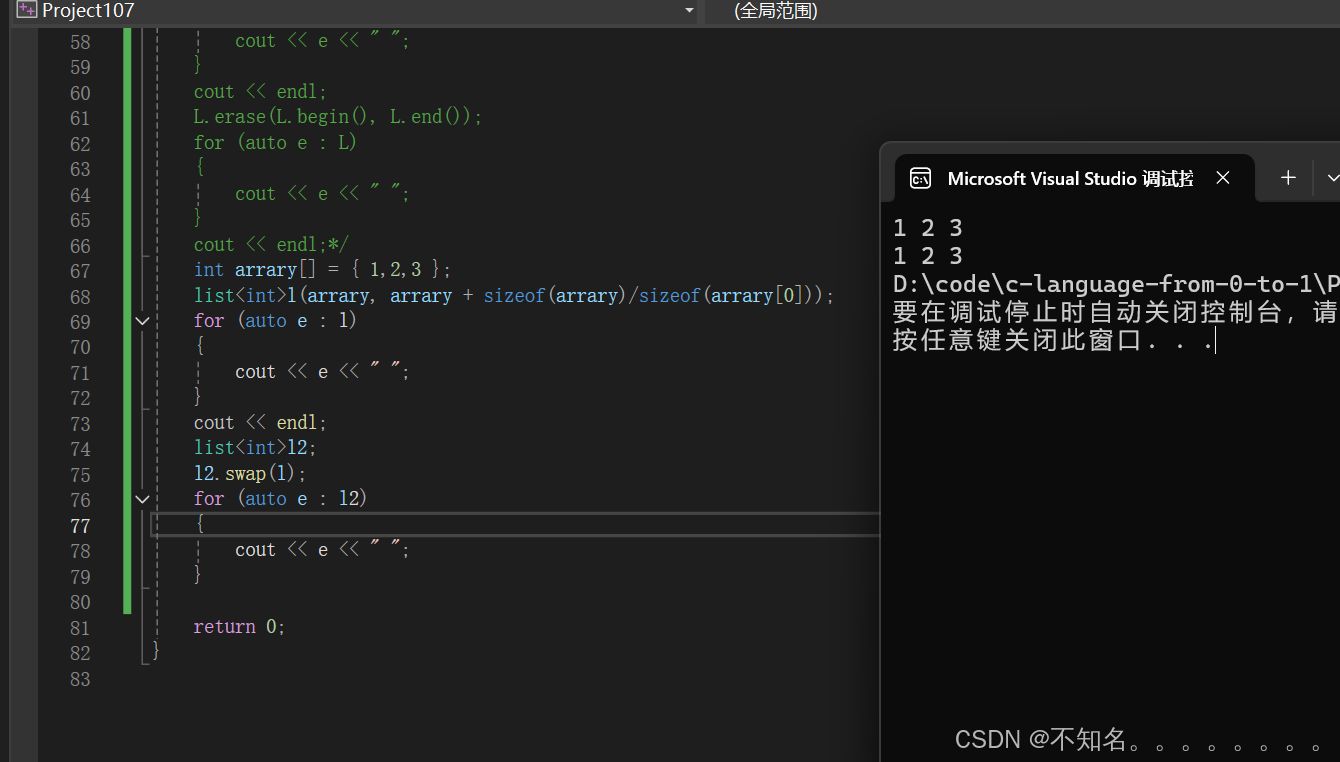
int arrary[] = { 1,2,3 };
list<int>l(arrary, arrary + sizeof(arrary)/sizeof(arrary[0]));
for (auto e : l)
{cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<int>l2;
l2.swap(l);
for (auto e : l2)
{cout << e << " ";
}二、list的模拟实现
1、迭代器的实现
普通迭代器
我们在vector 和list 的时候的迭代器都是原生指针,但是list 的原生指针明显不满足,所以我们要对指针进行封装
代码:
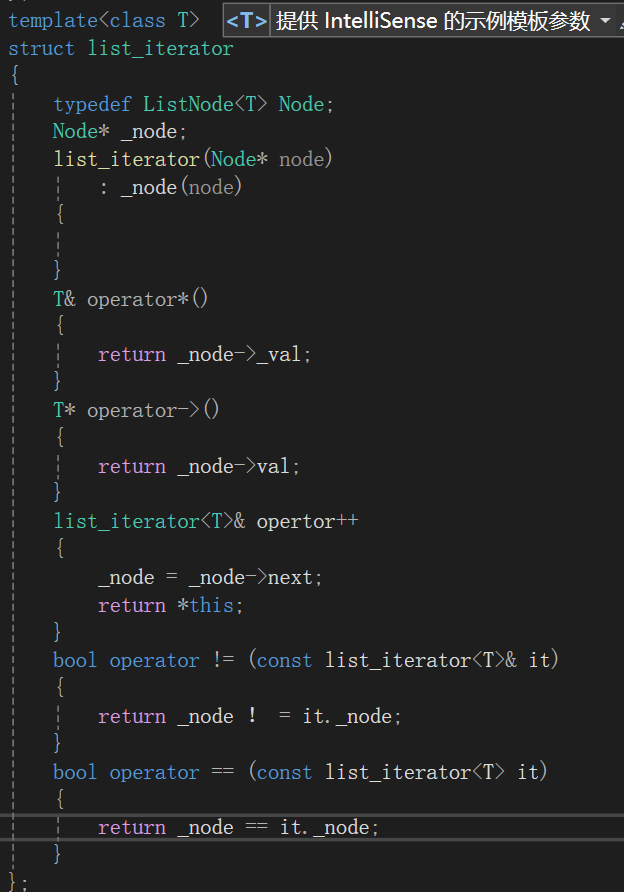
struct list_iterator
{typedef ListNode<T> Node;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node): _node(node){}T& operator*(){return _node->_val;}T* operator->(){return _node->val;}list_iterator<T>& opertor++{_node = _node->next;return *this;}bool operator != (const list_iterator<T>& it){return _node ! = it._node;}bool operator == (const list_iterator<T> it){return _node == it._node;}
};注意到我们重载了->的符号 ,那是因为防止T出现下图的类型,需要使用A->a,A->b,的场景
实际上我们调用的时候是调用了两个->,opertor->->a;但是为了可读性我们简化只调用一个

const迭代器
方法一:我们发现得到const迭代器只需要返回值 为const就行了,所以我们的一种方法就是重新写一份
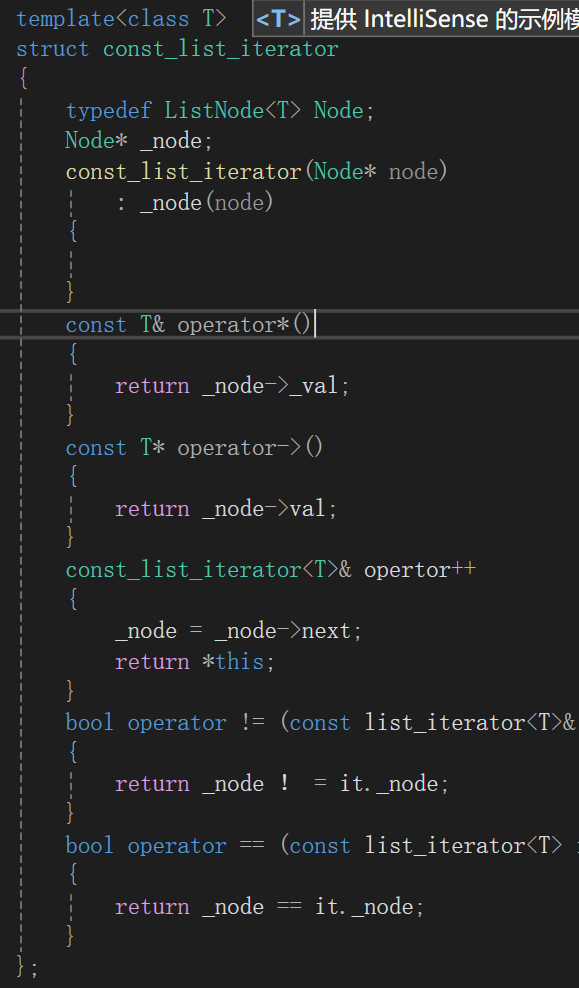
template<class T>
struct const_list_iterator
{typedef ListNode<T> Node;Node* _node;const_list_iterator(Node* node): _node(node){}const T& operator*(){return _node->_val;}const T* operator->(){return _node->val;}const_list_iterator<T>& opertor++{_node = _node->next;return *this;}bool operator != (const list_iterator<T>& it){return _node ! = it._node;}bool operator == (const list_iterator<T> it){return _node == it._node;}
};方法二:我们发现其实迭代器和const迭代器他们的代码高度相似,只有一个返回值不同,所以我们可以利用模板参数将它们合写成一个
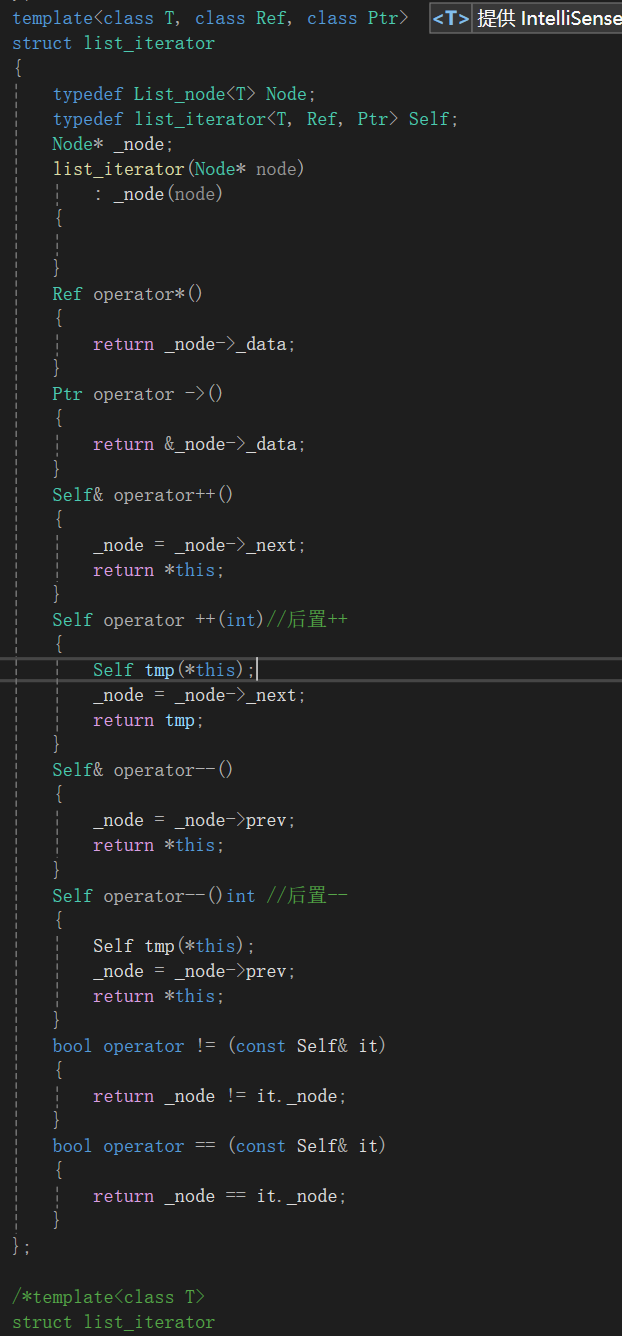
代码:
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct list_iterator
{typedef List_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node): _node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator ->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self operator ++(int)//后置++{Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->prev;return *this;}Self operator--()int //后置--{Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->prev;return *this;}bool operator != (const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator == (const Self& it){return _node == it._node;}
};2、begin end const begin ,const end
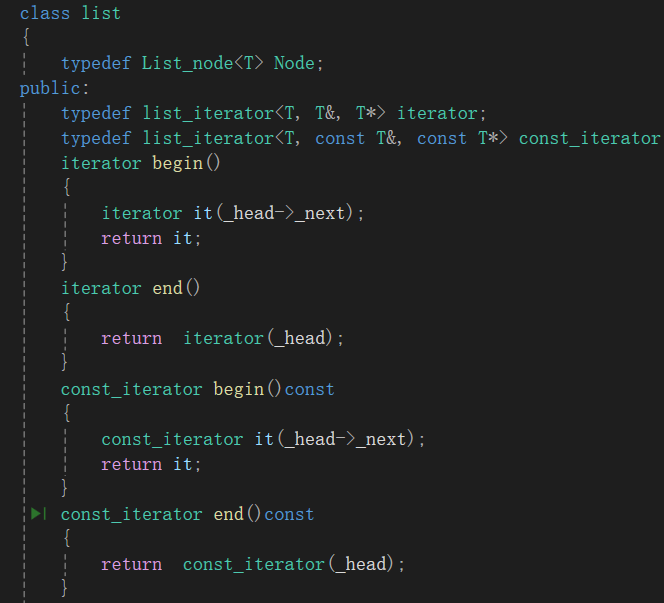
代码:
class list
{typedef List_node<T> Node;
public:typedef list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){iterator it(_head->_next);return it;}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin()const{const_iterator it(_head->_next);return it;}const_iterator end()const{return const_iterator(_head);}
}3、list的构造
默认构造
list 是一个双向带头链表,所以begin()指向头结点的下一个,end()指向头结点

list的拷贝构造
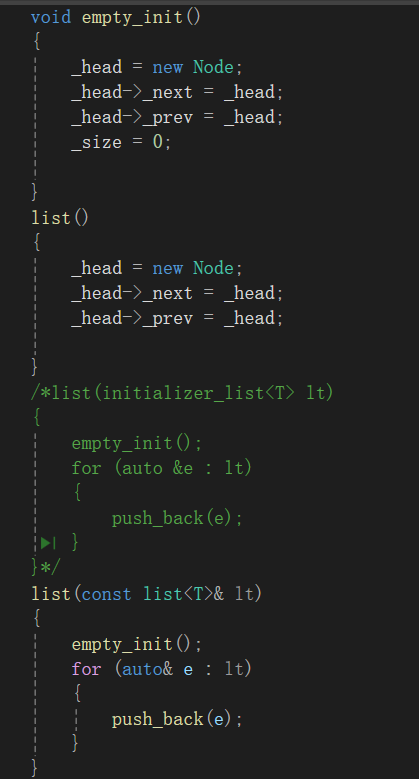
因为我们发现他和默认构造高度相似所以我们,写了一个 empty_init,将二者相似的地方进行复用
代码:
list()
{_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}
/*list(initializer_list<T> lt)
{empty_init();for (auto &e : lt){push_back(e);}
}*/
list(const list<T>& lt)
{empty_init();for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}
}赋值
我们使用现代写法,我们将参数写成非引用,当我们传参的时候,编译器会调用拷贝构造 ,生成局部变量lt,我们将this和lt交换数值,当我们结束这个函数的时候lt会自动销毁。

代码:
void swap(const list<T>& lt)
{std::swap(_head, lt._head);std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
list<T>& operator =(const list<T> lt)
{swap(lt);return *this;
}4、析构和clear
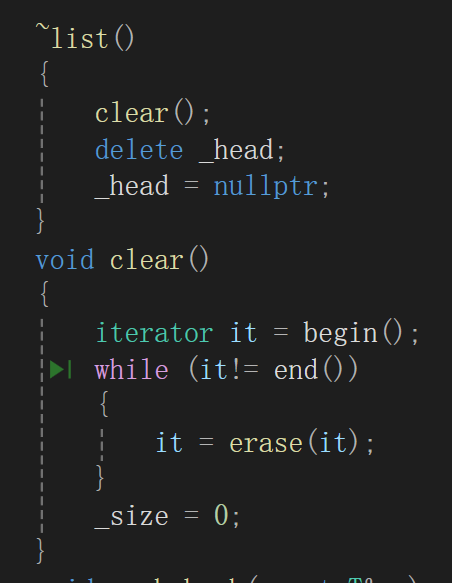
代码:
~list()
{clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;
}
void clear()
{iterator it = begin();while (it!= end()){it = erase(it);}_size = 0;5、insert 和erase
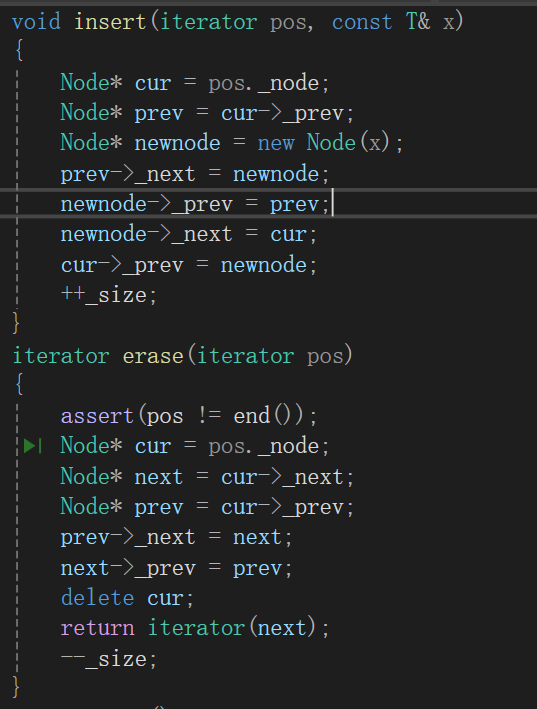
void insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;++_size;
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{assert(pos != end());Node* cur = pos._node;Node* next = cur->_next;Node* prev = cur->_prev;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;return iterator(next);--_size;
}
size_t6、push _back push_front
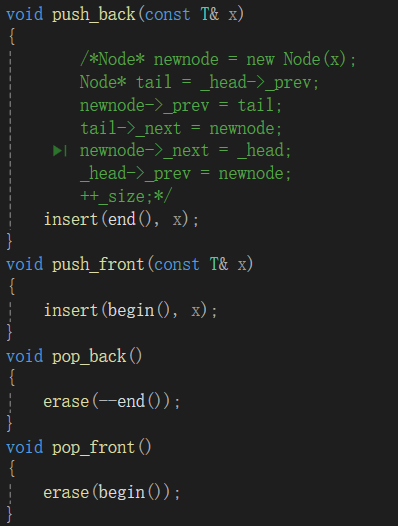
void push_back(const T& x)
{/*Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* tail = _head->_prev;newnode->_prev = tail;tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;++_size;*/insert(end(), x);
}
void push_front(const T& x)
{insert(begin(), x);
}
void pop_back()
{erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{erase(begin());
}7、size
如果我们使用遍历数据的方式来得到size 十分麻烦,所以我们将_size设置为成员变量,初始为0,当他插入数据的是后++,删除数据的时候--。

返回_size就好了

三、全部代码
list.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
namespace cx
{template<class T>struct List_node{List_node<T>* _prev;List_node<T>* _next;T _data;List_node(const T& x = T()):_prev(nullptr), _next(nullptr), _data(x){}};template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct list_iterator{typedef List_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node): _node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator ->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self operator ++(int)//后置++{Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->prev;return *this;}Self operator--()int //后置--{Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->prev;return *this;}bool operator != (const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator == (const Self& it){return _node == it._node;}};/*template<class T>struct list_iterator{typedef ListNode<T> Node;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node): _node(node){}T& operator*(){return _node->_val;}T* operator->(){return _node->val;}list_iterator<T>& opertor++{_node = _node->next;return *this;}bool operator != (const list_iterator<T>& it){return _node ! = it._node;}bool operator == (const list_iterator<T> it){return _node == it._node;}};*///template<class T>//struct const_list_iterator//{// typedef ListNode<T> Node;// Node* _node;// const_list_iterator(Node* node)// : _node(node)// {// }// const T& operator*()// {// return _node->_val;// }// const T* operator->()// {// return _node->val;// }// const_list_iterator<T>& opertor++// {// _node = _node->next;// return *this;// }// bool operator != (const list_iterator<T>& it)// {// return _node ! = it._node;// }// bool operator == (const list_iterator<T> it)// {// return _node == it._node;// }//};/*struct A{A(int a, int b):_a(a), _b(b){}int _a;int _b;};*/template <class T>class list{typedef List_node<T> Node;public:typedef list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){iterator it(_head->_next);return it;}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin()const{const_iterator it(_head->_next);return it;}const_iterator end()const{return const_iterator(_head);}void empty_init(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}list(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}/*list(initializer_list<T> lt){empty_init();for (auto &e : lt){push_back(e);}}*/list(const list<T>& lt){empty_init();for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}void swap(const list<T>& lt){std::swap(_head, lt._head);std::swap(_size, lt._size);}list<T>& operator =(const list<T> lt){swap(lt);return *this;}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it!= end()){it = erase(it);}_size = 0;}void push_back(const T& x){/*Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* tail = _head->_prev;newnode->_prev = tail;tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;++_size;*/insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}void insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;++_size;}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* cur = pos._node;Node* next = cur->_next;Node* prev = cur->_prev;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;return iterator(next);--_size;}size_t size(){return _size;}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};
}test.cpp
需要注意的是我们在测试的时候,push_back insert erase 都会导致迭代器失效,我们使用他们之后需要更新迭代器
#include "list.h"
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{//注意在push_back ,insert ,erase迭代器会失效,所以要更新迭代器cx::list<int> l;auto it = l.begin();l.push_back(3);l.push_back(4);l.push_back(5);it = l.begin();l.insert(it, 6);it = l.begin();for (auto e : l){cout << e;}cout << endl;l.erase(it);for (auto e : l){cout << e;}cout << endl;cx::list<int> lt(l);for (auto e : l){cout << e;}cout << endl;cout << lt.size();return 0;
}