1.NMS
def py_cpu_nms(dets, thresh):"""Pure Python NMS baseline."""#x1、y1、x2、y2、以及score赋值x1 = dets[:, 0]y1 = dets[:, 1]x2 = dets[:, 2]y2 = dets[:, 3]scores = dets[:, 4]#每一个检测框的面积areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)#按照score置信度降序排序order = scores.argsort()[::-1]keep = [] #保留的结果框集合while order.size > 0:i = order[0]keep.append(i) #保留该类剩余box中得分最高的一个#得到相交区域,左上及右下xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])#计算相交的面积,不重叠时面积为0w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)inter = w * h#计算IoU:重叠面积 /(面积1+面积2-重叠面积)ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)#保留IoU小于阈值的boxinds = np.where(ovr <= thresh)[0]order = order[inds + 1] #因为ovr数组的长度比order数组少一个,所以这里要将所有下标后移一位return keep2.交叉熵损失函数
实际输出(概率)与期望输出(概率)的距离,也就是交叉熵的值越小,两个概率分布就越接近。
![]()
a.Python 实现
def cross_entropy(a, y):
return np.sum(np.nan_to_num(-y*np.log(a)-(1-y)*np.log(1-a)))
b.# tensorflow version
loss = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y), reduction_indices=[1]))
c.# numpy version
loss = np.mean(-np.sum(y_*np.log(y), axis=1))
3.Softmax 函数
将激活值与所有神经元的输出值联系在一起,所有神经元的激活值加起来为1。
第L层(最后一层)的第j个神经元的激活输出为:
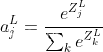
Python 实现:
def softmax(x):
shift_x = x - np.max(x) # 防止输入增大时输出为nan
exp_x = np.exp(shift_x)
return exp_x / np.sum(exp_x)
4.iou
def IoU(box1, box2) -> float:
"""
IOU, Intersection over Union
:param box1: list, 第一个框的两个坐标点位置 box1[x1, y1, x2, y2]
:param box2: list, 第二个框的两个坐标点位置 box2[x1, y1, x2, y2]
:return: float, 交并比
"""
weight = max(min(box1[2], box2[2]) - max(box1[0], box2[0]), 0)
height = max(min(box1[3], box2[3]) - max(box1[1], box2[1]), 0)
s_inter = weight * height
s_box1 = (box1[2] - box1[0]) * (box1[3] - box1[1])
s_box2 = (box2[2] - box2[0]) * (box2[3] - box2[1])
s_union = s_box1 + s_box2 - s_inter
return s_inter / s_union
if __name__ == '__main__':
box1 = [0, 0, 50, 50]
box2 = [0, 0, 100, 100]
print('IoU is %f' % IoU(box1, box2))
5. 将一维数组转变成二维数组
class Solution:def construct2DArray(self, original: List[int], m: int, n: int) -> List[List[int]]:return [original[i: i + n] for i in range(0, len(original), n)] if len(original) == m * n else []6.MAP
AP衡量的是对一个类检测好坏,mAP就是对多个类的检测好坏。就是简单粗暴的把所有类的AP值取平均就好了。比如有两类,类A的AP值是0.5,类B的AP值是0.2,那么mAP=(0.5+0.2)/2=0.35
# AP的计算
def _average_precision(self, rec, prec):"""Params:----------rec : numpy.arraycumulated recallprec : numpy.arraycumulated precisionReturns:----------ap as float"""if rec is None or prec is None:return np.nanap = 0.for t in np.arange(0., 1.1, 0.1): #十一个点的召回率,对应精度最大值if np.sum(rec >= t) == 0:p = 0else:p = np.max(np.nan_to_num(prec)[rec >= t])ap += p / 11. #加权平均return ap7.手写conv2d
class Conv2D(Layer):"""A 2D Convolution Layer.Parameters:-----------n_filters: intThe number of filters that will convolve over the input matrix. The number of channelsof the output shape.filter_shape: tupleA tuple (filter_height, filter_width).input_shape: tupleThe shape of the expected input of the layer. (batch_size, channels, height, width)Only needs to be specified for first layer in the network.padding: stringEither 'same' or 'valid'. 'same' results in padding being added so that the output height and widthmatches the input height and width. For 'valid' no padding is added.stride: intThe stride length of the filters during the convolution over the input."""def __init__(self, n_filters, filter_shape, input_shape=None, padding='same', stride=1):self.n_filters = n_filtersself.filter_shape = filter_shapeself.padding = paddingself.stride = strideself.input_shape = input_shapeself.trainable = Truedef initialize(self, optimizer):# Initialize the weightsfilter_height, filter_width = self.filter_shapechannels = self.input_shape[0]limit = 1 / math.sqrt(np.prod(self.filter_shape))self.W = np.random.uniform(-limit, limit, size=(self.n_filters, channels, filter_height, filter_width))self.w0 = np.zeros((self.n_filters, 1))# Weight optimizersself.W_opt = copy.copy(optimizer)self.w0_opt = copy.copy(optimizer)def parameters(self):return np.prod(self.W.shape) + np.prod(self.w0.shape)def forward_pass(self, X, training=True):batch_size, channels, height, width = X.shapeself.layer_input = X# Turn image shape into column shape# (enables dot product between input and weights)self.X_col = image_to_column(X, self.filter_shape, stride=self.stride, output_shape=self.padding)# Turn weights into column shapeself.W_col = self.W.reshape((self.n_filters, -1))# Calculate outputoutput = self.W_col.dot(self.X_col) + self.w0# Reshape into (n_filters, out_height, out_width, batch_size)output = output.reshape(self.output_shape() + (batch_size, ))# Redistribute axises so that batch size comes firstreturn output.transpose(3,0,1,2)def backward_pass(self, accum_grad):# Reshape accumulated gradient into column shapeaccum_grad = accum_grad.transpose(1, 2, 3, 0).reshape(self.n_filters, -1)if self.trainable:# Take dot product between column shaped accum. gradient and column shape# layer input to determine the gradient at the layer with respect to layer weightsgrad_w = accum_grad.dot(self.X_col.T).reshape(self.W.shape)# The gradient with respect to bias terms is the sum similarly to in Dense layergrad_w0 = np.sum(accum_grad, axis=1, keepdims=True)# Update the layers weightsself.W = self.W_opt.update(self.W, grad_w)self.w0 = self.w0_opt.update(self.w0, grad_w0)# Recalculate the gradient which will be propogated back to prev. layeraccum_grad = self.W_col.T.dot(accum_grad)# Reshape from column shape to image shapeaccum_grad = column_to_image(accum_grad,self.layer_input.shape,self.filter_shape,stride=self.stride,output_shape=self.padding)return accum_graddef output_shape(self):channels, height, width = self.input_shapepad_h, pad_w = determine_padding(self.filter_shape, output_shape=self.padding)output_height = (height + np.sum(pad_h) - self.filter_shape[0]) / self.stride + 1output_width = (width + np.sum(pad_w) - self.filter_shape[1]) / self.stride + 1return self.n_filters, int(output_height), int(output_width)
8.手写PyTorch加载和保存模型
仅保存和加载模型参数(推荐)
a.保存模型参数
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
model = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(128, 16), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(16, 1))
# 保存整个模型
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'sample_model.pt')
加载模型参数
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# 下载模型参数 并放到模型中
loaded_model = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(128, 16), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(16, 1))
loaded_model.load_state_dict(torch.load('sample_model.pt'))
print(loaded_model)
显示如下:
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=16, bias=True)
(1): ReLU()
(2): Linear(in_features=16, out_features=1, bias=True)
)
state_dict:PyTorch中的state_dict是一个python字典对象,将每个层映射到其参数Tensor。state_dict对象存储模型的可学习参数,即权重和偏差,并且可以非常容易地序列化和保存。
b. 保存和加载整个模型
保存整个模型
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(128, 16), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(16, 1))
# 保存整个模型,包含模型结构和参数
torch.save(net, 'sample_model.pt')
#加载整个模型
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# 加载整个模型,包含模型结构和参数
loaded_model = torch.load('sample_model.pt')
print(loaded_model)
显示如下:
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=16, bias=True)
(1): ReLU()
(2): Linear(in_features=16, out_features=1, bias=True)
)
