-
涉及到二叉树的构造,无论普通二叉树还是二叉搜索树一定前序,都是先构造中节点。
-
求普通二叉树的属性,一般是后序,一般要通过递归函数的返回值做计算。
-
求二叉搜索树的属性,一定是中序了,要不白瞎了有序性了。
1、二叉树的递归遍历
// 前序遍历·递归·LC144_二叉树的前序遍历
class Solution {public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();preorder(root, result);return result;}public void preorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) {if (root == null) {return;}result.add(root.val);preorder(root.left, result);preorder(root.right, result);}
}
// 中序遍历·递归·LC94_二叉树的中序遍历
class Solution {public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();inorder(root, res);return res;}void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {if (root == null) {return;}inorder(root.left, list);list.add(root.val); // 注意这一句inorder(root.right, list);}
}
// 后序遍历·递归·LC145_二叉树的后序遍历
class Solution {public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();postorder(root, res);return res;}void postorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {if (root == null) {return;}postorder(root.left, list);postorder(root.right, list);list.add(root.val); // 注意这一句}
}2、二叉树的迭代遍历(非递归)
递归的实现就是:每一次递归调用都会把函数的局部变量、参数值和返回地址等压入调用栈中,然后递归返回的时候,从栈顶弹出上一次递归的各项参数,所以这就是递归为什么可以返回上一层位置的原因。
2.1 前序遍历
前序遍历是根左右,每次先处理的是中间节点,那么先将根节点放入栈中,然后将右孩子加入栈,再加入左孩子。为什么要先加入 右孩子,再加入左孩子呢? 因为这样出栈的时候才是中左右的顺序。
class Solution {public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null){return result;}Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();stack.push(root);while (!stack.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = stack.pop();result.add(node.val);if (node.right != null){stack.push(node.right);}if (node.left != null){stack.push(node.left);}}return result;}
}2.2 中序遍历
中序遍历是左根右,先访问的是二叉树顶部的节点,然后一层一层向下访问,直到到达树左面的最底部,再开始处理节点(也就是在把节点的数值放进result数组中),这就造成了处理顺序和访问顺序是不一致的。那么在使用迭代法写中序遍历,就需要借用指针的遍历来帮助访问节点,栈则用来处理节点上的元素。
class Solution {public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null){return result;}Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();TreeNode cur = root;while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){if (cur != null){stack.push(cur);cur = cur.left;}else{cur = stack.pop();result.add(cur.val);cur = cur.right;}}return result;}
}2.3 后序遍历
后序遍历是左右中,那么我们只需要调整一下先序遍历的代码顺序,就变成中右左的遍历顺序,然后在反转result数组,输出的结果顺序就是左右中了,如下图:

所以后序遍历只需要前序遍历的代码稍作修改就可以了,代码如下:
// 后序遍历顺序 左-右-中 入栈顺序:中-左-右 出栈顺序:中-右-左, 最后翻转结果
class Solution {public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null){return result;}Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();stack.push(root);while (!stack.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = stack.pop();result.add(node.val);if (node.left != null){stack.push(node.left);}if (node.right != null){stack.push(node.right);}}Collections.reverse(result);return result;}
}3、二叉树的层序遍历
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {List<List<Integer>> resList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {fun(root,0);return resList;}/*** 整体逻辑就是:当reslist.size < deep时,那就创建list* 等于或者大于时,就该往相应的list里面添加元素了。* @param root* @param deep*/private void fun(TreeNode root,int deep) {//思路:每一层对应一个list,最后的结果是一个大的listif (root == null) return ;deep++; //代表当前在第几层if (resList.size() < deep){//当层级增加时,存放每层元素的集合数也增加,即当前在第几层那么reslist里面就有几个listList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();resList.add(list);}resList.get(deep -1).add(root.val);fun(root.left,deep);fun(root.right,deep);}//队列实现public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder1(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> resList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();if(root == null)return resList;Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();que.offer(root); //队列尾部插入元素while (!que.isEmpty()){List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();int len = que.size();while (len > 0){TreeNode tmpNode = que.poll();list.add(tmpNode.val);if (tmpNode.left !=null)que.offer(tmpNode.left);if (tmpNode.right != null)que.offer(tmpNode.right);len--;}resList.add(list);}return resList;}}3.1 二叉树的层序遍历II
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值自底向上的层次遍历。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历),相对于二叉树的层序遍历,就是最后把result数组反转一下就可以了。
3.2 二叉树的右视图
给定一棵二叉树,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。

思路:层序遍历,遍历每一层的最后一个节点
public class Case199 {//递归public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> resList = new ArrayList<>();fun(root,0,resList);return resList;}private void fun(TreeNode root,int deep,List<Integer>resList) {if (root == null)return;if (deep == resList.size()){ //这个深度首次达到resList.add(root.val);}fun(root.right,deep + 1,resList);fun(root.left,deep + 1,resList); //这个妙啊!!}//层序遍历,每次返回每层的最后一个节点public List<Integer> rightSideView1(TreeNode root) {Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null) return list;que.offer(root);while (!que.isEmpty()) {int len = que.size();while (len > 0){TreeNode tmp = que.poll();if (tmp.left != null) que.offer(tmp.left);if (tmp.right != null) que.offer(tmp.right);len--;if (len == 0)list.add(tmp.val);}}return list;}
}3.3 二叉树的层平均值
给定一个非空二叉树, 返回一个由每层节点平均值组成的数组。
public class Case637 {public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {List<Double> list = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null)return list;Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()){int len = queue.size();Double sum = 0.0;while (len > 0){TreeNode tem = queue.poll();sum += tem.val;if (tem.left !=null)queue.offer(tem.left);if (tem.right != null)queue.offer(tem.right);len--;if (len == 0){Double res = sum / len;list.add(res);}}}return list;}
}3.4 N叉树的层序遍历
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历。 (即从左到右,逐层遍历)。例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
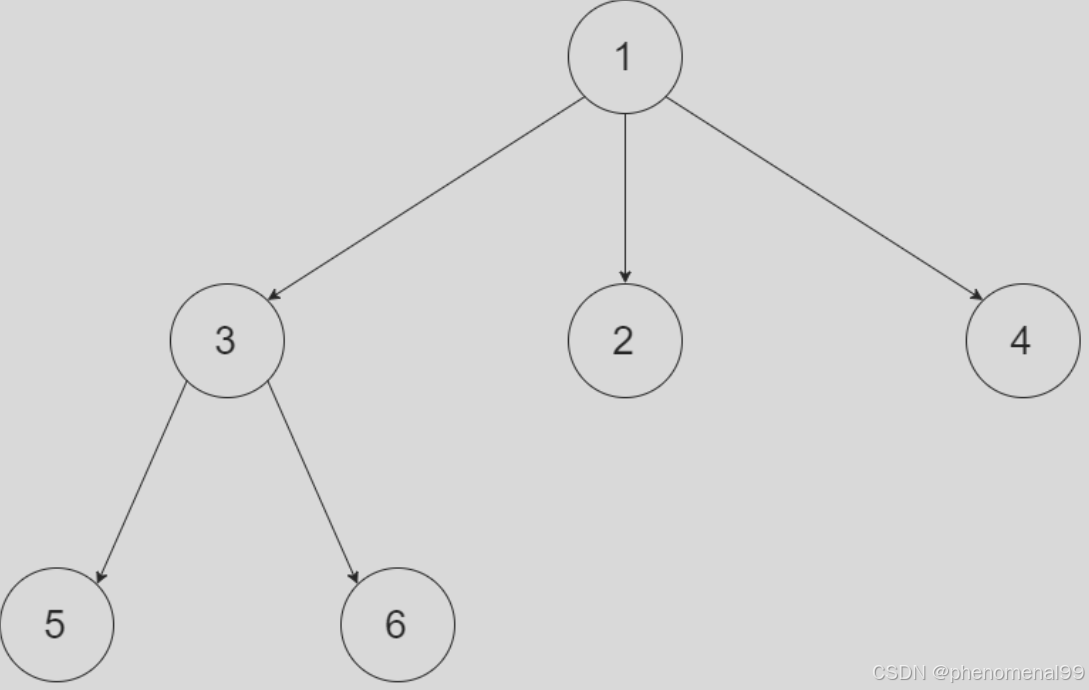
返回其层序遍历:[ [1], [3,2,4], [5,6] ]
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {public int val;public List<Node> children;public Node() {}public Node(int _val) {val = _val;}public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {val = _val;children = _children;}
};
*/
public class Case429 {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null ){return res;}Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()){List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();int len = queue.size();while (len > 0){Node p = queue.poll();list.add(p.val);if (p.children != null){for (Node child : p.children) {queue.offer(child);}}len--;}res.add(list);}return res;}
}
3.5 在每个树行中找最大值
public class Case515 {/*** 给定一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,请找出该二叉树中每一层的最大值。* @param root* @return*/public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();if (root == null) return res;queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int len = queue.size();int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {TreeNode p = queue.poll();max = Math.max(p.val, max);if (p.left != null)queue.offer(p.left);if (p.right != null)queue.offer(p.right);}res.add(max);}return res;}
}
3.6 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
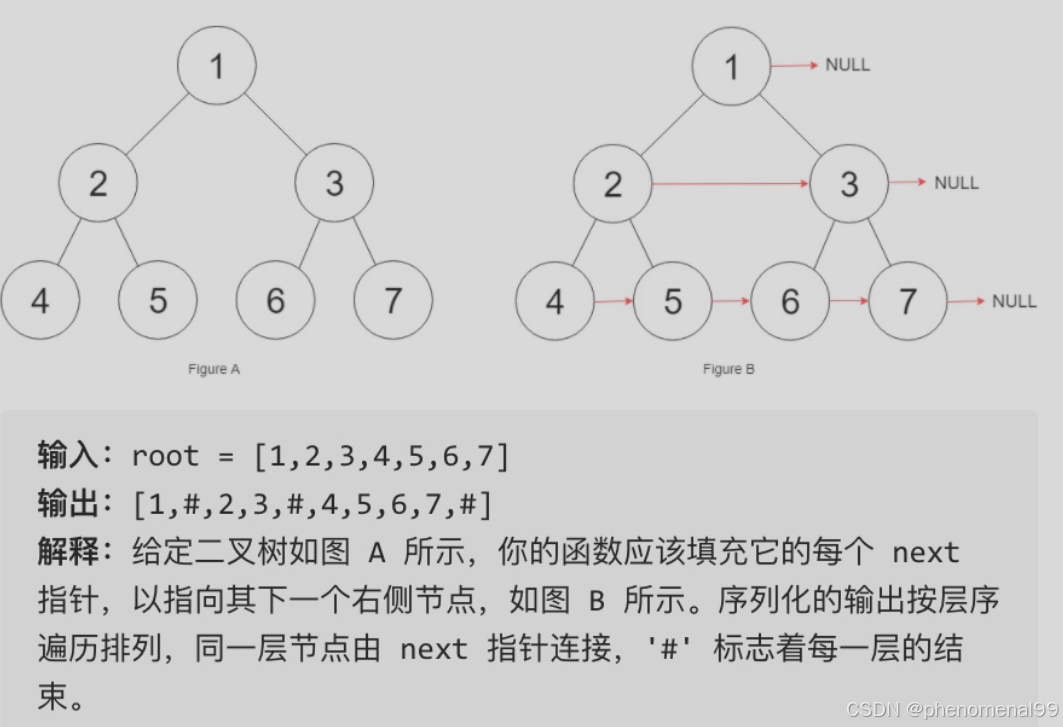
public class Case116 {public Pnode connect(Pnode root) {if (root == null) return null;Queue<Pnode> queue = new LinkedList<Pnode>();queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()){int len = queue.size();while (len > 0){Pnode tem = queue.poll();len--;if (len == 0){tem.next = null;}else {tem.next = queue.peek();}if (tem.left != null)queue.offer(tem.left);if (tem.right != null)queue.offer(tem.right);}}return root;}
}3.7 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
与上题一样
3.8 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
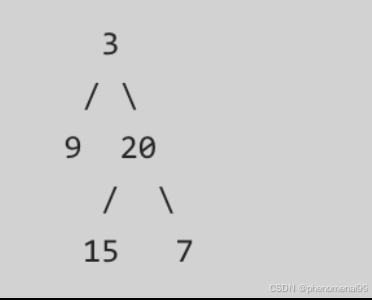
返回它的最大深度 3 。
使用迭代法的话,使用层序遍历是最为合适的,因为最大的深度就是二叉树的层数,和层序遍历的方式极其吻合。在二叉树中,一层一层的来遍历二叉树,记录一下遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度,如图所示:
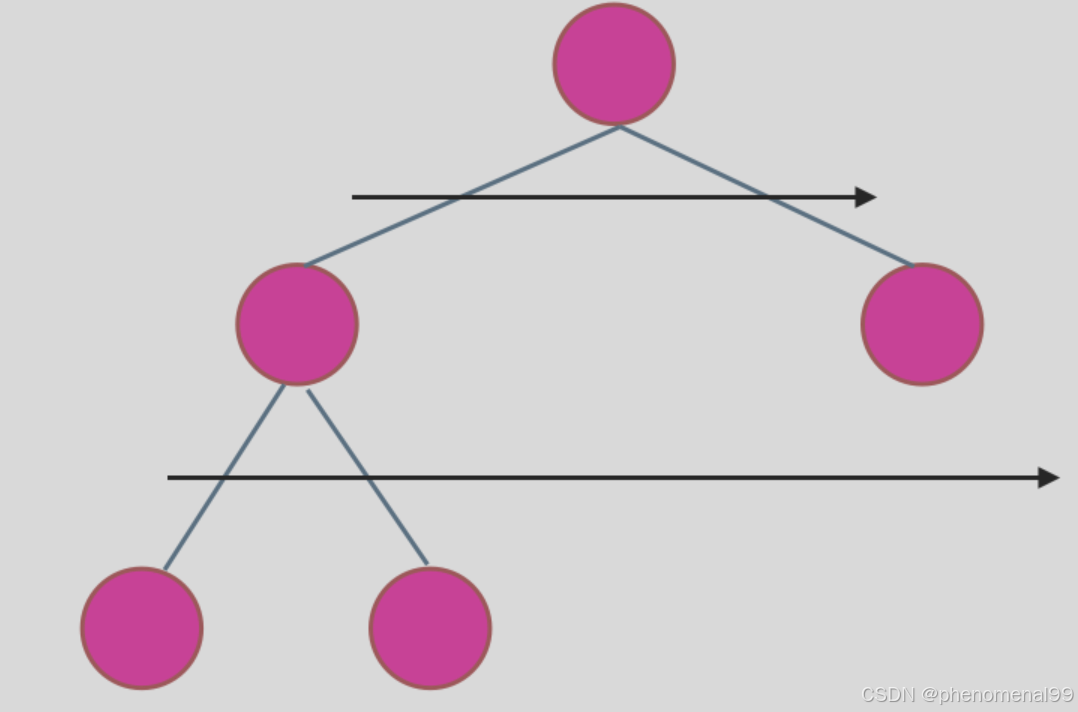
class Solution {public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();que.offer(root);int depth = 0;while (!que.isEmpty()){int len = que.size();while (len > 0){TreeNode node = que.poll();if (node.left != null) que.offer(node.left);if (node.right != null) que.offer(node.right);len--;}depth++;}return depth;}//递归public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null)return 0;int lDepth = maxDepth(root.left);int rDepth = maxDepth(root.right);int max = Math.max(lDepth,rDepth) + 1;return max;}
}3.9 二叉树的最小深度
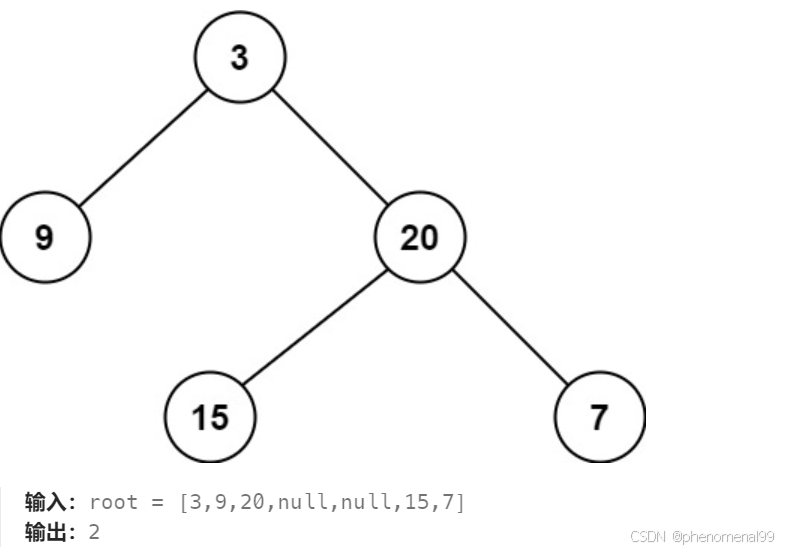
public class Case111 {/*** 与求最大深度还不一样,* @param root* @return*/public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {if(root == null) return 0;int m1 = minDepth(root.left);int m2 = minDepth(root.right);//1.如果左孩子和右孩子有为空的情况,直接返回m1+m2+1//2.如果都不为空,返回较小深度+1return root.left == null || root.right == null ? m1 + m2 + 1 : Math.min(m1,m2) + 1;}// 层序遍历public int minDepth1(TreeNode root){if (root == null) return 0;Queue<TreeNode>queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);int depth = 0;while (!queue.isEmpty()){depth++; //每遍历完一层深度+1int len = queue.size();while (len > 0) {TreeNode p = queue.poll();if (p.left == null && p.right == null) return depth; //到达叶子节点了if (p.left != null) queue.offer(p.left);if (p.right != null) queue.offer(p.right);len--;}}return depth;}
}4、反转二叉树
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
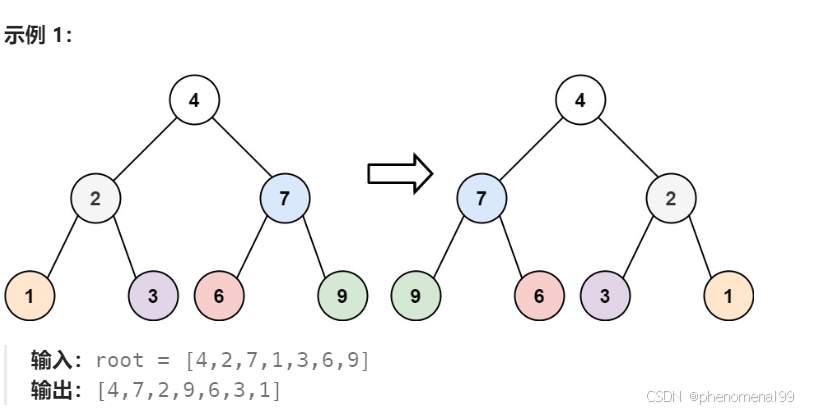
public class Case226 {public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return null;Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()){int len = queue.size();while (len > 0){TreeNode p = queue.poll();swap(p);if (p.left != null)queue.offer(p.left) ;if (p.right != null)queue.offer(p.right);len--;}}return root;}private void swap(TreeNode p) {TreeNode temp = p.left;p.left = p.right;p.right = temp;}//递归public TreeNode invertTree1(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return null;invertTree1(root.left);invertTree1(root.right);swap(root);return root;}5、对称二叉树
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
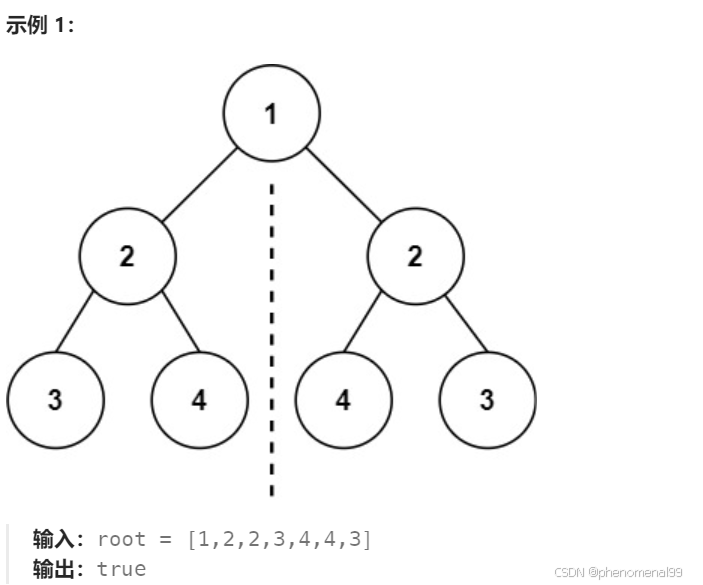
/*** 简单题并不简单* 按照普通层序遍历法,是行不通的,不应该一个一个出队列* 而是两个两个出队列*/
public class Case101 {public boolean isSymmetric1(TreeNode root) {Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offerFirst(root.left);queue.offerLast(root.right);while (!queue.isEmpty()){TreeNode a = queue.pollFirst();TreeNode b = queue.pollLast();if (a == null && b == null){continue;}if (a == null && b != null)return false;if (a != null && b == null)return false;if (a.val != b.val)return false;queue.offerFirst(a.left);queue.offerFirst(a.right);queue.offerLast(b.right);queue.offerLast(b.left);}return true;}//递归法public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {return compare(root.left,root.right);}private boolean compare(TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {if (left == null && right != null)return false;if (left != null && right == null) return false;if (left == null && right == null)return true;if (left.val != right.val) return false;//比较外侧boolean compareOutside = compare(left.left,right.right);//比较内测boolean compareInside = compare(left.right,right.left);return compareInside && compareOutside;}
}
6、平衡二叉树
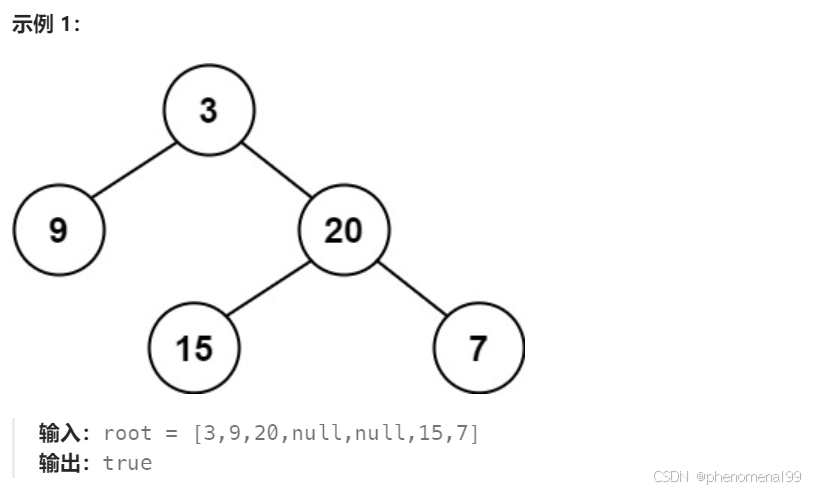
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
public class Case110 {public boolean isBalanced1(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return true;}int res = getHeight1(root);return res == -1 ? false : true;}private int getHeight1(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;int m = getHeight1(root.left);if (m == -1) return -1;int n = getHeight1(root.right);if (n == -1) return -1;if (Math.abs(m - n) > 1) return -1;return Math.max(m, n) + 1;}
7、二叉树的所有路径
给定一个二叉树,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。

这道题目要求从根节点到叶子的路径,所以需要前序遍历,这样才方便让父节点指向孩子节点,找到对应的路径。在这道题目中将第一次涉及到回溯,因为我们要把路径记录下来,需要回溯来回退一个路径再进入另一个路径。
前序遍历以及回溯的过程如图:
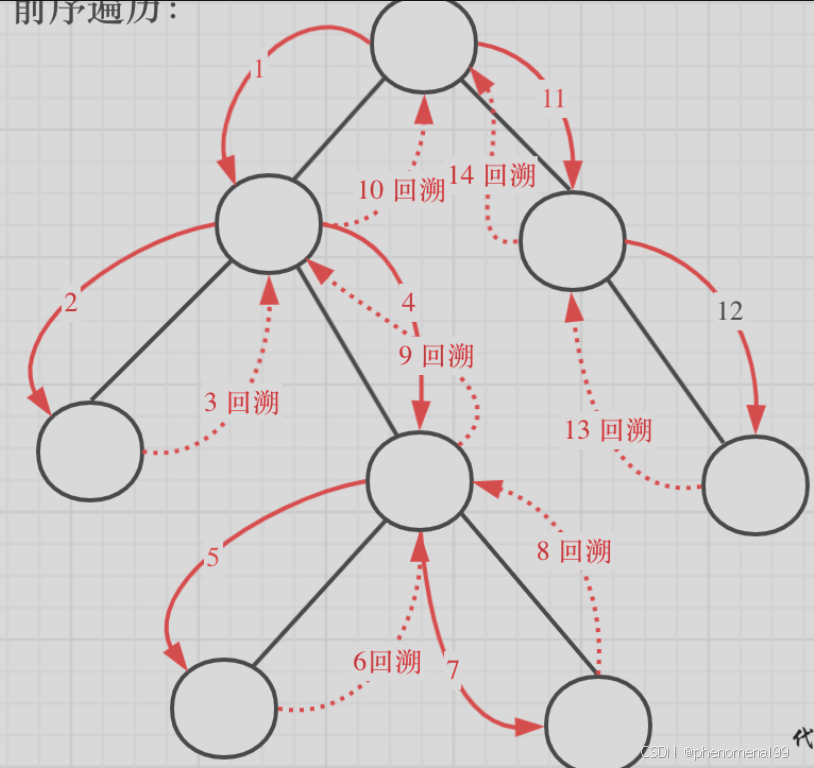
public class Case257 {public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null){return res;}List<Integer> paths = new ArrayList<>(); //作为结果中的路径traversal(root,paths,res);return res;}//前序遍历private void traversal(TreeNode root, List<Integer> paths, List<String> res) {paths.add(root.val);//遇到叶子节点if(root.left == null && root.right == null){StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();for (int i = 0; i < paths.size()-1; i++) {sb.append(paths.get(i)).append("->");}sb.append(paths.get(paths.size() -1)); //记录最后一个节点res.add(sb.toString()); //收集一个路径return;}// 递归和回溯是同时进行,所以要放在同一个花括号里if (root.left != null){traversal(root.left,paths,res);paths.remove(paths.size() - 1); //回溯}if (root.right != null){traversal(root.right,paths,res);paths.remove(paths.size() - 1); //回溯}}//迭代法public List<String> binaryTreePaths1(TreeNode root) {List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null)return result;//因为要掉头,所以不用队列要用栈了Stack<Object> stack = new Stack<>();//节点和路径同时ru栈stack.push(root);stack.push(root.val + "");while (!stack.isEmpty()){String path = (String) stack.pop();TreeNode node = (TreeNode) stack.pop();//若找到叶子节点if (node.left == null && node.right == null){result.add(path);}//右子节点不为空if (node.right != null){stack.push(node.right);stack.push(path + "->" + node.right.val);}//左节点不为空if (node.left != null){stack.push(node.left);stack.push(path + "->" + node.left.val);}}return result;}
}
8、左叶子之和

思路:层序遍历,该层的第一个元素且是叶子节点。
public class Case404 {// 递归(后续遍历)//如何只让左叶子节点加和?????public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {if (root == null)return 0;int a = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left);int b = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);int midvaule = 0;if (root.left != null && root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null){midvaule = root.left.val;}int sum = midvaule + a + b;return sum;}//层序遍历public int sumOfLeftLeaves1(TreeNode root) {int sum = 0;if (root == null) return 0;Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while (queue.isEmpty()){int len = queue.size();while (len-- > 0) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (node.left != null) {if (node.left.left == null && node.left.right == null) {sum += node.left.val;}}if (node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);}}return sum;}}9、找树左下角的值
给定一个二叉树,在树的最后一行找到最左边的值。
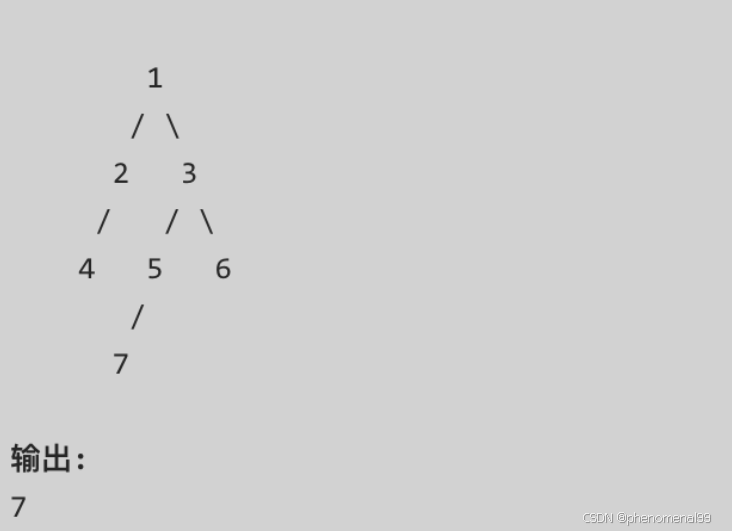
思路: 层序遍历,至最后一行,拿到第一个元素
public class Case513 {private int DEEP = -1;private int value = 0;public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);int res = 0;while (!queue.isEmpty()){int len = queue.size();//这样写会导致res的值最后会变成最后一个出队列元素的值,所以这样写循环是不对的/*while (len-- > 0){TreeNode p = queue.poll();res = p.val;if (p.left != null)queue.offer(p.left);if (p.right != null)queue.offer(p.right);}}*/for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {TreeNode p = queue.poll();if (i == 0) res = p.val;if (p.left != null)queue.offer(p.left);if (p.right != null)queue.offer(p.right);}}return res;}/*** 递归做法:* 1.确定最大深度,找到最后一层 维护一个全局变量DEEP* 2.因为是先对左孩子进行递归处理,也即先访问的左孩子。* 3.维护一个全局变量vaule来记录结果*/public int findBottomLeftValue1(TreeNode root) {value = root.val;findLeftVaule(root,0);return value;}private void findLeftVaule(TreeNode root, int deep) {if (root == null)return;if (root.left == null && root.right == null){if (deep > DEEP){value = root.val;DEEP = deep;}}if (root.left != null)findLeftVaule(root.left,deep + 1);if (root.right != null)findLeftVaule(root.right,deep + 1);}
}10、路径总和
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和。说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。示例: 给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22
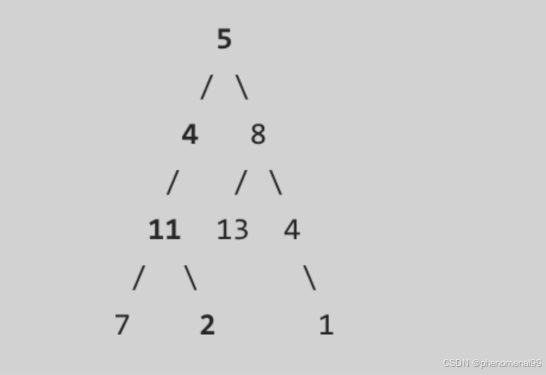
返回 true, 因为存在目标和为 22 的根节点到叶子节点的路径 5->4->11->2。
public class Case112 {public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root == null) return false;Stack<Object> stack = new Stack<>();stack.push(root);stack.push(root.val);while (!stack.isEmpty()){int res = (int) stack.pop();TreeNode node = (TreeNode) stack.pop();if (node.left == null && node.right == null){if (res == targetSum)return true;}if (node.right !=null){stack.push(node.right);stack.push(res + node.right.val);}if (node.left !=null){stack.push(node.left);stack.push(res + node.left.val);}}return false;}
}11、构造二叉树
11.1 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
注意: 你可以假设树中没有重复的元素。
例如,给出
- 中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
- 后序遍历 postorder = [9,15,7,20,3] 返回如下的二叉树:

public class Case106 {private static Map<Integer,Integer> map;public static void main(String[] args) {int[] inorder = {9,3,15,20,7};int[] postorder = {9,15,7,20,3};buildTree(inorder,postorder);}public static TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {map = new HashMap<>();for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {map.put(inorder[i],i);}return findNode(inorder,0,inorder.length,postorder,0,postorder.length);}private static TreeNode findNode(int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd, int[] postorder, int postBegin, int postEnd) {if (inBegin >= inEnd || postBegin >= postEnd){ //没有元素,返回空树,左闭右开[)return null;}int rootIndex = map.get(postorder[postEnd - 1]); //找到后续遍历的最后一个元素在中序遍历中的位置TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]); //构造节点int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inBegin; //保存中序左子树个数,用来确定后序数列的个数root.left = findNode(inorder,inBegin,rootIndex,postorder,postBegin,postBegin + lenOfLeft);root.right = findNode(inorder,rootIndex + 1,inEnd,postorder,postBegin+lenOfLeft,postEnd - 1);return root;}
}
11.2 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
public class Case105 {Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {map.put(inorder[i],i);}return findNode(inorder,0,inorder.length,preorder,0,preorder.length);}private TreeNode findNode(int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd, int[] preorder, int preBegin, int preEnd) {if (inBegin >= inEnd || preBegin >= preEnd)return null;int rootIndex = map.get(preorder[preBegin]); //根节点在中序遍历中的索引TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]);int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inBegin;root.left = findNode(inorder,inBegin,rootIndex,preorder,preBegin + 1,preBegin + lenOfLeft + 1);root.right = findNode(inorder,rootIndex + 1,inEnd,preorder,preBegin+lenOfLeft + 1,preEnd);return root;}
}11.3、最大二叉树
给定一个不含重复元素的整数数组。一个以此数组构建的最大二叉树定义如下:
- 二叉树的根是数组中的最大元素。
- 左子树是通过数组中最大值左边部分构造出的最大二叉树。
- 右子树是通过数组中最大值右边部分构造出的最大二叉树。
通过给定的数组构建最大二叉树,并且输出这个树的根节点。

/*** 给定一个不重复的整数数组 nums 。 最大二叉树 可以用下面的算法从 nums 递归地构建:* 创建一个根节点,其值为 nums 中的最大值。* 递归地在最大值左边的子数组前缀上 构建左子树。* 递归地在最大值右边的子数组后缀上 构建右子树。* 返回 nums 构建的 最大二叉树*/
public class Case654 {public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {if (nums == null)return null;return findNode(nums,0,nums.length);}private TreeNode findNode(int[] nums, int leftIndex, int rightIndex) {if (leftIndex >= rightIndex){ //数组不合法(左闭右开)return null;}int rootIndex = leftIndex;int max = nums[rootIndex];//max = Arrays.stream(nums).max().getAsInt(); //问题出在这,不应该在整个数组中找最大值了for (int i = leftIndex; i < rightIndex; i++) {if (nums[i] > max){max = nums[i];rootIndex = i;}}TreeNode root = new TreeNode(max);root.left = findNode(nums,leftIndex,rootIndex);root.right = findNode(nums,rootIndex + 1,rightIndex);return root;}
}
12、合并二叉树
给定两个二叉树,想象当你将它们中的一个覆盖到另一个上时,两个二叉树的一些节点便会重叠。你需要将他们合并为一个新的二叉树。合并的规则是如果两个节点重叠,那么将他们的值相加作为节点合并后的新值,否则不为 NULL 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。

public class Case617 {public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {/*if (root1 == null) return root2;if (root2 == null) return root1;*/if (root1 == null || root2 == null) {return root1 == null ? root2:root1;}root1.val += root2.val;root1.left = mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left);root1.right = mergeTrees(root1.right,root2.right);return root1;}
}13、二叉搜索树
13.1 二叉搜索树中的搜索
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点和一个值。 你需要在BST中找到节点值等于给定值的节点。 返回以该节点为根的子树。 如果节点不存在,则返回 NULL。

public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {/* if (root == null) return null;if (root.val == val) return root;TreeNode left = searchBST(root.left,val);if (left != null){return left;}return searchBST(root.right,val);*///利用二叉搜索树的特点if (root == null || root.val == val) return root;if (root.val < val){return searchBST(root.right,val);}else {return searchBST(root.left,val);}}13.2、验证二叉搜索树
给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。假设一个二叉搜索树具有如下特征:
- 节点的左子树只包含小于当前节点的数。
- 节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
- 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。

/*** 验证二叉搜索树* 问题所在:不能局部判断,要保证左子树的全部节点都要比root小.......*/
public class Case98 {public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return true;/* if (root.left.val >= root.val || root.right.val <= root.val){return false;报空指针异常:如果左子树上来为空,那么问题就出现了}*/Boolean left = isValidBST(root.left);Boolean right = isValidBST(root.right);return left && right;}//上述代码问题就出现在全局问题!!!public boolean isValidBST1(TreeNode root ){return isValidBSTHelper(root,Long.MIN_VALUE,Long.MAX_VALUE);}private boolean isValidBSTHelper(TreeNode root, long minValue, long maxValue) {if (root == null) return true;if (root.val <= minValue || root.val >= maxValue){return false;}//确定范围:左孩子一定要比根节点的值小,右孩子一定要比根节点的值要大return isValidBSTHelper(root.left,minValue, root.val) &&isValidBSTHelper(root.right, root.val, maxValue);}//迭代法public boolean isValidBST2(TreeNode root ){if (root == null) return true;Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();TreeNode pre = null; //记录父节点while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()){while (root != null){stack.push(root);root = root.left;}TreeNode pop = stack.pop();if (pre!=null && pop.val <= pre.val){return false;}pre = pop;root = root.right;}return true;}
}
13.3、二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
给你一棵所有节点为非负值的二叉搜索树,请你计算树中任意两节点的差的绝对值的最小值。

public class Case530 {int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;TreeNode pre; //记录上一个遍历的节点public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {func(root);return res;}private void func(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return;func(root.left);if (pre != null) {res = Math.min(res, root.val - pre.val);}pre = root;func(root.right);}//迭代法-中序遍历public int getMinimumDifference1(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;TreeNode pre = null;Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();TreeNode cur = root;int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {if (cur != null) {stack.push(cur); //将要访问的节点放进栈cur = cur.left;} else {cur = stack.pop();if (pre != null) { //中res = Math.min(res, cur.val - pre.val);}pre = cur;cur = cur.right; //右}}return res;}
}
13.4 二叉搜索树中的众数
给定一个有相同值的二叉搜索树(BST),找出 BST 中的所有众数(出现频率最高的元素)。结果集合中可以是多个元素。
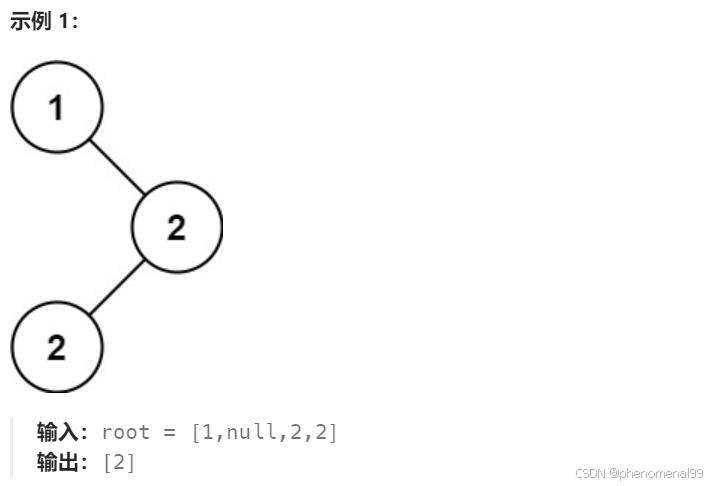
思路:定义全局变量 count 记录节点值出现的次数,maxCount记录出现次数最多的节点值,
public class Case501 {//迭代遍历public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {if(root == null)return null;List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();int maxCount = 0;int count = 0;TreeNode pre = null;Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();TreeNode cur = root;while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){if (cur != null){stack.push(cur);cur = cur.left;}else {cur = stack.pop();if (pre == null || pre.val != cur.val){count = 1;}else {count ++;}//更新结果if (count > maxCount){maxCount = count;res.clear(); //重新清空集合res.add(cur.val);}else if (count == maxCount){res.add(cur.val);}pre = cur;cur = cur.right;}}int[] a = new int[res.size()];for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++) {a[i] = res.get(i);}return a;//return res.stream().mapToInt(Integer:: intValue).toArray();}
}
13.5 二叉树的最近公共祖先
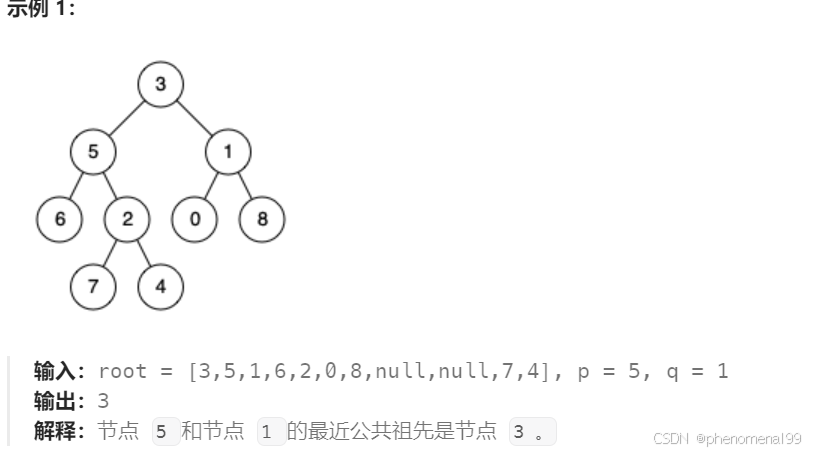
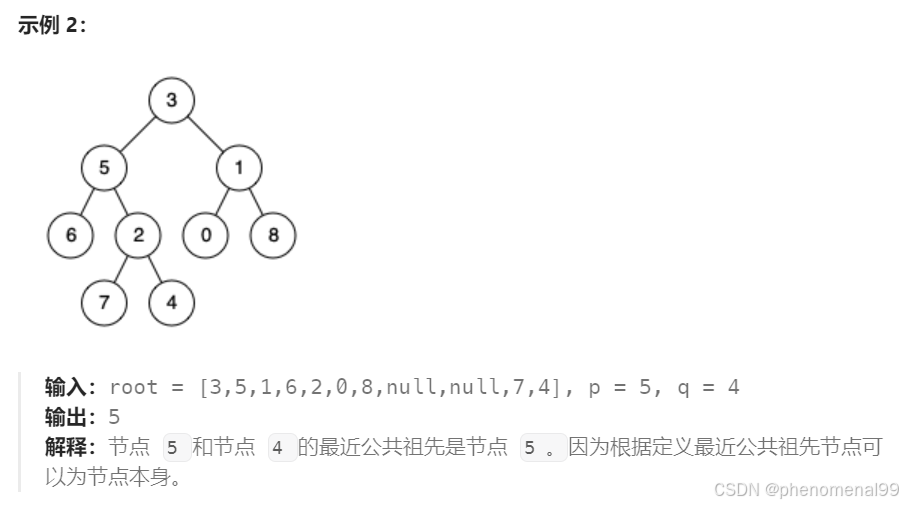
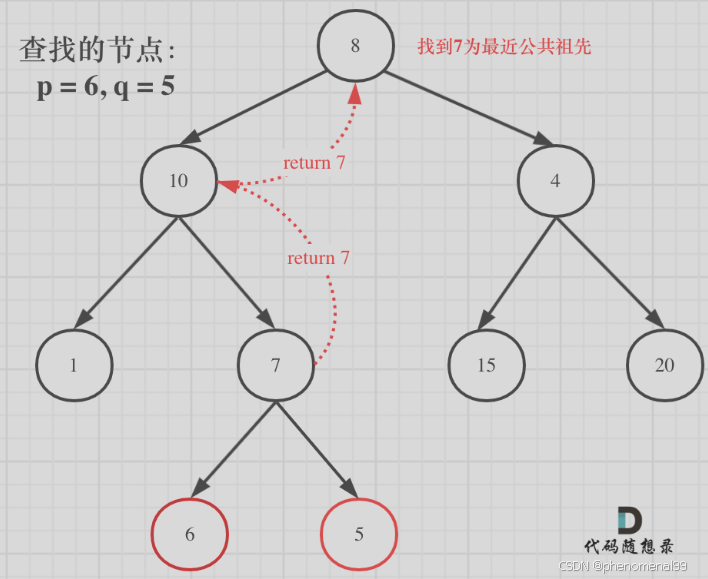
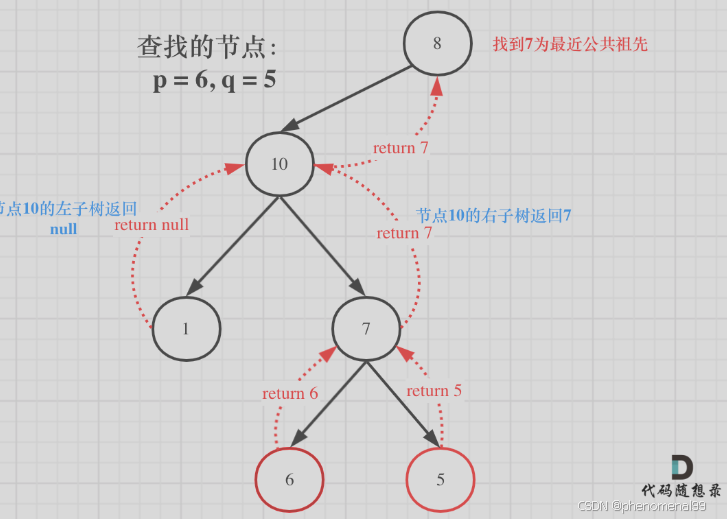
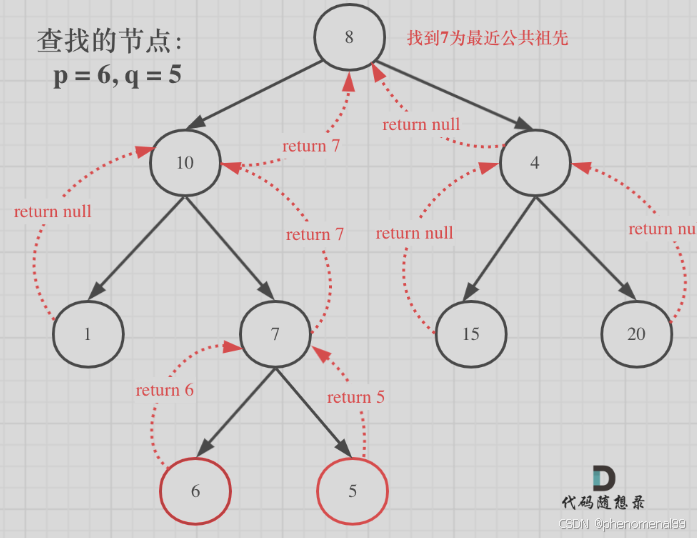
public class Case236 {/*** 1.求最小公共祖先,需要从底向上遍历,二叉树,只能通过后序遍历,实现从底向上的遍历方式* 2.在回溯过程中,必然要遍历整颗二叉树,即使已经找到结果了,依然要把其他节点遍历完,因为要使用递归函数的* 返回值* 3.要理解如果返回值为空,right不为空为什么要返回right,为什么可以用返回right传给上一层结果。* 可以说这里每一步,都是有难度的,都需要对二叉树,递归和回溯有一定的理解。*本题没有给出迭代法,因为迭代法不适合模拟回溯的过程。理解递归的解法就够了。*///写得太牛逼了!!!! 值得反复揣摩。优雅public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root == null || root == p || root == q){ //强啊return root;}//后序遍历TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);if (left == null && right == null){ //如果未找到节点p或qreturn null;}else if (left == null && right != null){ //若找到一个节点return right;}else if (left != null && right == null){return left;}else { // 若找到两个节点return root;}}
}
13.6 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
public class Case235 {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if(root == null) return null;
// 如果一个节点比root大,一个比root小,那就最近祖先就是root了啊while (root != null){if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val){root = root.left;}else if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val){root = root.right;}else {break;}}return root;}//递归public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor1(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val){return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);}if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val){return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);}return root;}
}13.7 二叉搜索树中的插入操作
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点和要插入树中的值,将值插入二叉搜索树。 返回插入后二叉搜索树的根节点。 输入数据保证,新值和原始二叉搜索树中的任意节点值都不同。注意,可能存在多种有效的插入方式,只要树在插入后仍保持为二叉搜索树即可。 你可以返回任意有效的结果。
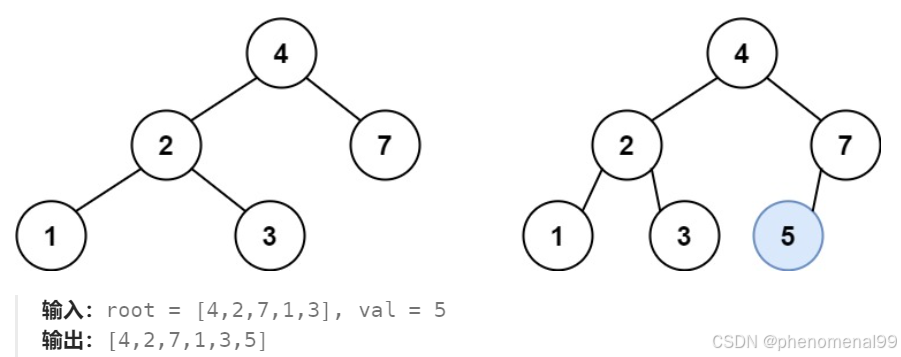
public class Case701 {public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {if (root == null){TreeNode p = new TreeNode(val);return p;}if (root.val > val){root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left,val);}else {root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right,val);}return root;}//非递归public TreeNode insertIntoBST1(TreeNode root, int val) {if (root == null) return new TreeNode(val);TreeNode newRoot = root;TreeNode pre = root;while (root != null){pre = root;if (root.val > val){root = root.left;}else if (root.val < val){root = root.right;}}if (pre.val > val){pre.left = new TreeNode(val);}else {pre.right = new TreeNode(val);}return newRoot;}
}
13.8 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
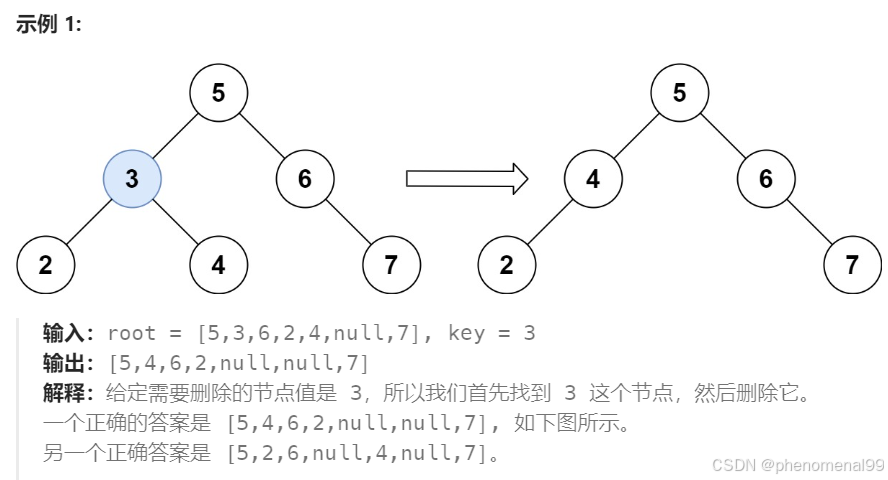
class Solution {public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {if (root == null) return root;if (root.val == key) {if (root.left == null) {return root.right;} else if (root.right == null) {return root.left;} else {TreeNode cur = root.right;while (cur.left != null) {cur = cur.left;}cur.left = root.left;root = root.right;return root;}}if (root.val > key) root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);if (root.val < key) root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);return root;}
}13.9 修剪二叉搜索树
给定一个二叉搜索树,同时给定最小边界L 和最大边界 R。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[L, R]中 (R>=L) 。你可能需要改变树的根节点,所以结果应当返回修剪好的二叉搜索树的新的根节点。
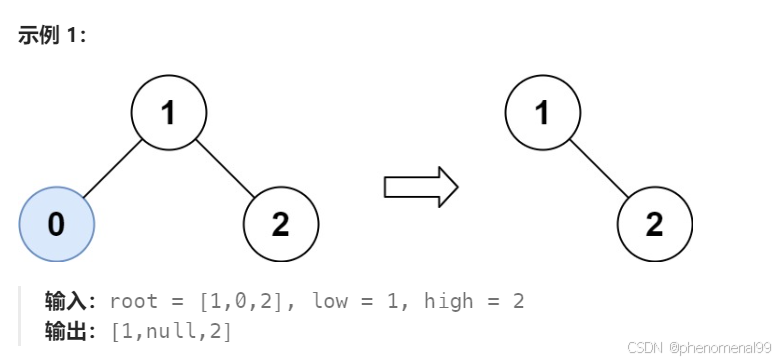
public class Case669 {public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {if(root == null || low > high) return root;//如果根节点就不在合法范围内,那就先找到第一个合法的节点while (root != null && (root.val < low || root.val > high)){if (root.val < low){root = root.right;}else {root = root.left;}}TreeNode curr = root;//处理左子树while (curr != null){while (curr.left != null && curr.left.val < low){curr.left = curr.left.right;}curr = curr.left;}curr = root; //重新回到根节点//处理右子树while (curr != null){while (curr.right != null && curr.right.val > high){curr.right = curr.right.left;}curr = curr.right;}return root;}//递归public TreeNode trimBST1(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {/*if (root == null || root.val < low || root.val > high) return null;root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high);root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high);return root;*/if (root == null){return null;}if (root.val < low){return trimBST1(root.right,low,high);}if (root.val > high){TreeNode a = trimBST1(root.left,low,high);return a;}//root 在合法的范围内root.left = trimBST1(root.left,low,high);root.right = trimBST1(root.right,low,high);return root;}
}
13.10 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
将一个按照升序排列的有序数组,转换为一棵高度平衡二叉搜索树。本题中,一个高度平衡二叉树是指一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1。
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {if (nums == null) return null;return sortedArrayToBST(nums,0,nums.length);}private TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums, int left, int right) {if (left >= right){ //要求左闭右开return null;}int mid = (left + right) / 2;TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);root.left = sortedArrayToBST(nums,left,mid);root.right = sortedArrayToBST(nums,mid + 1,right);return root;}
}13.11 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
给出二叉 搜索 树的根节点,该树的节点值各不相同,请你将其转换为累加树(Greater Sum Tree),使每个节点 node 的新值等于原树中大于或等于 node.val 的值之和。提醒一下,二叉搜索树满足下列约束条件:节点的左子树仅包含键 小于 节点键的节点。 节点的右子树仅包含键 大于 节点键的节点。 左右子树也必须是二叉搜索树。
public class Case538 {private int num = 0;public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {if (root == null)return null;/*root.right = convertBST(root.right);if (root.right != null){root.val = root.val + root.right.val;}root.left = convertBST(root.left);if (root.left != null){root.left.val = root.val + root.left.val;}return root;*///上述代码虽然遵从了逆中序遍历,但是由于递归,convertBST(root.right);root.val = root.val + num;num = root.val;convertBST(root.left);return root;}
}